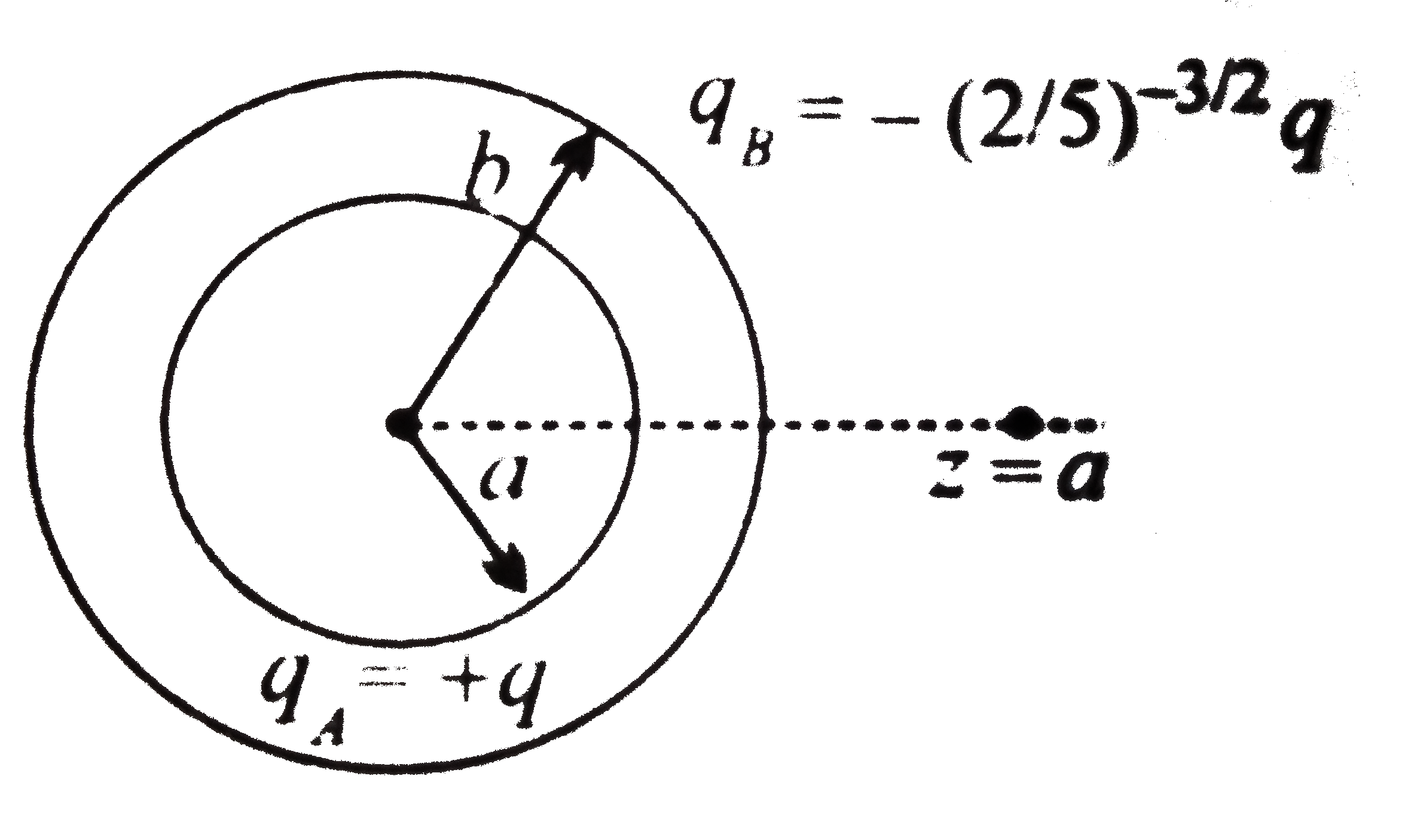Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct Ansewr Type|20 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|2 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Comprehension|25 VideosCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|19 VideosCurrent Electricity
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise QUESTION BANK|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD-Integer
- Two concentric rings, one of radius a and the other of radius b, have ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB of length L and mass M is uniformly charged with a charge Q, ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particle of masses in the ration 1:2 with charges in the ratio 1:1...
Text Solution
|
- There is and electric field E in the +x direction. If the work done by...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field is given by vec(E )=(yhat(i)+hat(j))NC^(-1). Find th...
Text Solution
|
- Four charge particles each having charge Q=1 C are fixed at the corner...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius R has charge -Q distributed uniformly over it. Calcul...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical small equally charged conducting balls are suspended fro...
Text Solution
|