Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CP SINGH-CENTER OF MASS-Exercises
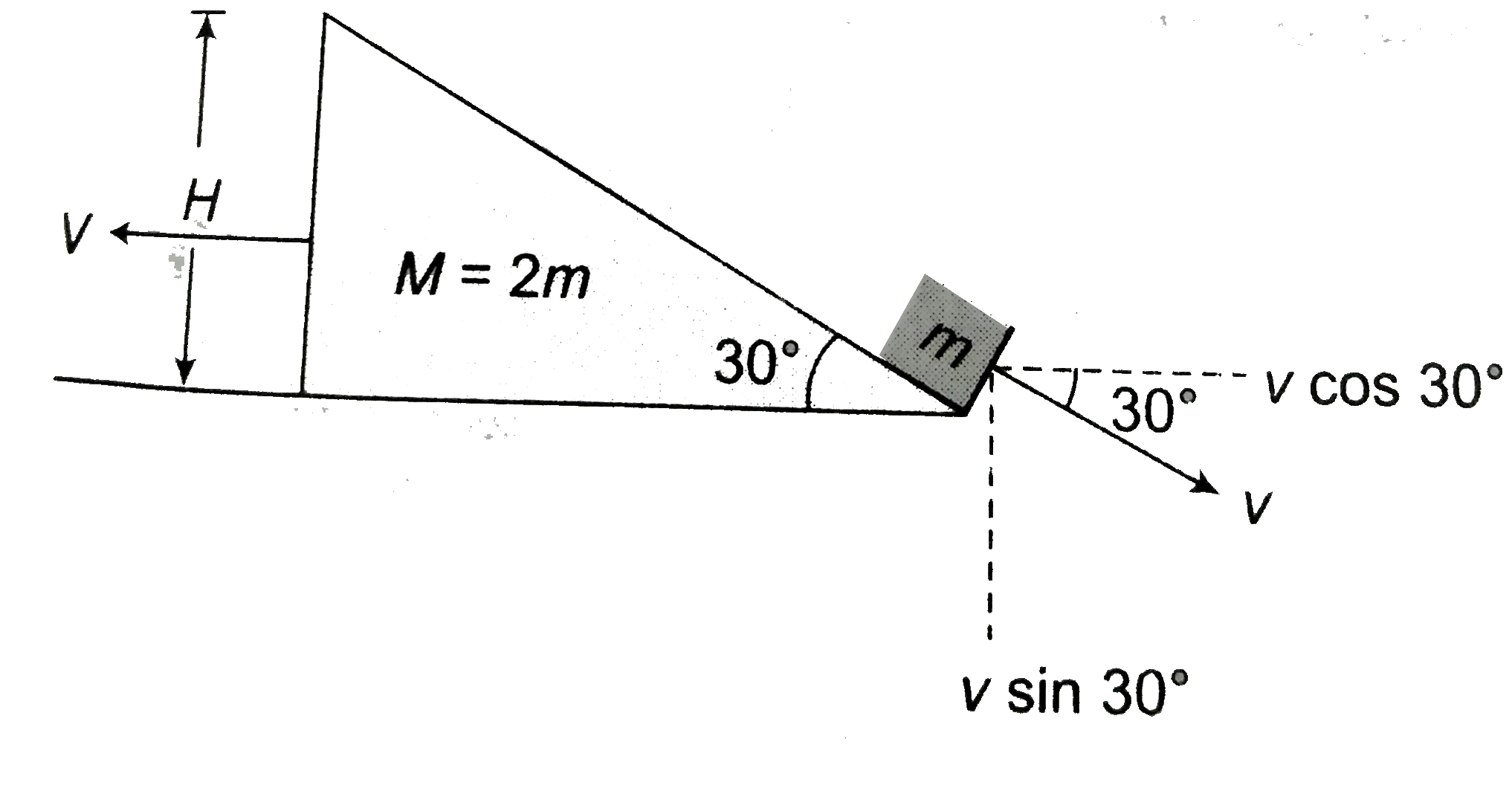
- A block of mass m is placed on a triangular block of mass M(M = 2m) , ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass 1kg and 3 kg have position v ectors hat(i) + 2 hat...
Text Solution
|
- All the particles of a body situated at distance d from the origin. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Particle of masses m, 2m,3m,…,nm grams are placed on the same line at ...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical metal balls each of radius r are placed touching each ...
Text Solution
|
- Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of radius R is removed from a bigger circular disc of ...
Text Solution
|
- A hemisphere and a solid cone have a common base. The center of mass o...
Text Solution
|
- If the linear density (mass per unit length) of a rod of length 3 m is...
Text Solution
|
- The mass per unit length of a non - uniform rod of length L is given m...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod of length 'L' is lying along the x-axis with its ends at x...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is true for center of mass ? (i) The center o...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of ice of maas m and edge L is placed in a large tray ...
Text Solution
|
- Two paricle A and B initially at rest, move towards each other under m...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder is leaned against a smooth wall and it is allowed to slip on ...
Text Solution
|
- A pulley fixed to the ceiling carries a string with blocks of mass m a...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls are thrown simultaneously from top of tower in air as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are true ? (i) A uniform wooden pl...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is true ? (i) A car of mass M is t...
Text Solution
|
- A boy of mass 40 kg stands on a rail road car of mass 60 kg, moving wi...
Text Solution
|
- A boy (mass of 40 kg) is standing at one end of a boat (mass of 60 kg)...
Text Solution
|