A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions-III|12 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Integer type questions|9 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions-I|59 VideosGRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion-Reason Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY-Multiple choice questions-II
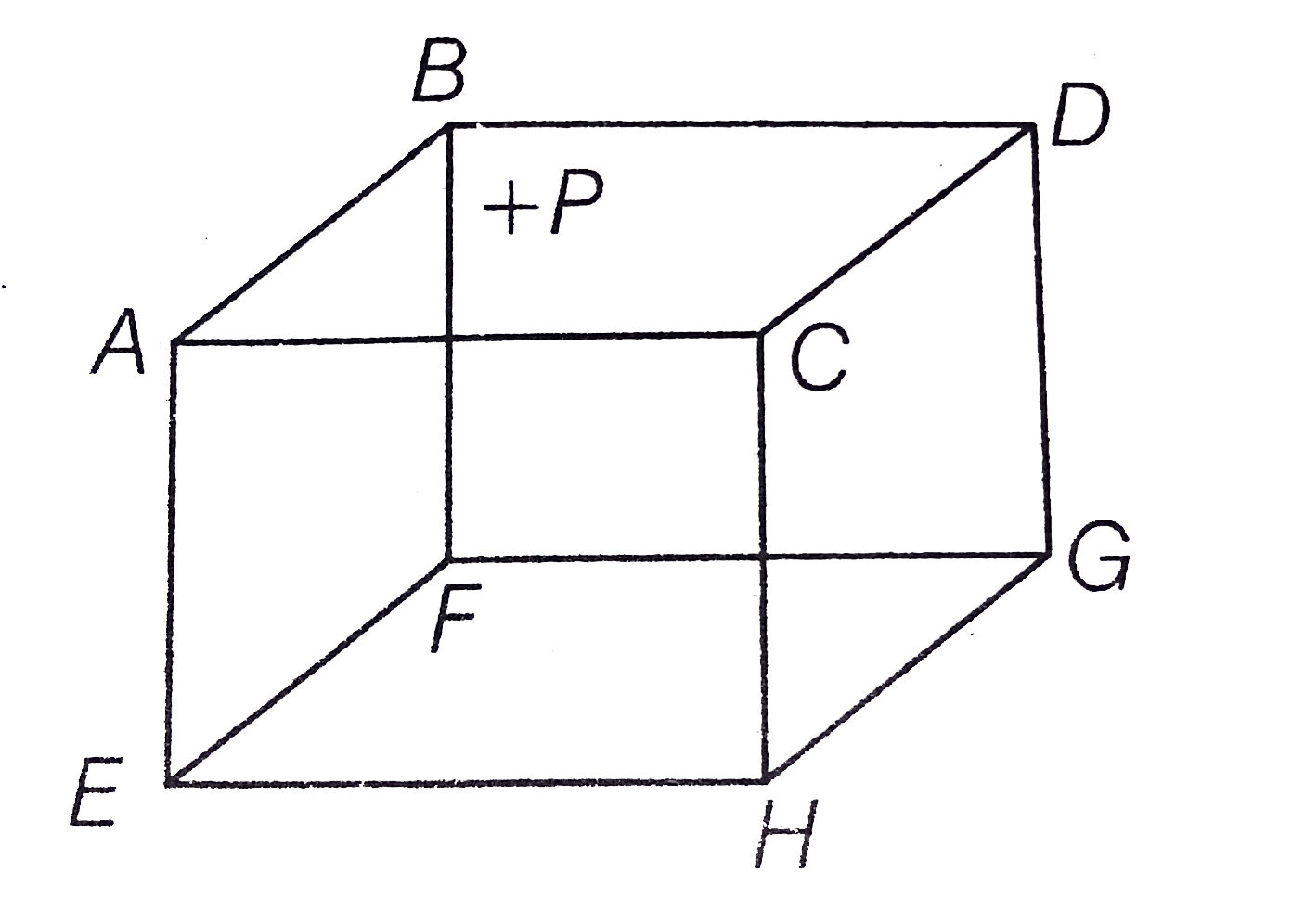
- ABCDEFGH is a hollow cube made of an insulator (figure) face ABCD has...
Text Solution
|
- A container of fixed volume has a mixture of a one mole of hydrogen an...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at t...
Text Solution
|
- The rms speed of the perfect gas molecules is doubled if.
Text Solution
|
- At ordinary temperatures, the molecules of an ideal gas have only tran...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is taken from the state A (P, V) to the state B (P//2, 2 ...
Text Solution
|
- Let barv,v(rms) and vp respectively denote the mean speed. Root mean s...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following processes are reversible ?
Text Solution
|