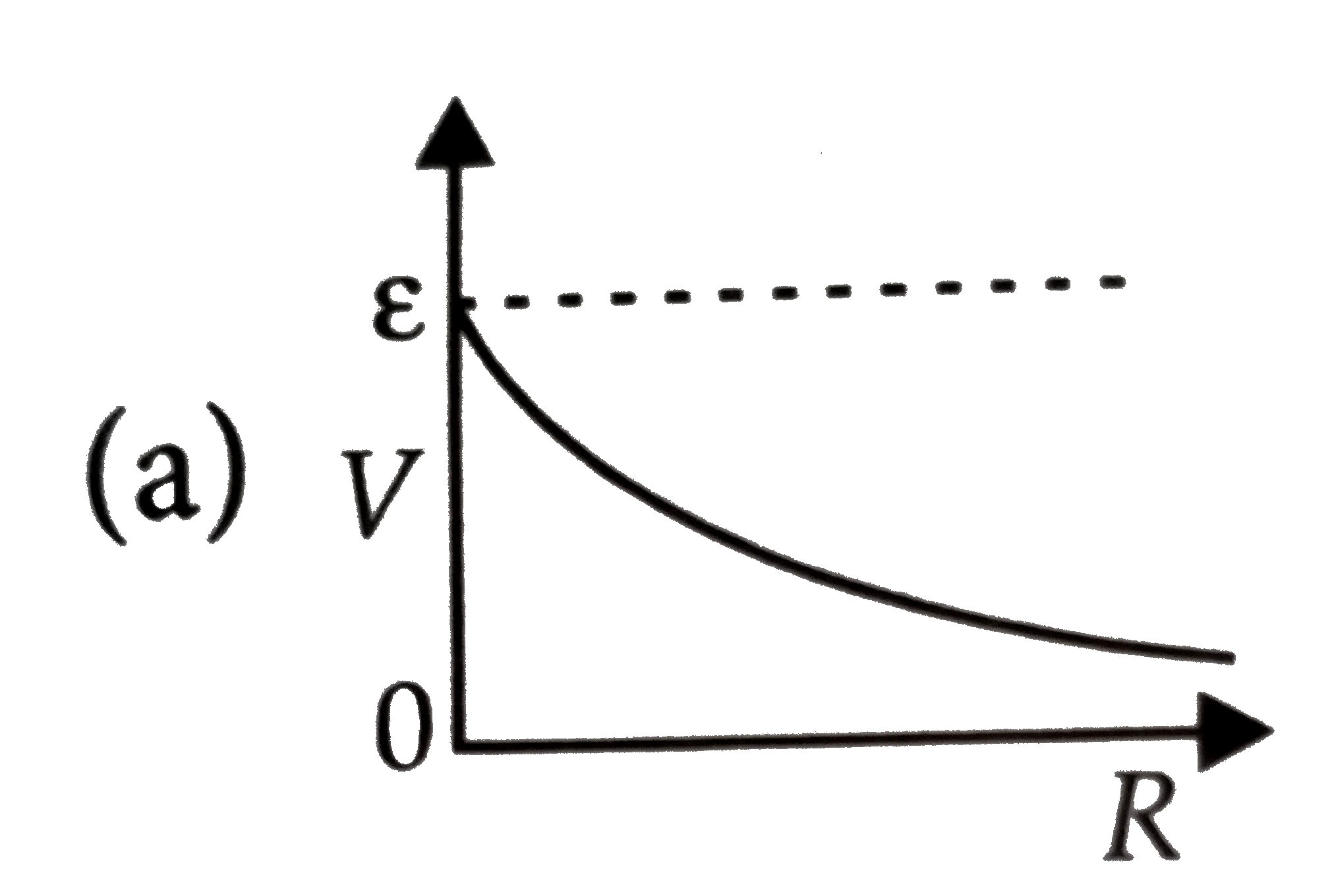
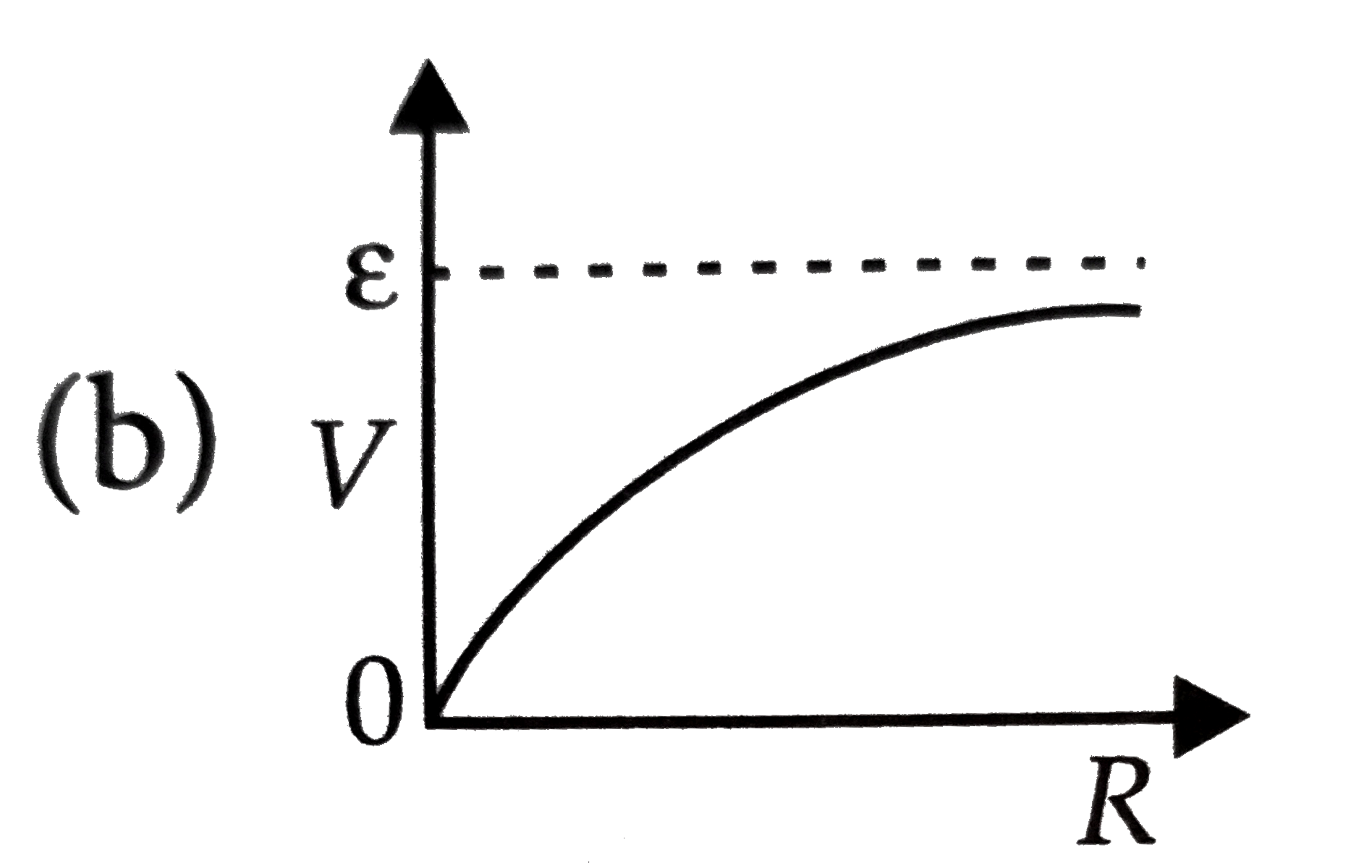
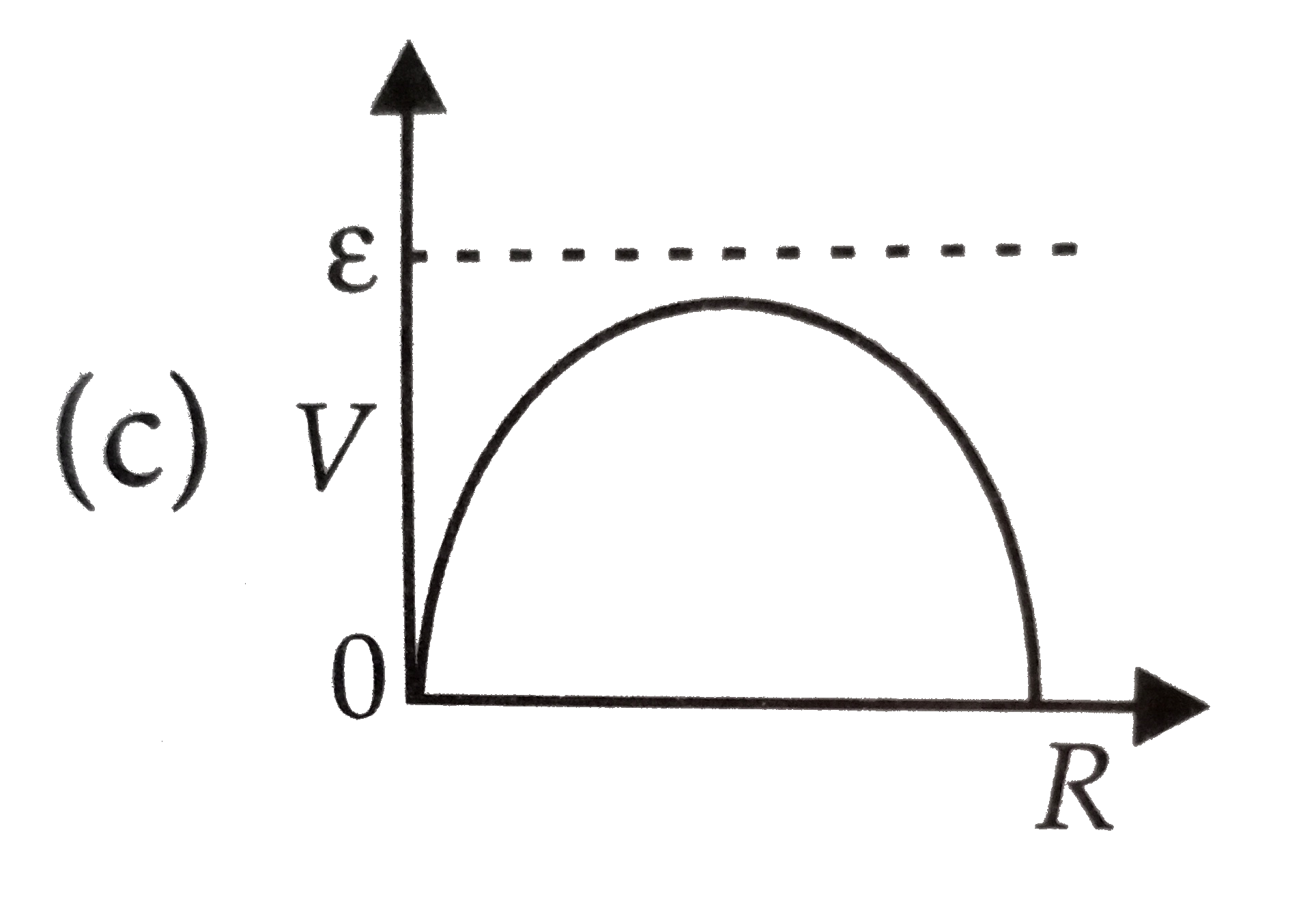
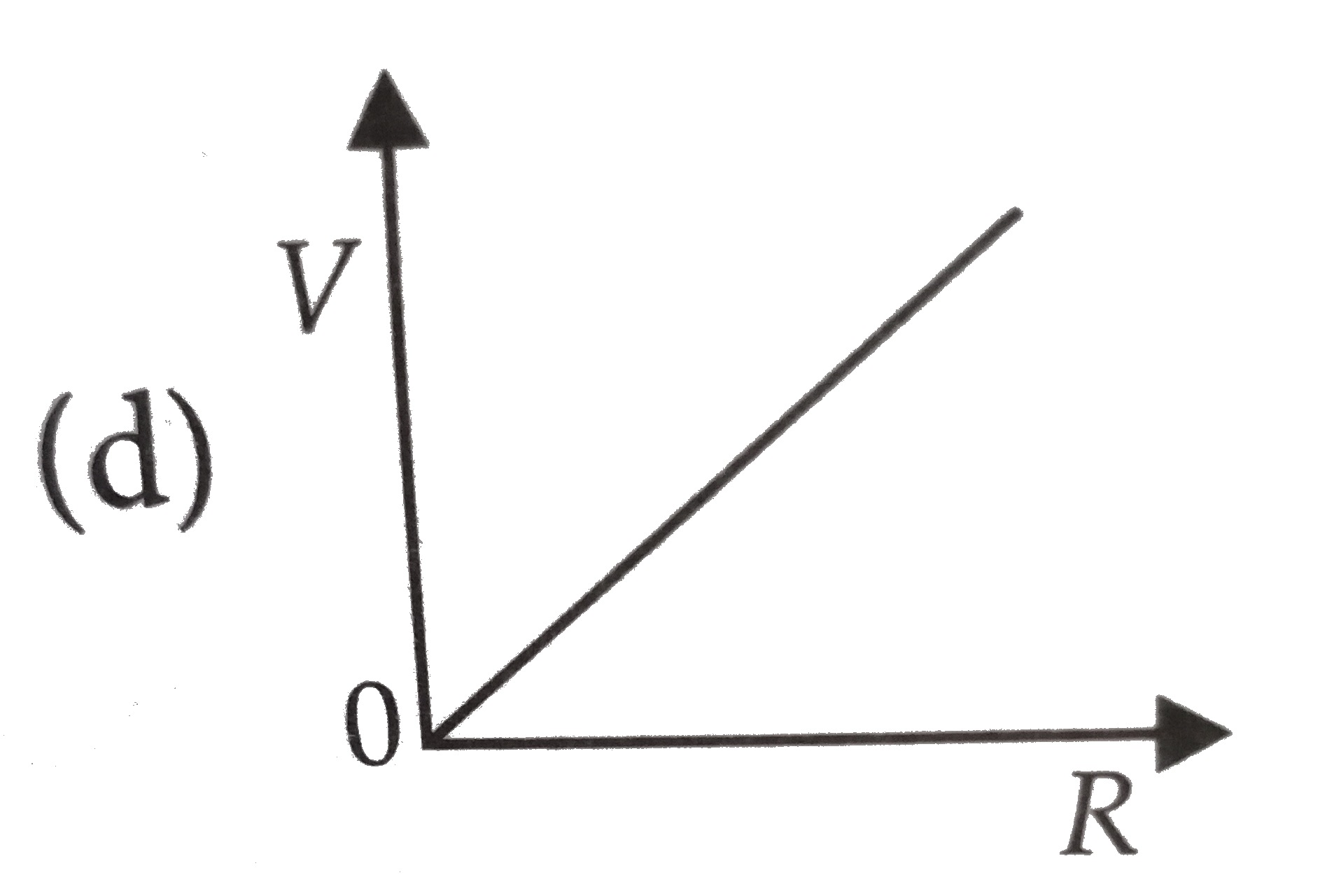
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Cell In Series And In Parallel|3 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Kirchoff'S Law|11 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Combination Of Resistors : Series And Parallel|22 VideosCOMMUNITCATION SYSTEMS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise HOTS|10 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-Cells, Emf, Internal Resistance
- A cell having an emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a...
Text Solution
|
- A battery of emf 15 V and internal resistance of 4Omega is connected ...
Text Solution
|
- The battery of a trunk has an emf of 24 V. If the internal resistance ...
Text Solution
|
- A battery having 12V emf and internal resistance 3Omega is connected t...
Text Solution
|
- When a current of 2 A flows in a battery from negative to positive ter...
Text Solution
|
- In a circuit a cell with internal resistance r is connected to an exte...
Text Solution
|