Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MODEL PAPER 1
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION C|5 VideosMODEL PAPER 1
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION C|5 VideosFINAL TOUCH (MOST IMPORTANT QUESTIONS)
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS) |14 VideosMODEL PAPER 10
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION-C|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-MODEL PAPER 1-SECTION B
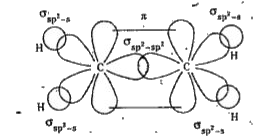
- Define sp^(2) Hybridisation. Explain the structure of Ethylene (C(2)H(...
Text Solution
|
- Write the postulates of kinetic molecular theory of gases .
Text Solution
|
- How does diborane react with CO ?
Text Solution
|
- How does Dibroane react with the following: NH(3)
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by the term Bond order? Calculate the bond orders in the...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by the term Bond order? Calculate the bond orders in the...
Text Solution
|
- A carbon compound contains 12.8% Carbon, 2.1% Hydrogen, 85.1% Bromine....
Text Solution
|
- Derive the relation between K(p) and K(c) for the equilibrium reaction...
Text Solution
|
- Write two oxidizing and two reducing properties of H(2)O(2).
Text Solution
|
- SiF6^(2-) is known while SiCl6^(-2) is not - explain.
Text Solution
|
- Diamond has high melting point - Explain.
Text Solution
|