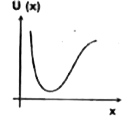
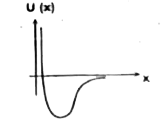
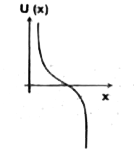
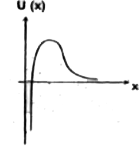
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER -COMPREHENSIONS ( Comprehension-II)
- The potential energy function for the force between two in a diatomic ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy function for the force between two in a diatomic ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy function for the force between two in a diatomic ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a graph of potential energy. Consider the following...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a graph of potential energy. Consider the following ...
Text Solution
|