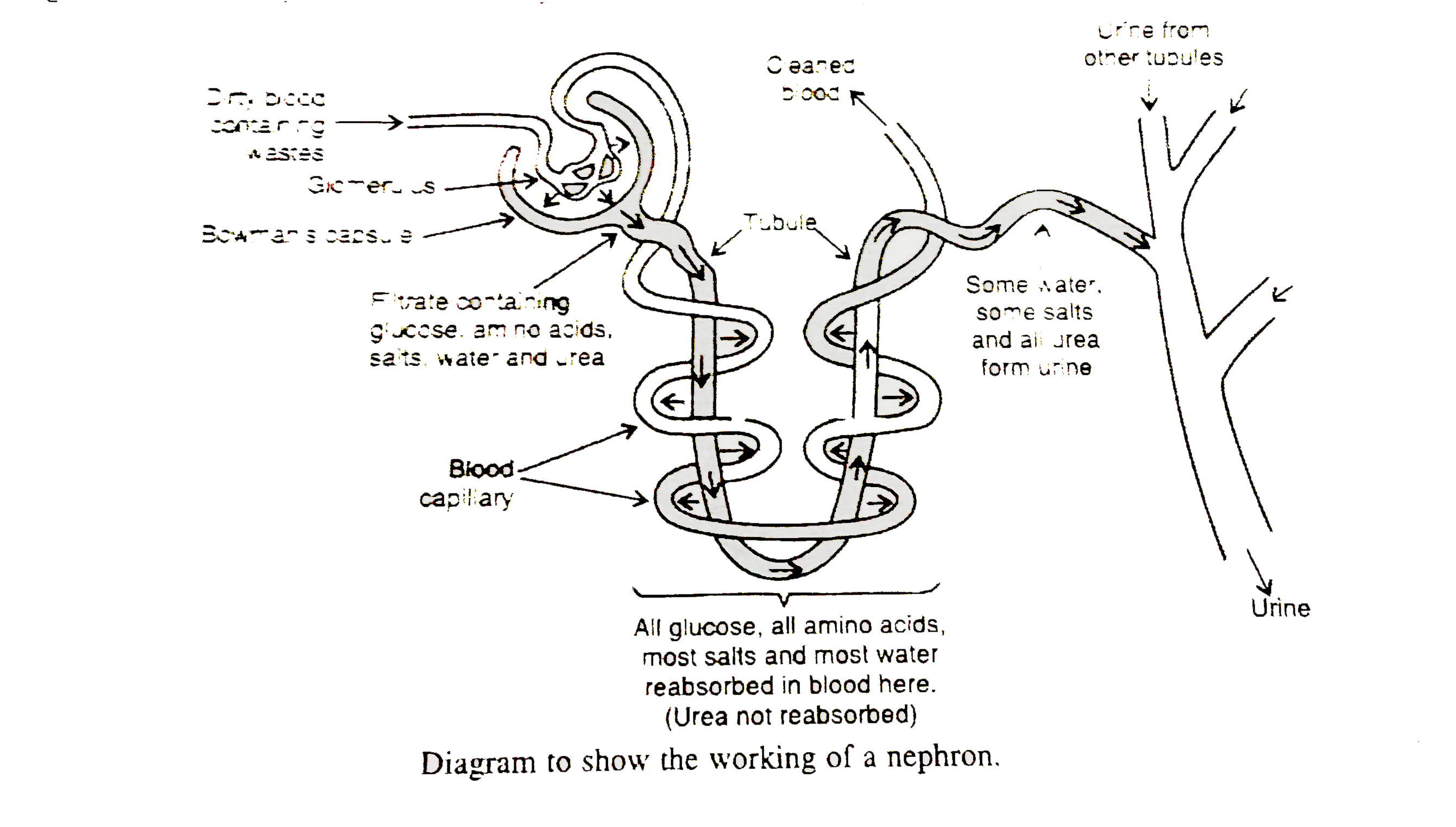Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LIFE PROCESSES
LAKHMIR SINGH & MANJIT KAUR|Exercise very short answer type question|1 VideosLIFE PROCESSES
LAKHMIR SINGH & MANJIT KAUR|Exercise short answer type question|3 VideosLIFE PROCESSES
LAKHMIR SINGH & MANJIT KAUR|Exercise question based on high order thinking skills|1 VideosHOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE
LAKHMIR SINGH & MANJIT KAUR|Exercise QUESTIONS BASED ON HIGH ORDER THINKING SKILLS (HOTS)|27 VideosMANAGEMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES
LAKHMIR SINGH & MANJIT KAUR|Exercise VALUE BASED QUESTIONS|25 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
LAKHMIR SINGH & MANJIT KAUR-LIFE PROCESSES-Exercise
- How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Text Solution
|
- How is food transported in plants?
Text Solution
|
- Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Text Solution
|
- What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products
Text Solution
|
- How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Text Solution
|
- The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
Text Solution
|
- The xylem in plants are responsible for
Text Solution
|
- The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
Text Solution
|
- The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy tak...
Text Solution
|
- How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take plac...
Text Solution
|
- What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Text Solution
|
- What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what a...
Text Solution
|
- What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Na...
Text Solution
|
- How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Text Solution
|
- What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our b...
Text Solution
|
- Describe double circulation of blood in human beings. Why is it necess...
Text Solution
|
- What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem a...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the ki...
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Text Solution
|
- What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Text Solution
|