Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise SOLVED WBCHSE SCANNER|38 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise SLOVED NCERT EXERCISE|38 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise WARM UP EXERICSE|132 VideosMODEL QUESTIONS PAPER
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise SET III (SECTION II) (GROUP D )|12 VideosP-BLOCK ELEMENTS
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise PRACTICE SET 7 (ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS) : -|17 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CHHAYA PUBLICATION-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES -SHORT ANSWER TYPE
- Which atoms in a toluene molecule always remain in the same plane and ...
Text Solution
|
- Write the state of hybridisation of C-atoms in the following compounds...
Text Solution
|
- Write IUPAC name of the compound, mentioning secondary primary prefix...
Text Solution
|
- Expand each of the following condensed formulas into their complete st...
Text Solution
|
- (1) How many sigma and pi bonds are present in (i) CH(2) = CH - CN and...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the given compounds may exist as two or more isomeric forms? ...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structures and IUPAC names of the compounds with molecular f...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structures and IUPAC names of the compounds with molecular f...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will exhibit tautomerism and which do...
Text Solution
|
- Designte following pairs as metamers, chain isomers, position isomers,...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism an...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds are optically active and why? (1) CH...
Text Solution
|
- Which type of stereoisomerism is exhibited by the compound, CH(3)CH=CH...
Text Solution
|
- Name a compound having two dissimilar asymmetric carbon atoms and writ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why the C-C bond length in benzene is in between the carbon-ca...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange cis - but - 2 ene, trans - but - 2 - ene and but - 1 ene in in...
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)Cl is unreactive towards S(N)1 reaction - why?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the orders of acidity of carboxylic acids: (1) Cl(3)C COOHg...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange in order of increasing stability : (1) (CH3)2overset(o+)C H...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why an orgainc liquid vaporises below its boiling point when i...
Text Solution
|
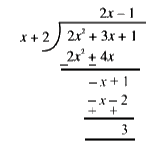 , all the atoms except 3 H-atoms of methly group (i.e, seven C - and five H - atoms) remain in the same plane.
, all the atoms except 3 H-atoms of methly group (i.e, seven C - and five H - atoms) remain in the same plane.