A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Chapter Test
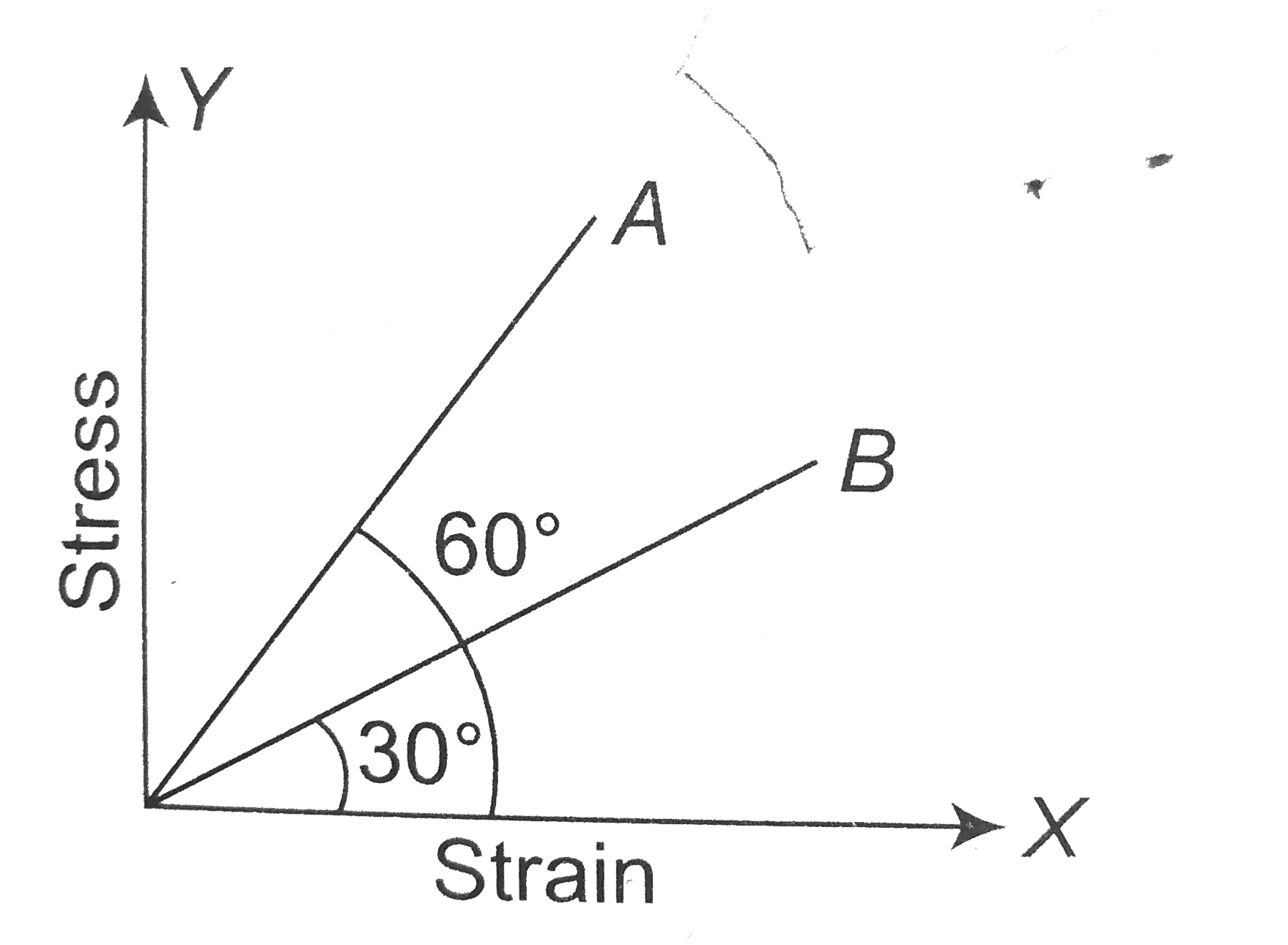
- The stress versus strain graphs for wires of two materials A and B are...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L and radius r is fixed at one end. When a stretching...
Text Solution
|
- The area of a cross section of steel wire is 0.1cm^2 and Young's modul...
Text Solution
|
- The bulk modulus of water if its volume changes from 100litres to 99.5...
Text Solution
|
- A steel cable with a radius 2cm supports a chairlift at a ski area. If...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of length 4.5m and cross-sectional area 3xx10^-5m^2 stret...
Text Solution
|
- The young's modulus of a wire of length (L) and radius (r ) is Y. If t...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire can support a maximum load of W before reaching its elast...
Text Solution
|
- How does Young's modulus change with rise in temperature?
Text Solution
|
- A sphere contracts in volume by 0.01% when taken to the bottom of sea ...
Text Solution
|
- The metal cube of side 10 cm is subjected to a shearing stress of 10^(...
Text Solution
|
- A mercury drop of radius 1 cm is broken into 10^6 droplets of equal si...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical liquid drop of radius R is divided into eight equal drople...
Text Solution
|
- Air is pushed inot a soap bubble of radius r to duble its radius. If t...
Text Solution
|
- A water drop is divided into eight equal droplets. The pressure differ...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid drop of radius R is broken into 1000 drops each of radius r. ...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel whose bottom has round holes with diameter 0.1 mm, is filled ...
Text Solution
|
- Water rises to a height of 10 cm in a capillary tube and mercury falls...
Text Solution
|
- The radii and Young's moduli of two uniform wires A and B are in the r...
Text Solution
|
- The dimensions of four wires of the same material an given below. In w...
Text Solution
|