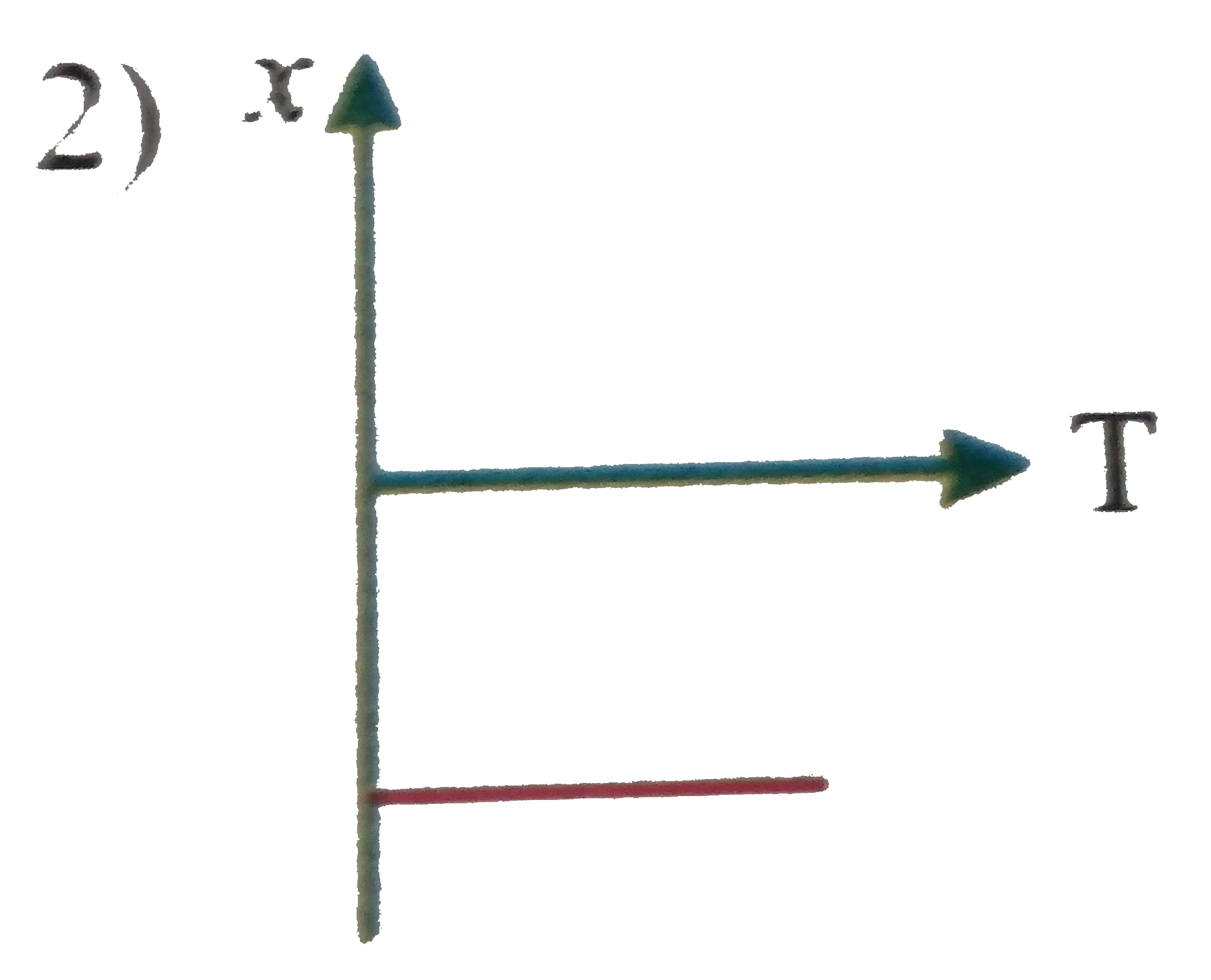
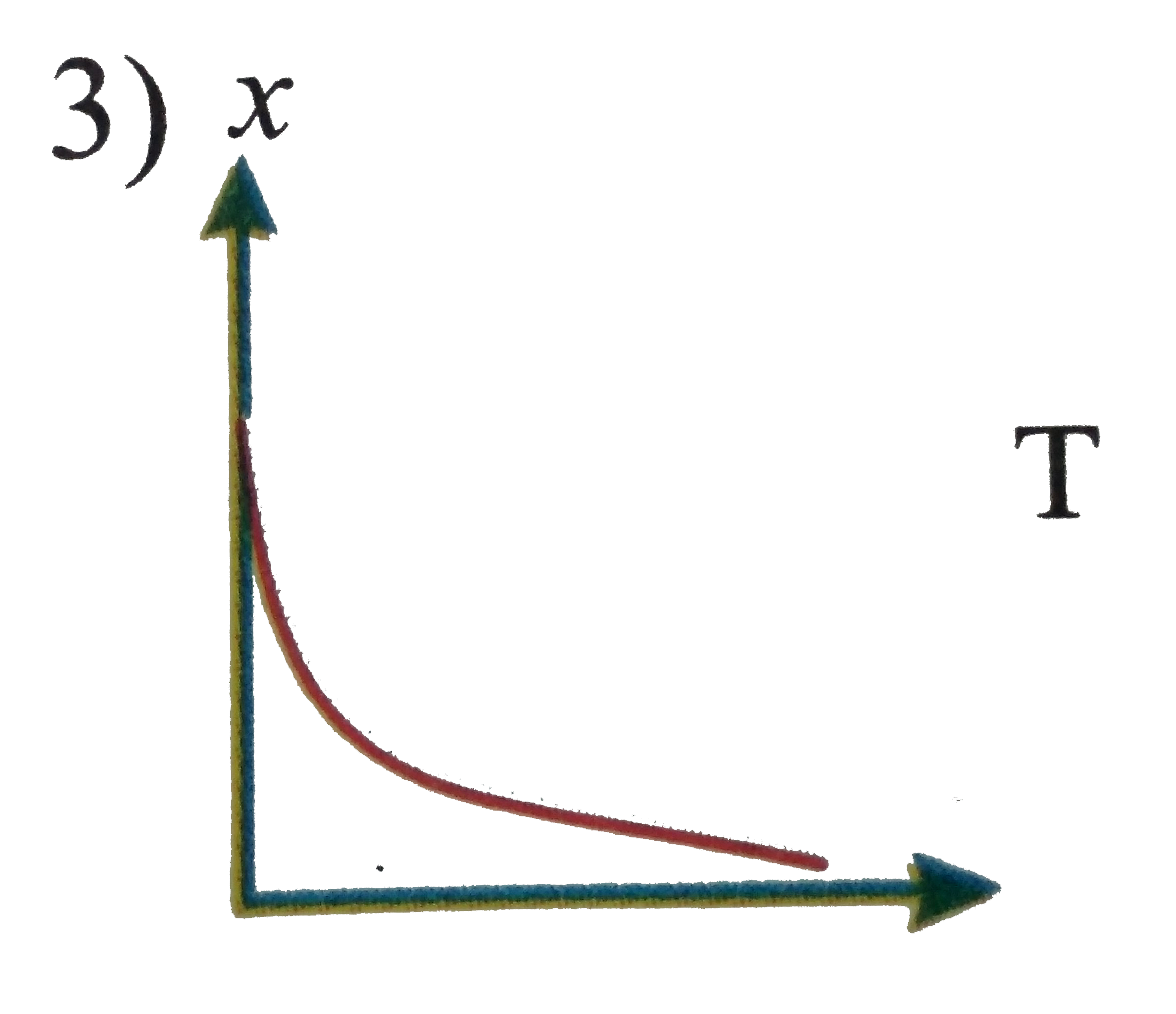
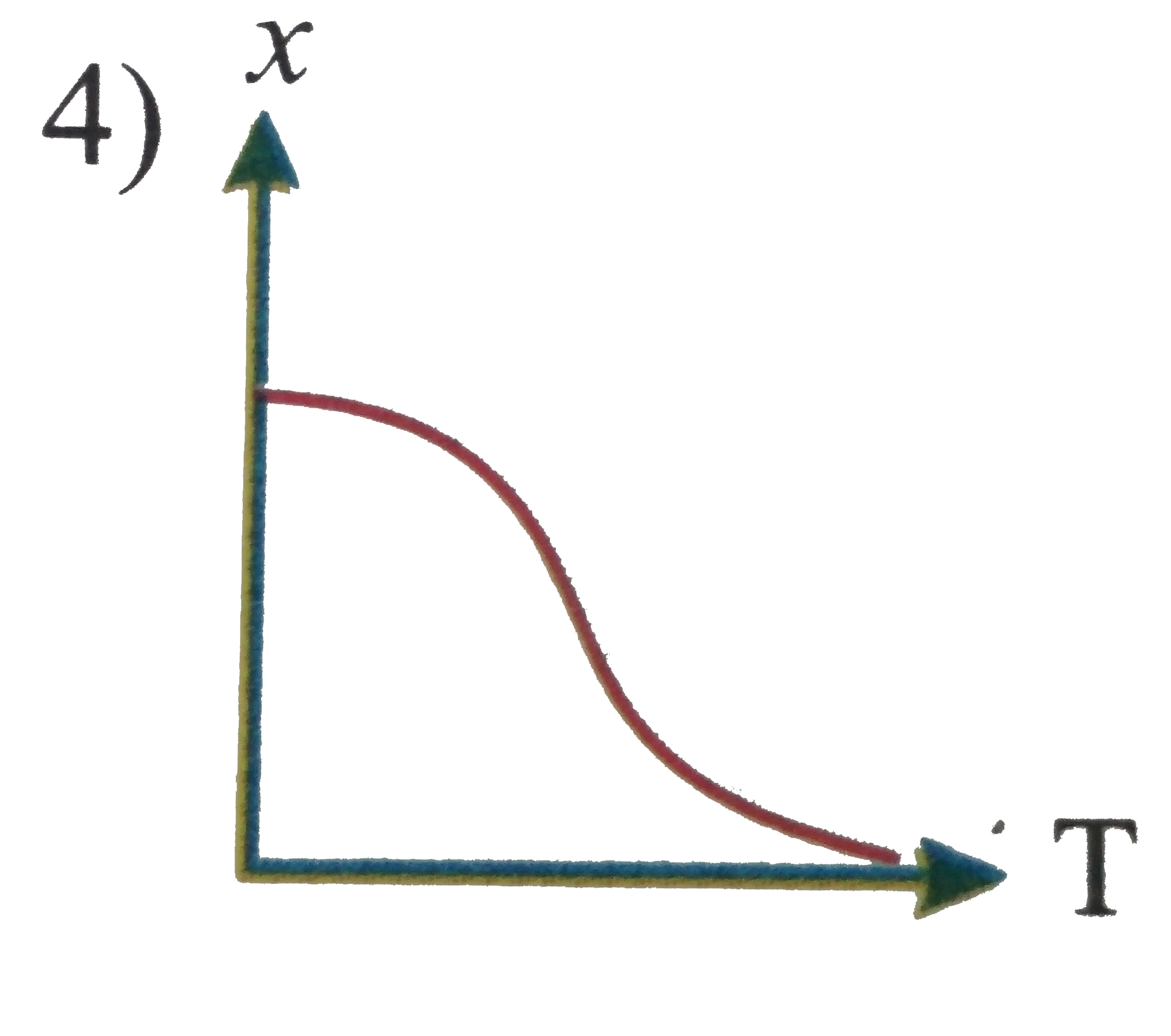
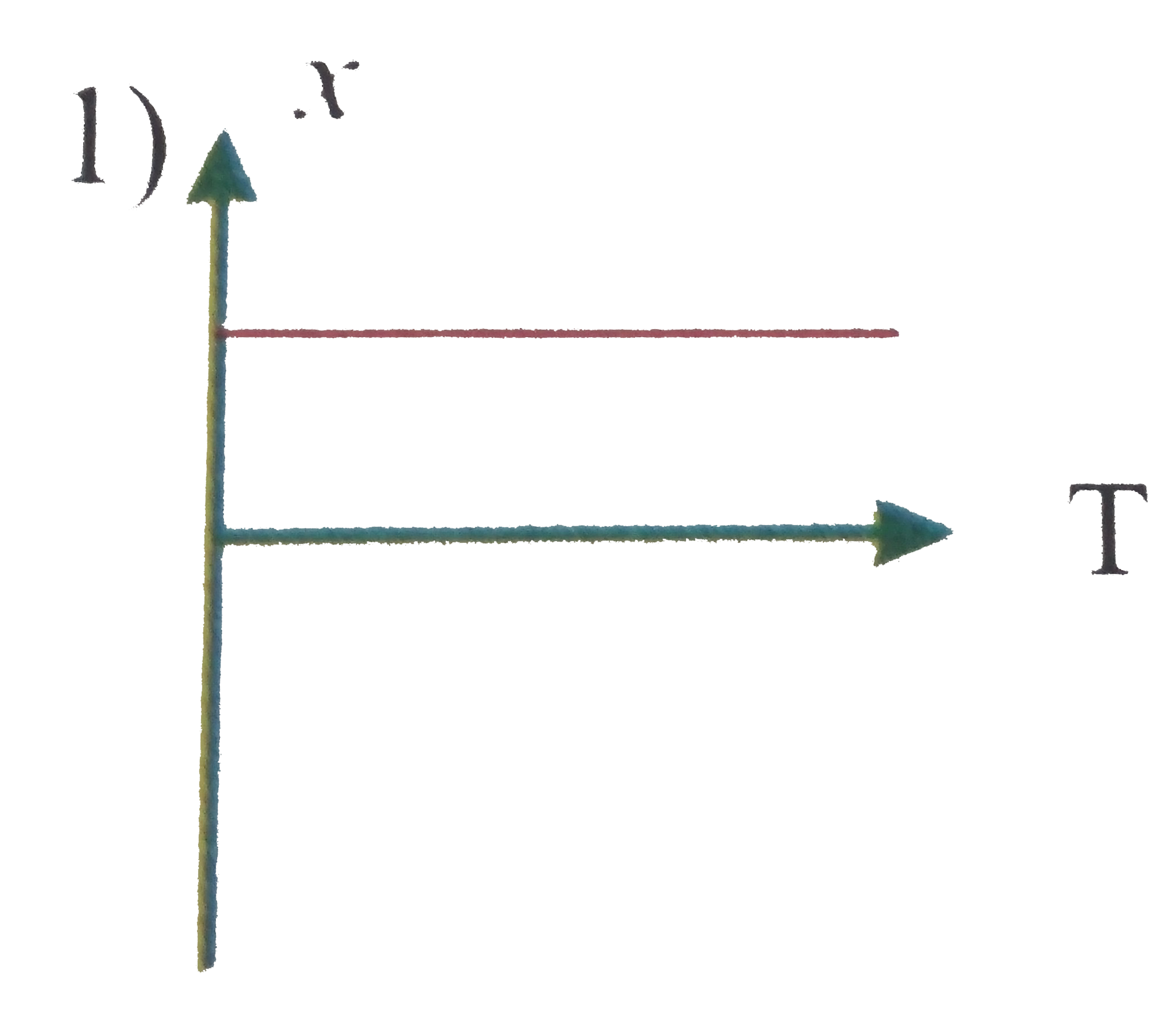A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-MAGNETISM-LEVEL-I (H.W)
- A short bar magnet placed with its axis at 30^(@) with a uniform exter...
Text Solution
|
- When a bar magnet is placed at 90^(@) to a uniform magnetic field, it ...
Text Solution
|
- A magnet of moment 4Am^(2) is kept suspended in a magnetic field of in...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in rotating the magnet form the direction of uniform fie...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in rotating a magnet of pole strength 1 A-m and length 1...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in turning a magnet normal to field direction from the d...
Text Solution
|
- A magnet is parallel to a uniform magnetic field. The work done in rot...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic induction field strength at a distance 0.2 m on the axial...
Text Solution
|
- A short bar magnet of magnetic moment 1.2Am^(2) is placed in the magne...
Text Solution
|
- A very long magnet of pole strength 4 Am is placed vertically with its...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet of magnetic moment M and moment of inertial I is in the d...
Text Solution
|
- If the moments of inertia of two bar magnets are same, and if their ma...
Text Solution
|
- If the strength of the magnetic field is increased by 21% the frequenc...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet has a magnetic moment equal to 65xx10^(-5) wever x metre....
Text Solution
|
- Two bar magnets are placed in vibration magnetometer and allowed to vi...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic induction and the intensity of magnetic field inside an i...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of an iron rod is 80 gm and its magnetic moment is 10 Am^(2)....
Text Solution
|
- A rod of cross sectional area 10cm^(2) is placed with its length paral...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet of magnetic moment 10Am^(2) has a cross sectional area of...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of magnetic susceptibility (chi) with temperature for a ...
Text Solution
|