Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.1|2 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.2|3 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.6|20 VideosARCHIVES 2 VOLUME 6
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|4 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-BASIC MATHEMATICS-Solved Examples
- A police jeep, approaching a right-angled intersection from the north,...
Text Solution
|
- From point A located on a highway (figure) one has to get by car as so...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles, 1 and 2, move with constant velocities v1 and v2 along ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies start moving in the same straight line at the same instant ...
Text Solution
|
- Water pours out rate of Q from a tap, into a cylindrical vessel of rad...
Text Solution
|
- Using the method of integration show that the area of triangle of base...
Text Solution
|
- Using the method of integration, show that the volume of a right circu...
Text Solution
|
- An experiment on the take off performance of an aeroplane shows that t...
Text Solution
|
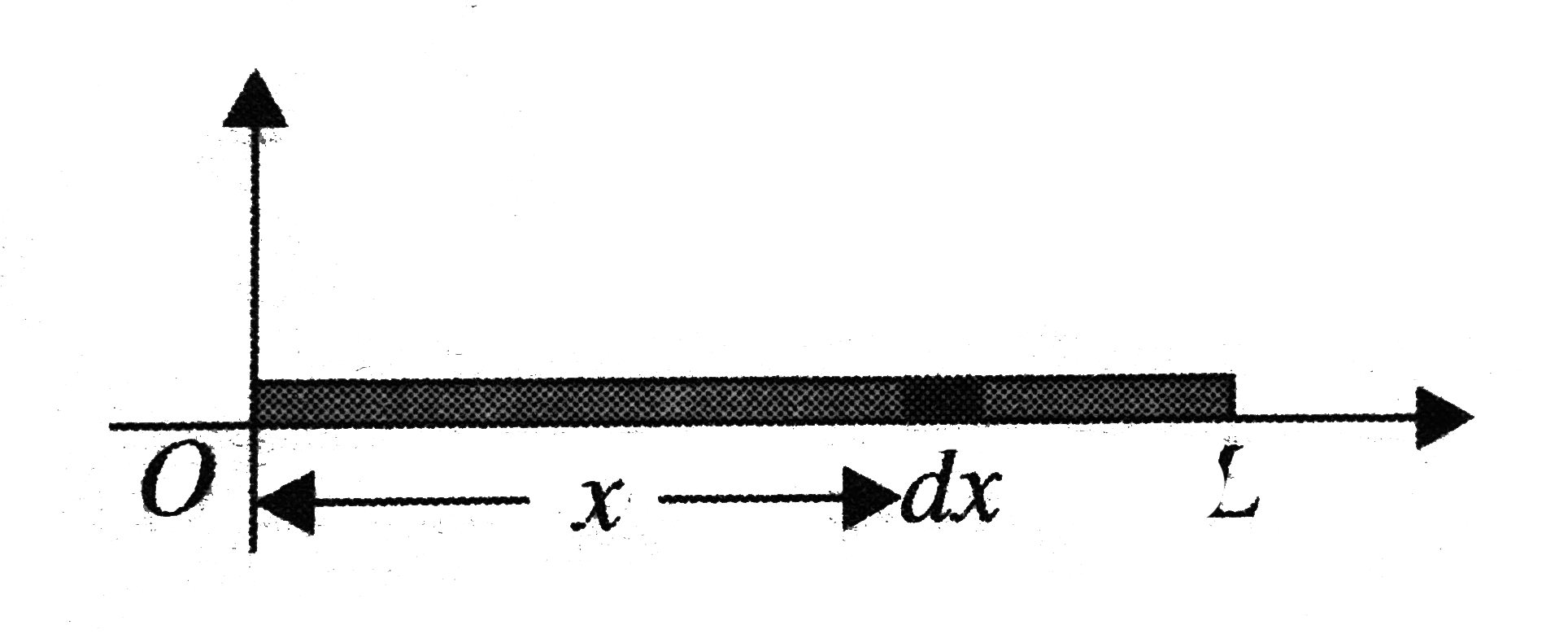
- You are given a rod of length L. The linear mass density is lambda suc...
Text Solution
|