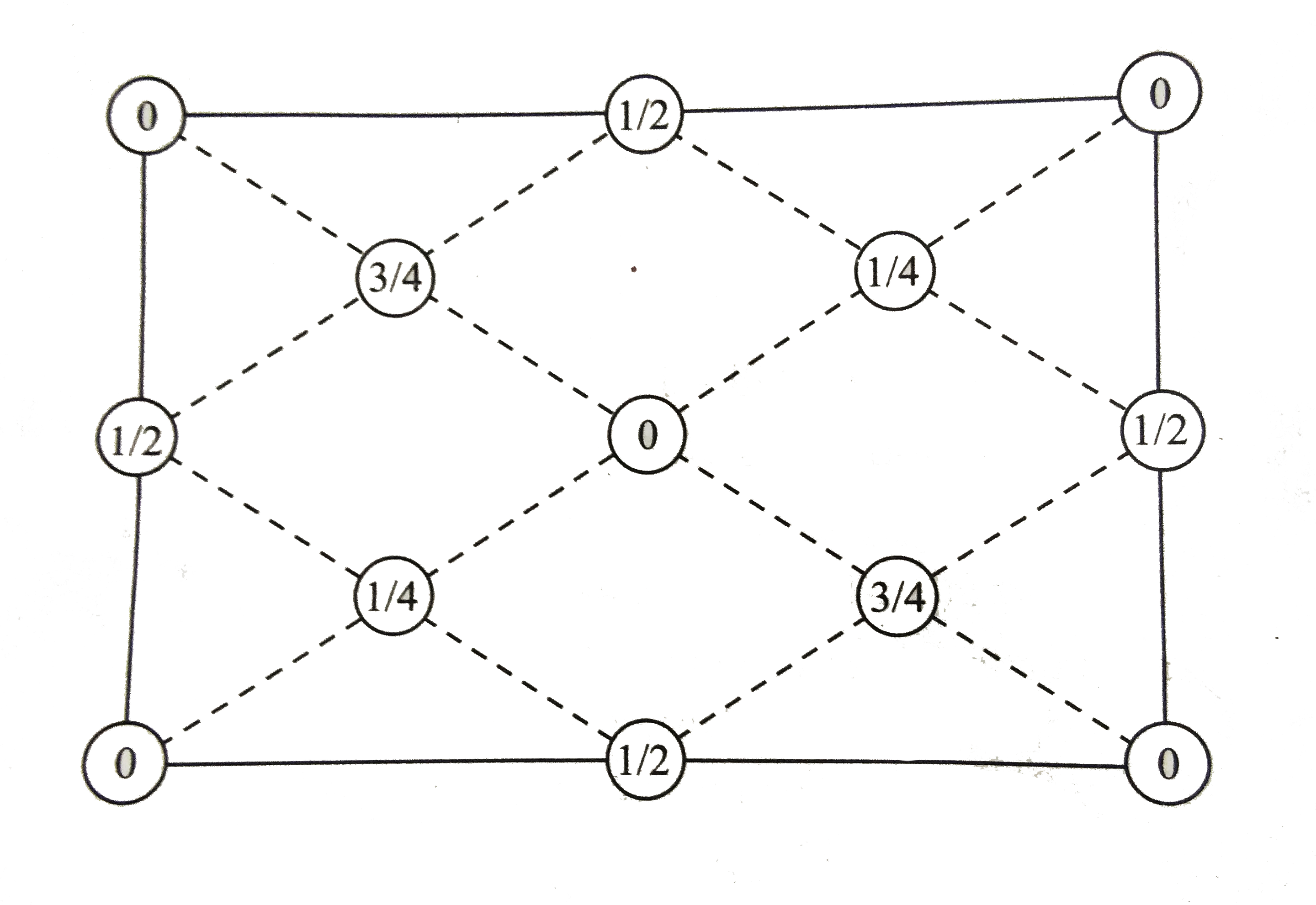
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOLID STATE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Assertion-Reasoning)|19 VideosSOLID STATE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Interger)|9 VideosSOLID STATE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correct)|39 VideosREDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise SUBJECTIVE TYPE|3 VideosSOLUTIONS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 2.3 (Objective)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-SOLID STATE-Exercises (Single Correct)
- In the crystals of which of the following ionic compounds would you ex...
Text Solution
|
- Schottky defect to crystals is observed when
Text Solution
|
- How many kinds of space lattices are possible in a crystal?
Text Solution
|
- Potassium crystallizes with a
Text Solution
|
- A compound formed by element A and B crystallizes in the cubic structu...
Text Solution
|
- The number of unit cells in 58.5 g of NaCl is nearly
Text Solution
|
- The number of octahedral sites per sphere in fcc structure is
Text Solution
|
- The packing fraction for a body-centred cube is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has Frenkel defect?
Text Solution
|
- In NaCl, the chloride ions occuphy the space in a fashion of
Text Solution
|
- To get n-type doped semiconductor, impurity to be added to silicon sho...
Text Solution
|
- The range of radius ratio (cationic to anionic) for an octahedral arra...
Text Solution
|
- When molten zinc is cooled to solid state, it assumes hcp structure. T...
Text Solution
|
- Superconductors are derived from the compounds of
Text Solution
|
- A semiconductor of Ge can be made p-type by adding
Text Solution
|
- The interionic distance for cesium chloride crystal will be
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following metal oxides is anti-ferromagnetic in nature?
Text Solution
|
- What are types of following semiconductors I and II.
Text Solution
|
- In the structure of diamond, carbon atoms appear at
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following figures represents the cross section of an OV?
Text Solution
|