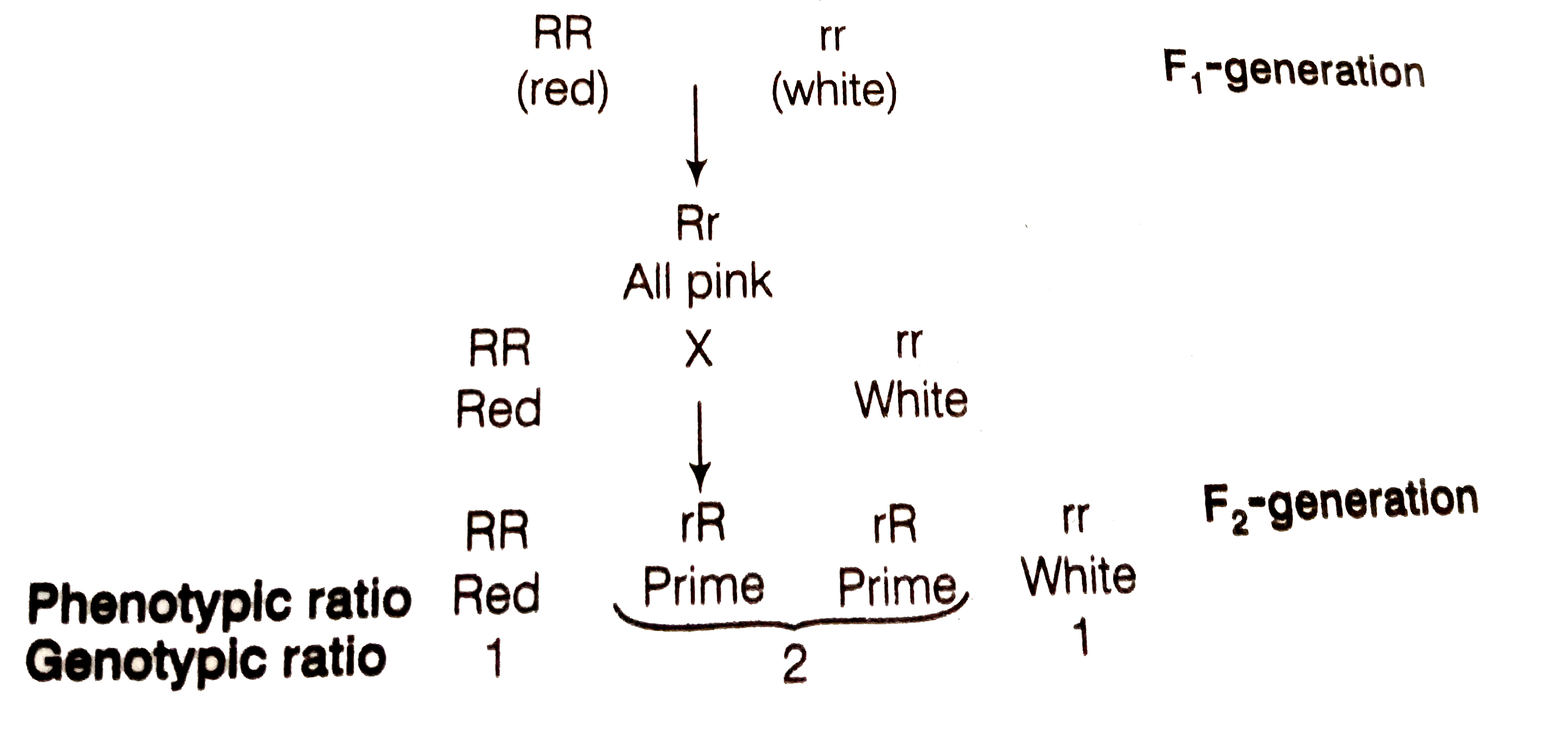Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-PRINCIPLE OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATIONS -Principle Of Inheritance And Variations
- Even if a character shows multiple allelism, an individual will only h...
Text Solution
|
- How does a mutagen induce mutation? Explain with example.
Text Solution
|
- In a Mendelian monohybrid cross, the F(2)-generation shows identcal ge...
Text Solution
|
- Can a child have blood group 'O' if his parents have blood group 'A' a...
Text Solution
|
- What is Down's syndrome? Give its symotoms and cause. Why is it that t...
Text Solution
|
- How was it concluded that genes are located on chromosomes?
Text Solution
|
- A plant with red flowers was crossed with another plant with yellow fl...
Text Solution
|
- What are the characteristic features of a trur-breeding line?
Text Solution
|
- In peas, tellenss is dominate over dqarfness, and red colour of flower...
Text Solution
|
- Why is the frequency of red-green colourblindness is many times higher...
Text Solution
|
- If a father and son are both defective in red-greenn colour vision, is...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss why Drosophila has been used extensively for genetical studies...
Text Solution
|
- How do genes and chromosomes share similarity from the point of view o...
Text Solution
|
- What is recombination? Discuss the applications of recombination from ...
Text Solution
|
- What is artificial selection? Do you think it affects the process of n...
Text Solution
|
- With the help of an example differntiate between incomplete dominance ...
Text Solution
|
- It is said, that the harmful alleles get eliminated from population ov...
Text Solution
|
- In a plant tallenss is dominant over dwarfness and red flower is domin...
Text Solution
|
- (a) In humans, males are heterogametic and frmales are homogametic, Ex...
Text Solution
|
- A normal visioned woman, whose father is colour blind, marries a norma...
Text Solution
|