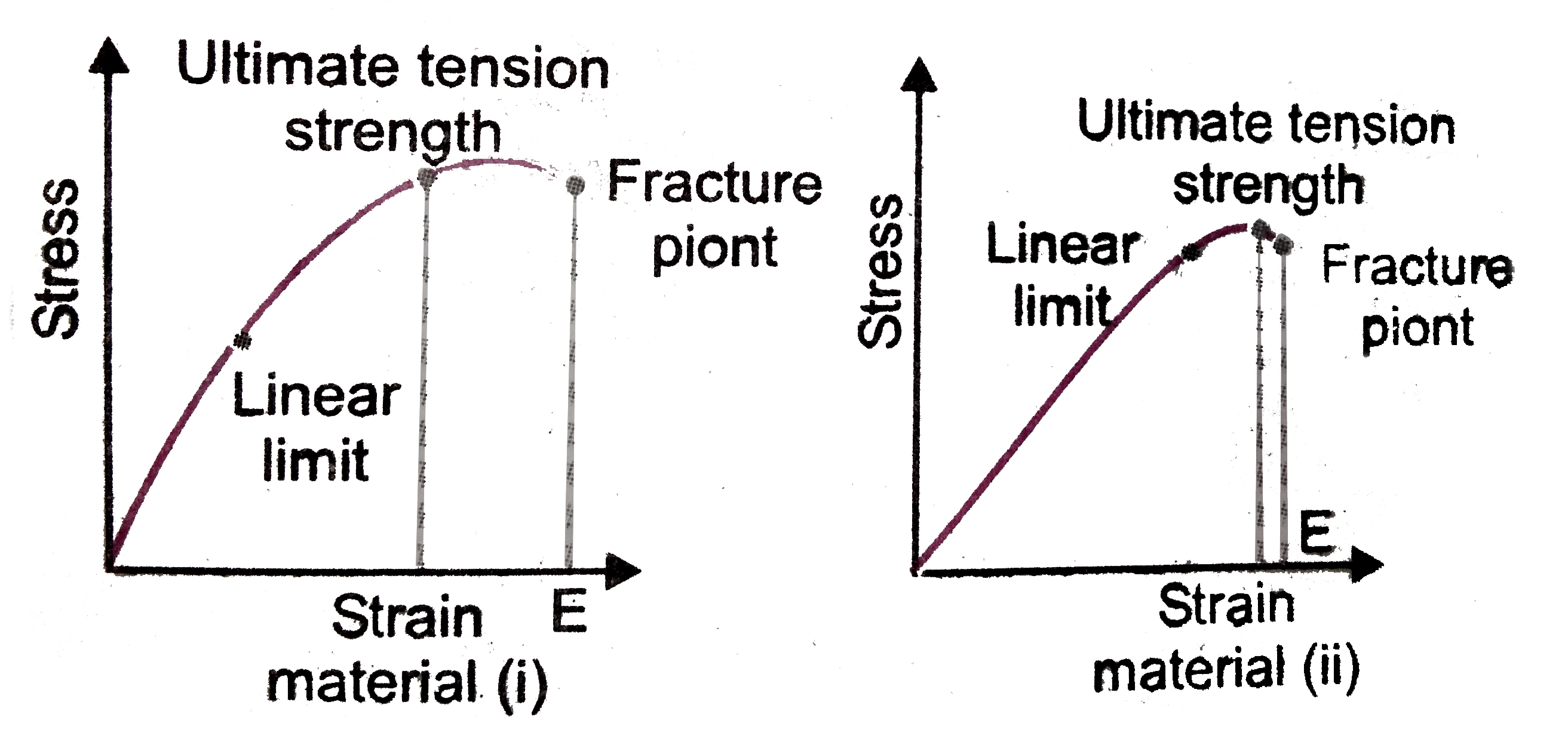A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions-I|173 VideosPROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Integer Type Questions|12 VideosPROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Problmes for Practice|198 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD AND MEASUREMENT
PRADEEP|Exercise Competiton Focus Jee Medical Entrance|18 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Problem For Practice(a)|25 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER-Multiple choice questions-II
- The stress-strain graphs for two materials are shown in Fig. 7(EP).3 ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is suspended from the ceiling and stretched under the action of...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 1.05 m having negliaible mass is supported at its ends...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal liquid
Text Solution
|
- A Copper wire and steel of the same diameter and length are connected...
Text Solution
|
- For a surface molecule,
Text Solution
|
- Pressure is a scalar quantity, because
Text Solution
|
- A wooden block, with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as show...
Text Solution
|
- With increase in temperature the viscosity of
Text Solution
|
- Streamline flow is more likely for liquid with
Text Solution
|
- Mark the correct option:
Text Solution
|
- Gulab jamuns (assumed to be spherical) are to be heated in on oven The...
Text Solution
|
- Refer to the plot of temperature versus time (figure) showing the chan...
Text Solution
|
- A glass full of hot milk is poured on the table. It begins to cool gra...
Text Solution
|