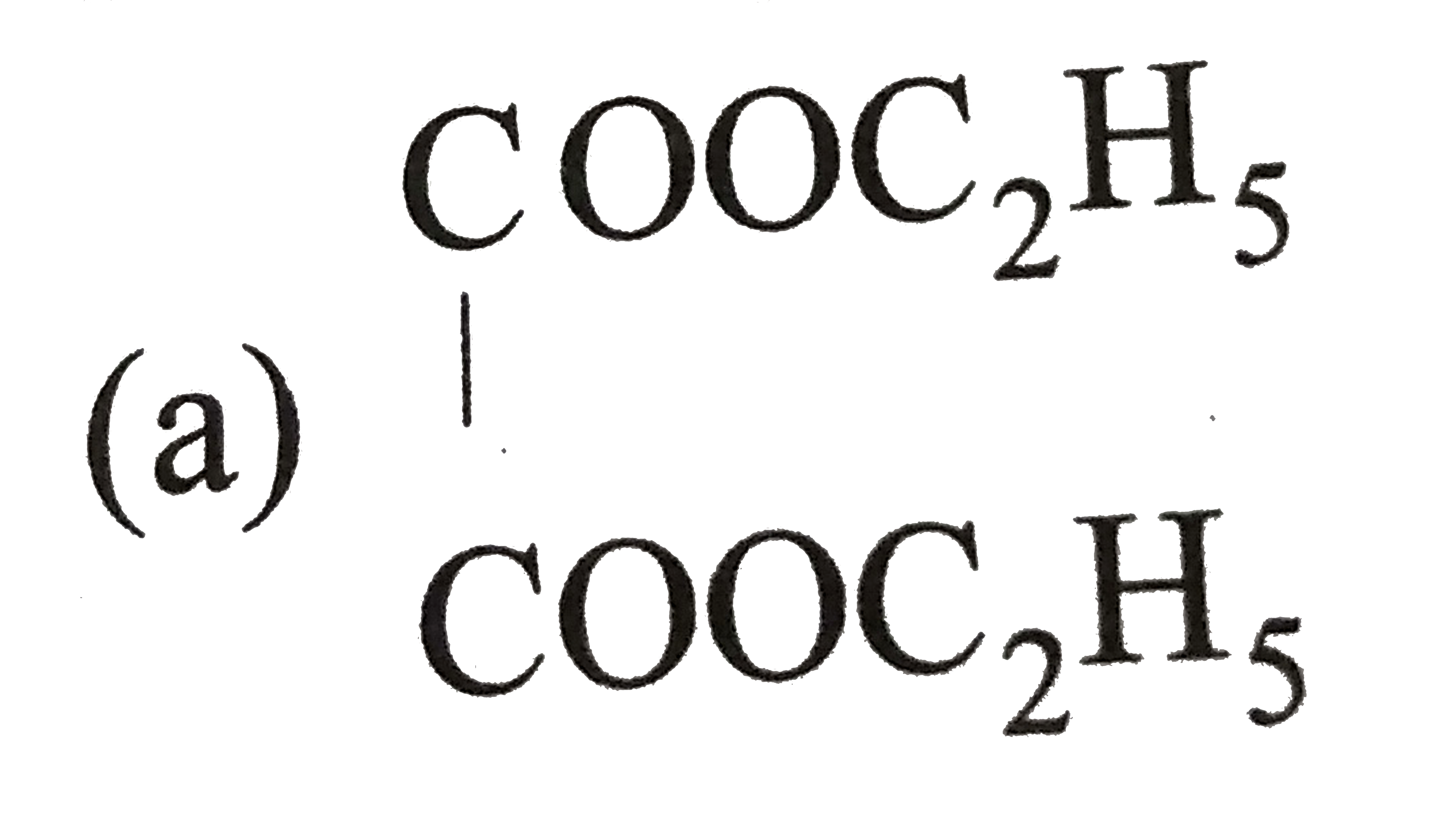A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN
A2Z|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning Questions|7 VideosORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 VideosORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN
A2Z|Exercise AIPMT/NEET Questions|26 VideosORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING HALOGENS
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 VideosP BLOCK ELEMENTS ( GROUP 15,16,17,18)
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN-AIIMS Questions
- Hinsberg's reagent is
Text Solution
|
- The product formed by the reaction of acetamide with bromine in presen...
Text Solution
|
- Promary amine reacts with carbon disulphide and HgCl2 to produce alkyl...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is involved in sandmeyer's reaction?
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction C6H5CHO+C6H5NH2toC6H5N=CHC6H5+H2O The compound C6H5N...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following the weakest base is .
Text Solution
|
- Nitrobenzene gives N-phenylhydroxylamine by
Text Solution
|
- Among the following the dissociation constant is highest for
Text Solution
|
- The strongest base among the following .
Text Solution
|
- Aromatic nitriles (ArCN) are not prepared by reaction .
Text Solution
|
- Melting points are normally highest for
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following chemicals are used to manufacture methy1 isocya...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following which one does not act as an intermediate in hofma...
Text Solution
|
- Pyridine is less basic than triethylamine because .
Text Solution
|
- The following sequence of reactions on gives
Text Solution
|
- Thymine is
Text Solution
|
- overset("Heat")(rarr) In the following sequency of the reactions, w...
Text Solution
|
- Cyanogen gas is obtained in the reaction
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is true?
Text Solution
|
- The reaction is called
Text Solution
|