A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Transmission Of Heat : Radiation|28 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Problems Baesd On Mixed Concepts|18 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Calorimetry|41 VideosROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|29 VideosUNIT, DIMENSION AND ERROR ANALYSIS
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|28 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Transmission Of Heat : Conduction
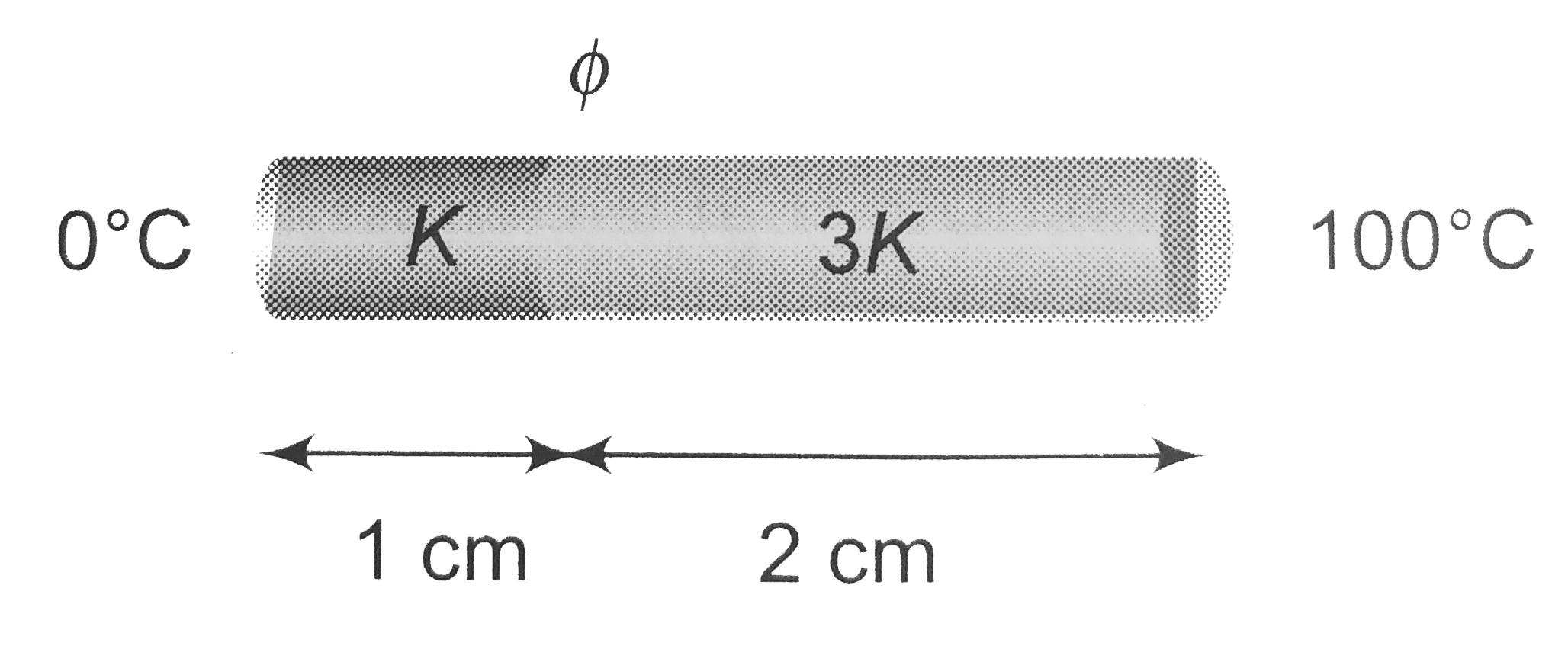
- Two bars of thermal conductivities K and 3K and lengths 1 cm and 2 cm ...
Text Solution
|
- A compound slab is made of two parallel plates of copper and brass of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical vessels are filled with equal amounts of ice. The vessel...
Text Solution
|
- The heat is flowing through two cylinderical rods of same material. Th...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature gradient in a rod of 0.5 m length is 80^(@)C//m. It th...
Text Solution
|
- If the coefficient of conductivity of aluminium is 0.5 cal cm^(-1) s^(...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of thermal conductivity of copper, mercury and glass a...
Text Solution
|
- Ice has formed on a shallow pond, and a steady state has been reached,...
Text Solution
|
- If l is the length, A is the area of cross-section and K the thermal c...
Text Solution
|
- A wall has two layers A and B each made of different materials. The la...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods (one semi-circular and other straight) of same material and o...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres of different materials one with double the radius and one-...
Text Solution
|
- A wall has two layers A and B each made of different materials. The th...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of radius R made of a material of thermal conductivity K1 i...
Text Solution
|
- Two ends of a conducting rod of varying cross-section are maintained a...
Text Solution
|
- One end of conducting rod is maintained at temperature 50^(@)C and at ...
Text Solution
|
- A wall has two layers A and B each made of different materials. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods made of the same material and having the same cross-section...
Text Solution
|
- All the rods have same conductance 'K' and same area of cross section ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical long, solid cylinders are used to conduct heat from temp...
Text Solution
|