A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Interger Type questions|11 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type Questions|19 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions (NCERT)|10 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type questions|20 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion-Reason Type Questions|24 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-THERMODYNAMICS-Multiple choice questions.
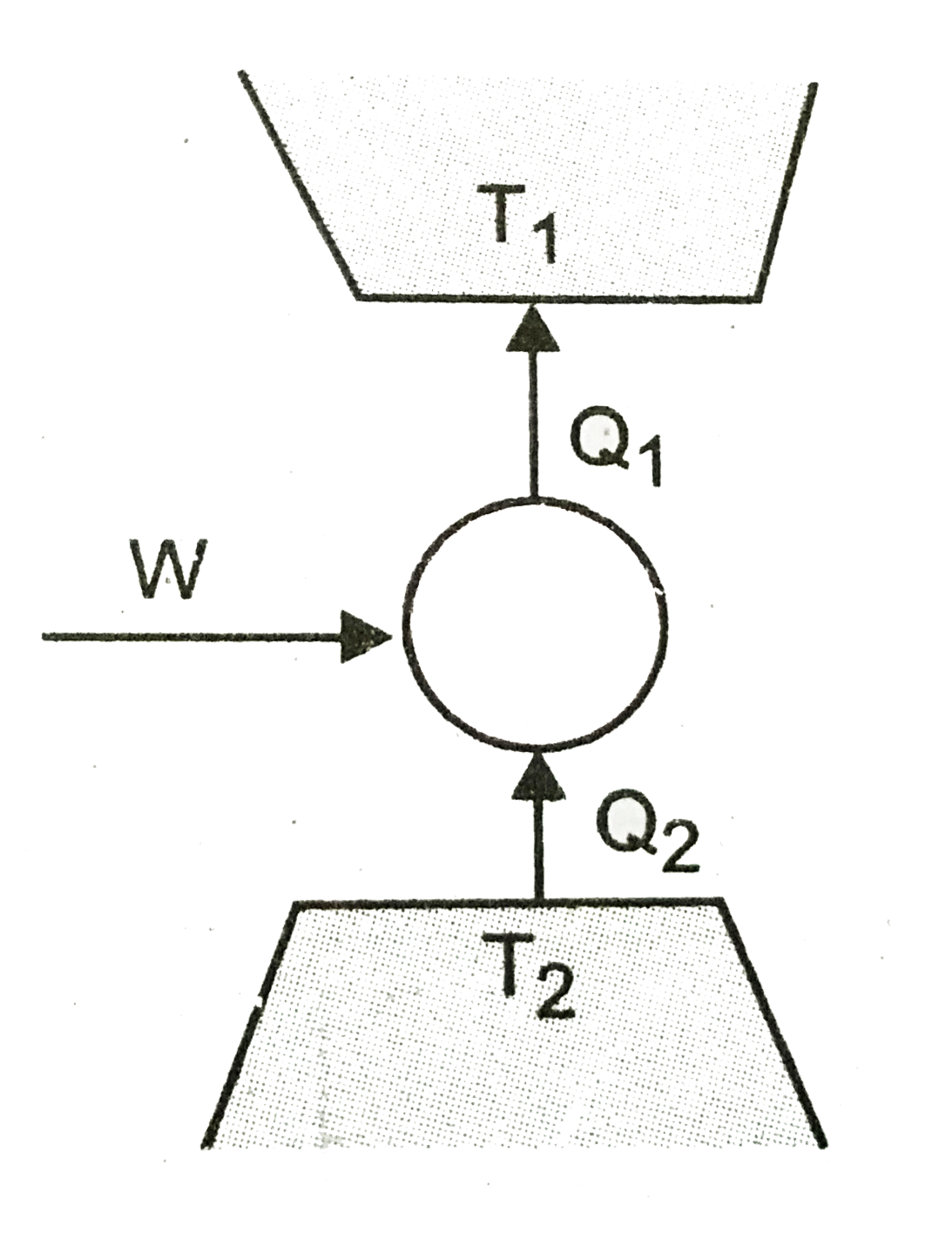
- Consider a heat engine as shown in (figure). Q(1) and Q(2) are heat ad...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a spherical shell of radius R at temperature T. The black bod...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following P-V diagrams best represents an isothermal proc...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of a gas is increased by 50% at constant temperature. The...
Text Solution
|
- A thermodynamic system undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal diatomic gas undergoes a transition from A to B a...
Text Solution
|
- At 27^@C two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas occupy a volume V. The g...
Text Solution
|
- In the above question, change in internal energy of gas is
Text Solution
|
- 400 c c volume of gas having gamma=5/2 is suddenly compressed to 100 c...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a diatomic ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process ABC as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state I with internal ...
Text Solution
|
- During an adiabatic process, the pressure of a gas is found to be prop...
Text Solution
|
- Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from v...
Text Solution
|
- P-V plots for two gases during adiabatic processes are shown in the fi...
Text Solution
|
- The work of 142kJ is performed in order to compress one kilo mole of g...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas at an initial temperature true of TK does 6R ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given (V-T) diagram, what is the relation between pressure P(1)...
Text Solution
|
- The P-V diagram of a gas undergoing a cyclic process ABCDA is shown in...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of helium gas are taken over the cycle ABCDA, as shown in th...
Text Solution
|