Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-LIQUID SOLUTION-EXERCISE-4 (Level-II) PREVIOUS YEAR JEE ADVANCED
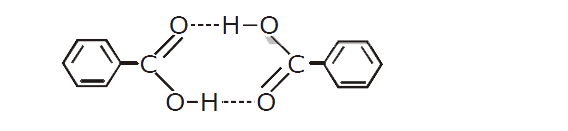
- 1.22 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in (i) 100g acetone (K(b) for acet...
Text Solution
|
- The elevation in boiling point, when 13.44 g of freshly prepared CuCI(...
Text Solution
|
- 72.5g of phenol is dissolved in 1kg of a solvent (k(f) = 14) which lea...
Text Solution
|
- When 20 g of naphthoic acid (C(11)H(8)O(2)) is dissolved in 50 g of be...
Text Solution
|
- The freezing point of the solution M is
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of the solution M is
Text Solution
|
- Water is added to the solution M such that the mole fraction of water ...
Text Solution
|
- The Henry's law constant for the solubility of N(2) gas in water at 29...
Text Solution
|
- The freezing point (in .^(@)C) of a solution containing 0.1g of K(3)[F...
Text Solution
|
- For a dilute solution containing 2.5 g of a non-volatile non-electroly...
Text Solution
|
- Benzene and naphthalene form an ideal solution at room temperature. Fo...
Text Solution
|
- MX(2) dissociates into M^(2+) and X^(ө) ion in an aqueous solution, wi...
Text Solution
|
- A compound H(2)X with molar weigth of 80g is dissolved in a solvent ha...
Text Solution
|
- If the freezing point of a 0.01 molal aqueous solution of a cobalt (II...
Text Solution
|
- Mixture (s) showing positive deviation from Raoult's law at 35^(@)C is...
Text Solution
|
- For a solution formed by mixing liquids L and M, the vapour pressure o...
Text Solution
|
- Pure water freezes at 273 K and 1 bar. The addition of 34.5 g of ethan...
Text Solution
|
- The plot given below shows P -T curves (where P is the pressure and T ...
Text Solution
|
- Liquids A and B form ideal solution over the entire range of compositi...
Text Solution
|