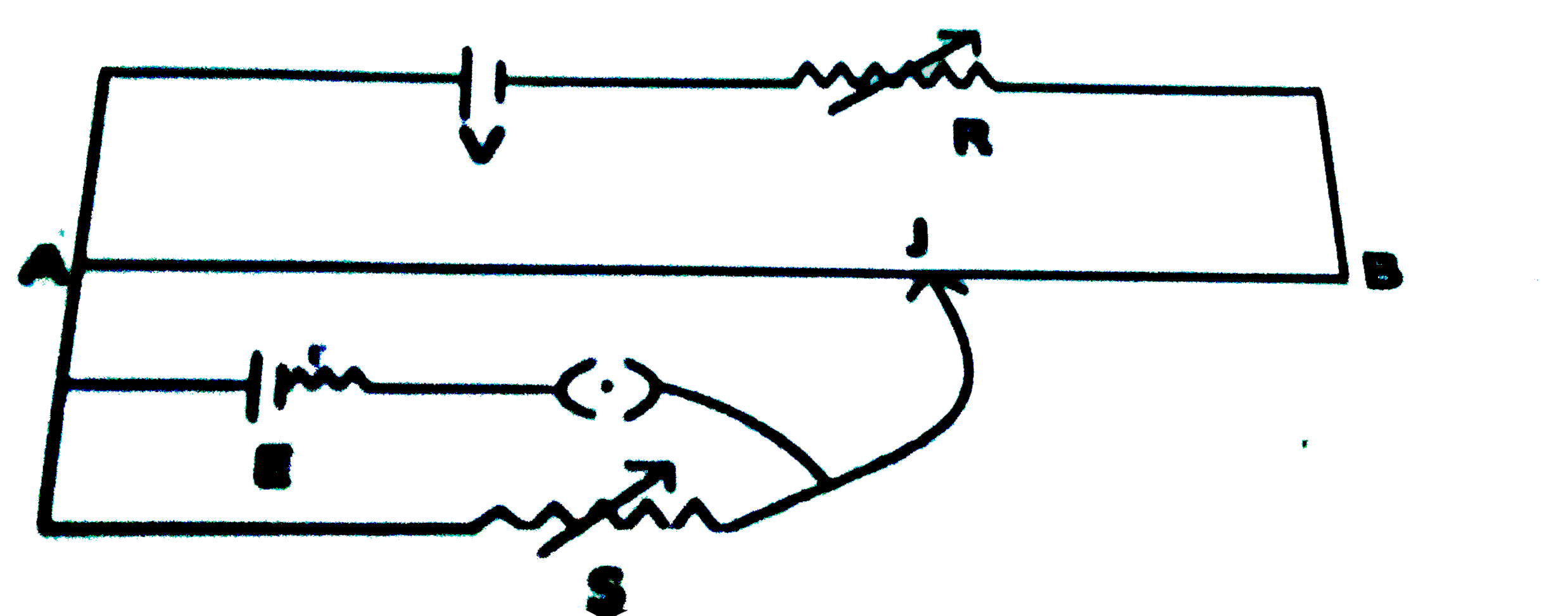
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-SAMPLE PAPER 2019-SECTION C
- State working principle of potentiometer. Explain how the balance poin...
Text Solution
|
- Using Biot-Savart’s law, derive an expression for magnetic field at an...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the resonant frequency and Q – factor of a series LCR circuit w...
Text Solution
|
- State the conditions of total internal reflection. Refractive indices ...
Text Solution
|
- Define resolving power of an astronomical refracting telescope and wri...
Text Solution
|
- Derive lens maker's formula for a thin convex lens.
Text Solution
|
- Show that ""(92)^(238)U can not spontaneously emit a proton. Given: ...
Text Solution
|
- Suggest an idea to convert a full wave bridge rectifier to a half wave...
Text Solution
|