Let the acceleratuib of the oartucke be (a)
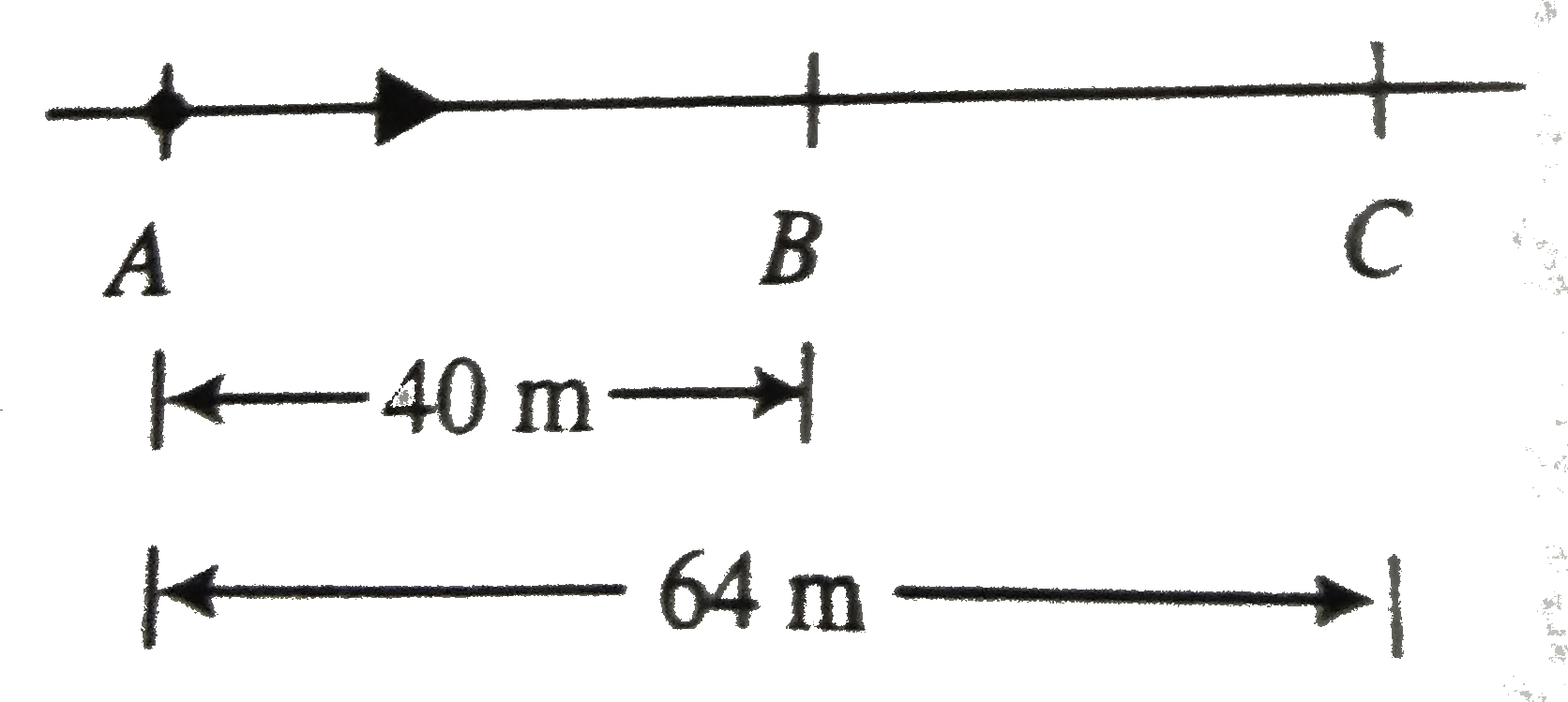
.
For motion between `A` and `B`
`u=12 m s^(-1)`,s=40 m, t=4 s`
`s=ut+1//2 at^(2)`
`rArr 40=12xx4+(1)/(2)xxaxx(4)^(4) rArra=-1 m s^(-2)`
For motion berween ` A and C`
`64=12t+(1)/(2)(-1)t^(2)`
`rArrt^(2)-24 t+128=0`
`rArr (t-8)(t-16)=0`
` rArr t=8 s, 16 s`
a. The particle will be at `C` two, at `t=8 s` and `1=16 s`.
b. Velocity of the particle at `c`
At `t=8 s`, velocity of the particle `v=12+(-1)xx8`
`=4 m s^(-1)`
At `t=16 s`, velpcoty of the particle `v=12+(-1) xx16`
`=-4 m s^(-1)`
As the acceleration of the particle is negative, it will retard as it moves alon `ABC`. At a point beyond `C` i.e., at `D`, the particle will come to rest momentarily, and then it will move backward with increasing speed.Throughout the motion, the particle decelerates, its velocity decrases continuously, velocity varies as (12, 11, 10, ..., 2, 1, 0, -1, -2,...,-10, -11, -12,) etc. Only from `A` to `D` the motion is retarded, during which speed varies as (12, 11, 10, ...,2, 1, 0.)
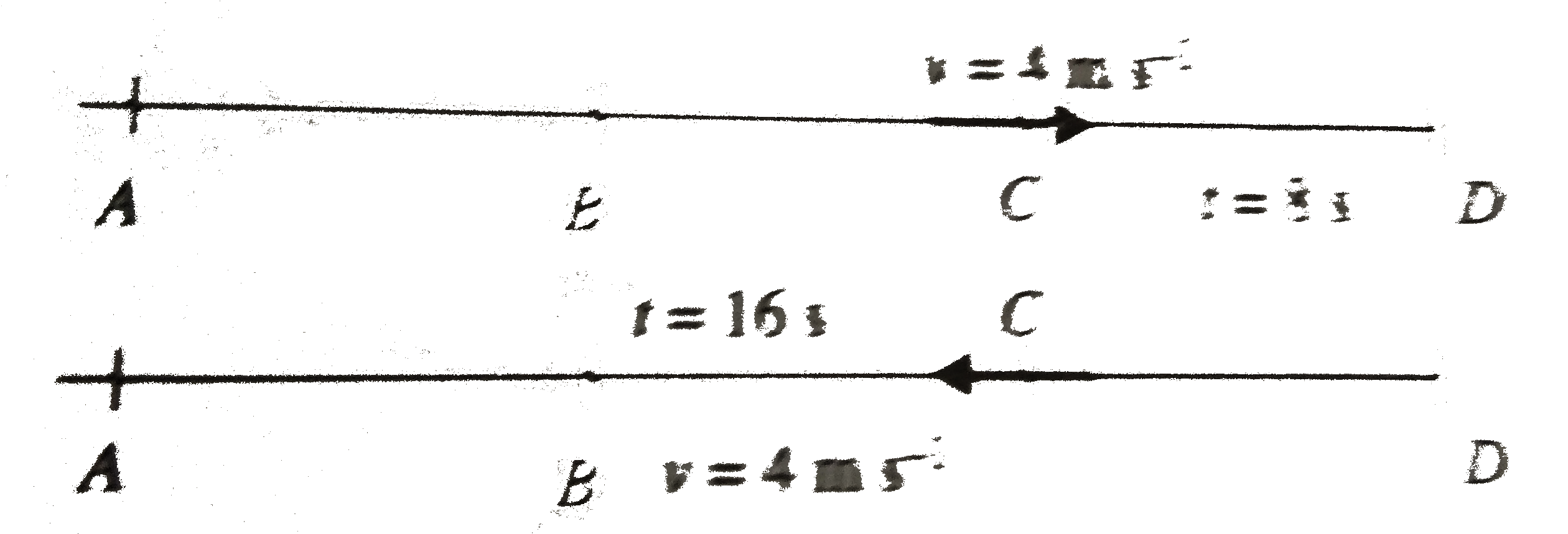
.
Subsequently, the particle speeds up, speed changing as (1, 2, 3,....,)etc.
Notice the differnce between deceleration and retarda-tion.
c. When the particle reaches `A` again, its displacement=0`
`becuase 0=12 xxt+(1)/(2) (-1)t^(2)`
`rArrt=0, 24 s`
At `t=0`, Velocity at ` A =12 m s^(-1)`,
At `t=24 s`, velocity at `A` is
`12+(-1)xx24=-12 m s^(-1)`.
d. The particle reveses the direction of motion at `D`. For the motion between `A` and `D`

.
`u=12 m s^(-1), v=0, a=-1 m s^(-2)`. If `AD=s`, From the equation
`v^(2)=u^(2)+2as`
`(0)^(2)^(2)+2xx(-1)xxs`
`s=(12xx2)/2=72 m`
You can also calculate the time taken by the particle to reach `D` from `0=12+(-1)t_(D)` and then
from `s=12 xxt_(D)+(1)/(2)(-1)t_(D)^(2)`, you can find `s`.
But then again you must be intersted in optimising the steps of calculation and must not proceed so
c. After `12 s` the particle comes to rest momentarily at `D` after covering a distance of `72 m`.

.
Distance in subsequent `3 s`
`=0xx3+(1)/(2)xx(-1)xx(3)^(2) =4.5 m`
`becuase d=72 m +4.5 m =76.5 m`.
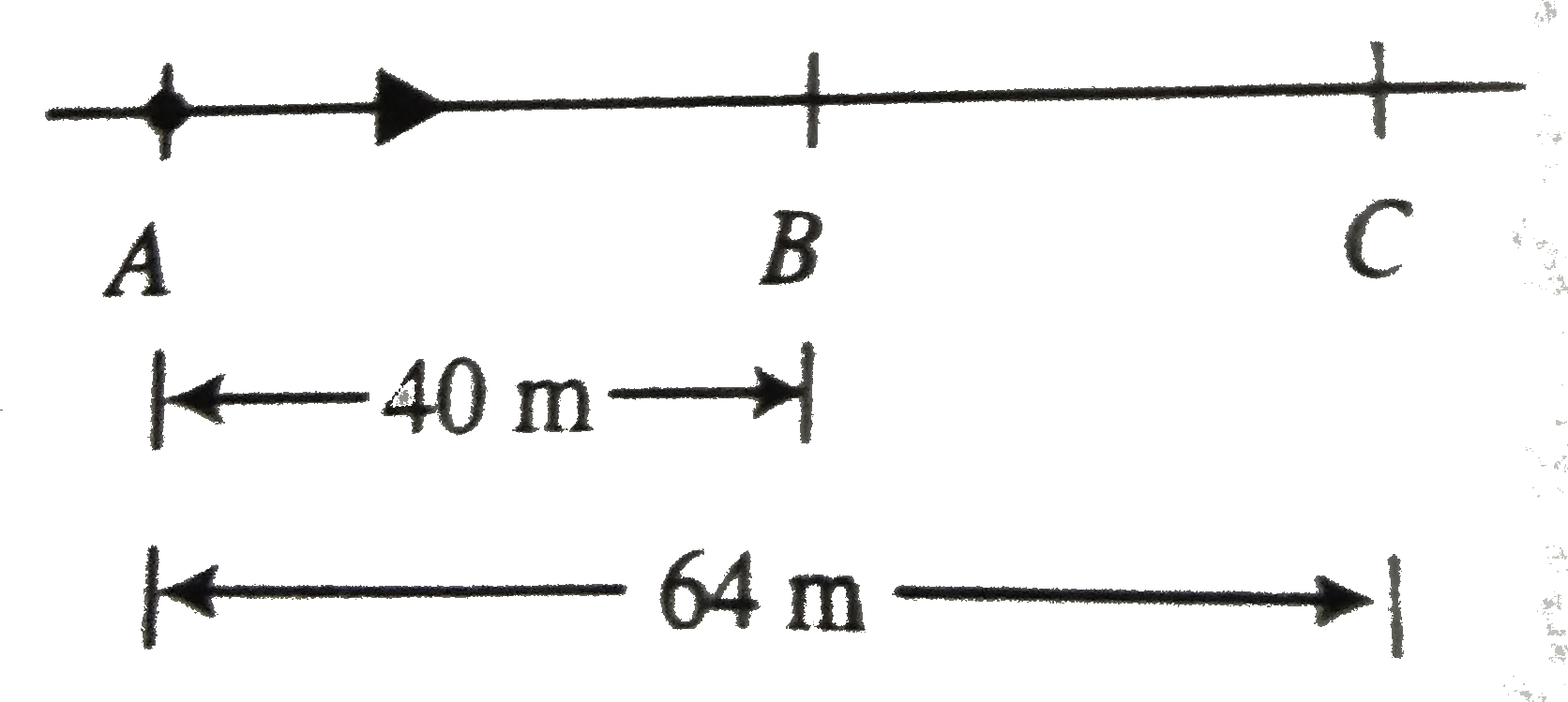 .
. 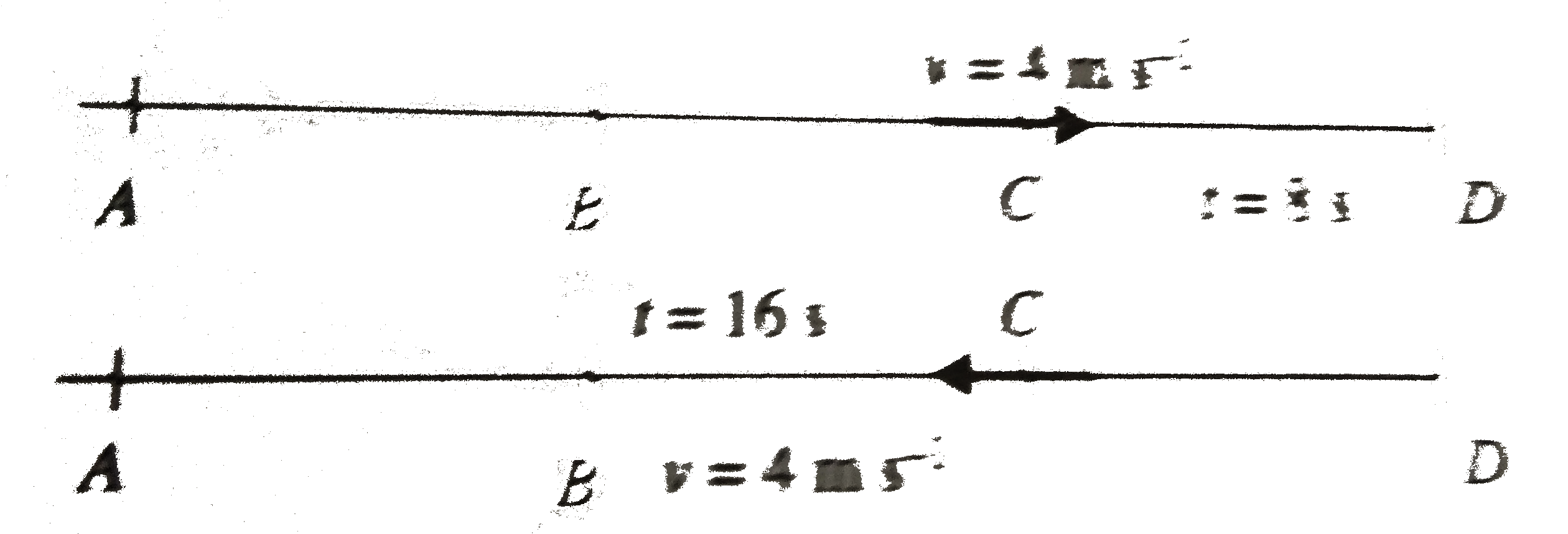 .
.  .
.  .
.