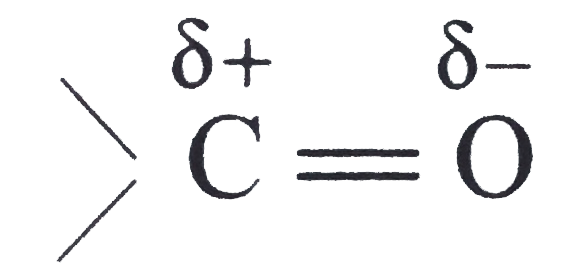A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
OP TANDON|Exercise PASSAGE 2|5 VideosALDEHYDES AND KETONES
OP TANDON|Exercise PASSAGE 3|5 VideosALDEHYDES AND KETONES
OP TANDON|Exercise MATRIX-MATCH TYPE QUESTIONS|8 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
OP TANDON|Exercise SINGLE INETER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS / ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS|15 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES
OP TANDON|Exercise SECTION V INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTION|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OP TANDON-ALDEHYDES AND KETONES -PASSAGE 1
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
 is polar (due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen)
is polar (due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen)