A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA NEET SET 29-PHYSICS
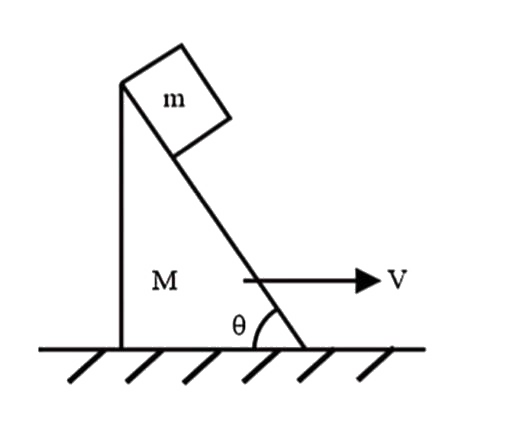
- A block of mass m is stationary with respect to the wedge of mass M mo...
Text Solution
|
- The wavelength of light coming from a distant galaxy is found to be 0....
Text Solution
|
- In a single slit diffraction of light of wavelength lambda by a slit o...
Text Solution
|
- When a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids, the in...
Text Solution
|
- If the diameter of a cylinder is 12.6 pm0.1 cm and its height is 34.2 ...
Text Solution
|
- Four molecules of ags have speeds 1,2,3 and 4 km//s.The volume of the ...
Text Solution
|
- An amount of water of mass 20 g at 0^(@)C is mixed with 40 g of water ...
Text Solution
|
- A crystal of intrinsic silicon at room temperature has a carrier conce...
Text Solution
|
- The output of the given logic circuit is
Text Solution
|
- When a silicon PN junction is in forwards biased condition with series...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the centres of carbon and oxygen atoms in the car...
Text Solution
|
- What is the magnitude of torque acting on a particle moving in the xy ...
Text Solution
|
- If two mirrors are inclined at some angle and an object is placed betw...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on an equilateral glass prism placed on a h...
Text Solution
|
- The excess pressure inside an air bubble of radius r just below the su...
Text Solution
|
- A small tiny lead shot is gently dropped on the surface of a viscous l...
Text Solution
|
- The kinetic energy of the most energetic photoelectrons emitted from a...
Text Solution
|
- In a photoelectric experiment under conditions of saturation current ,...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of a particle varies with its displacement as v=(sqrt(9-x...
Text Solution
|
- A mass (M) is suspended from a spring of negligible mass. The spring i...
Text Solution
|