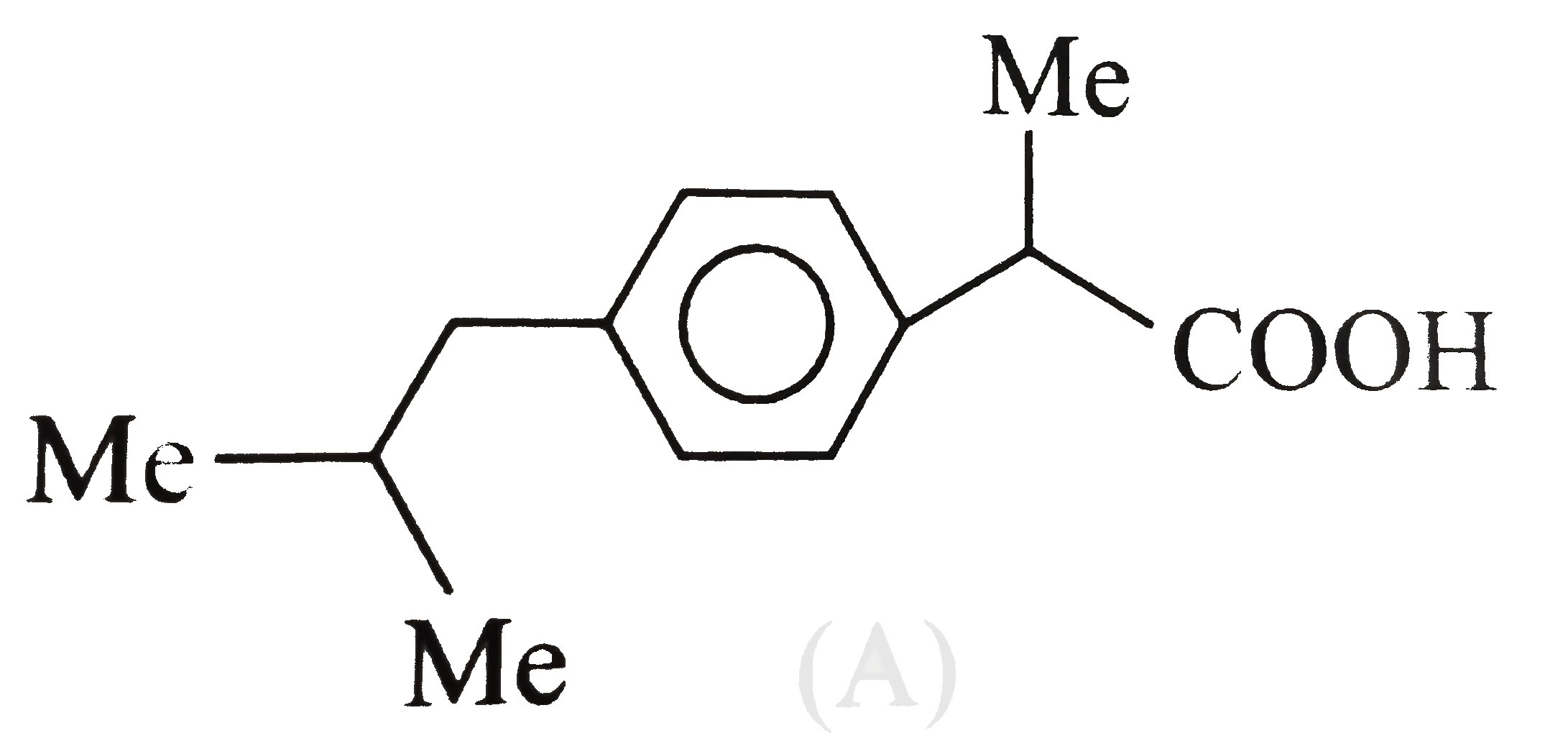
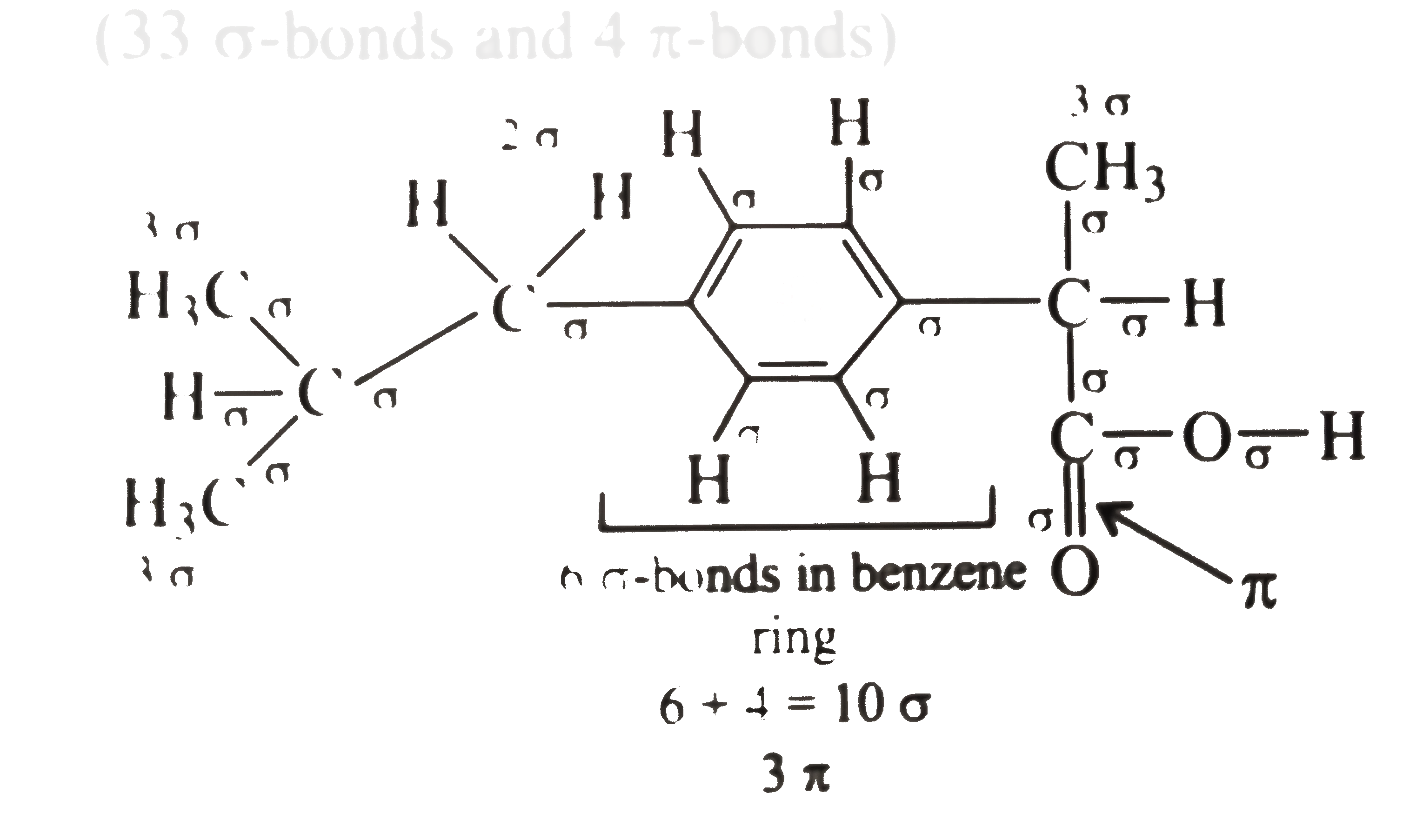
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Multiple corrcct Answers Types|11 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Single correct Answer Type|44 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Concept Application Type|7 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives (Subjective)|11 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS-Linked Comprehesion Type
- The analgesic drug ibuprofen (A) is chiral and exists in (+) and (-) f...
Text Solution
|
- The analgesic drug ibuprofen (A) is chiral and exists in (+) and (-) f...
Text Solution
|
- The analgesic drug ibuprofen (A) is chiral and exists in (+) and (-) f...
Text Solution
|
- The analgesic drug ibuprofen (A) is chiral and exists in (+) and (-) f...
Text Solution
|
- Aspirin is widely used as an analgesic drug. It is optically inactive....
Text Solution
|
- Aspirin is widely used as an analgesic drug. It is optically inactive....
Text Solution
|
- Aspirin is widely used as an analgesic drug. It is optically inactive....
Text Solution
|
- Aspirin is widely used as an analgesic drug. It is optically inactive....
Text Solution
|
- Crixivan, a drug produced by Merck and Co., is widely used in the figh...
Text Solution
|
- Crixivan, a drug produced by Merck and Co., is widely used in the figh...
Text Solution
|
- Crixivan, a drug produced by Merck and Co., is widely used in the figh...
Text Solution
|
- Crixivan, a drug produced by Merck and Co., is widely used in the figh...
Text Solution
|