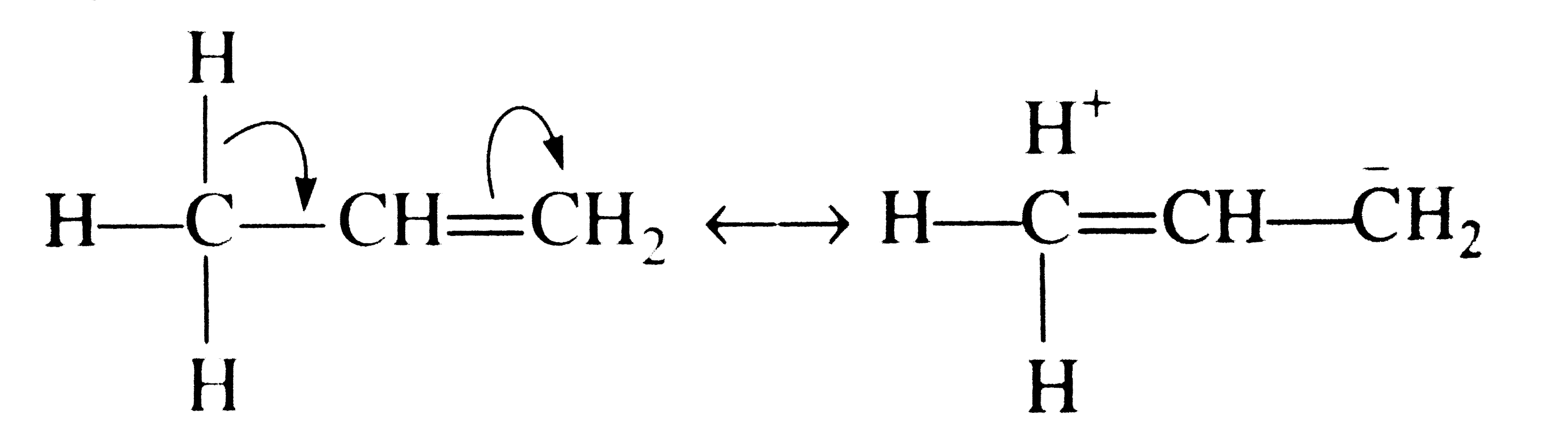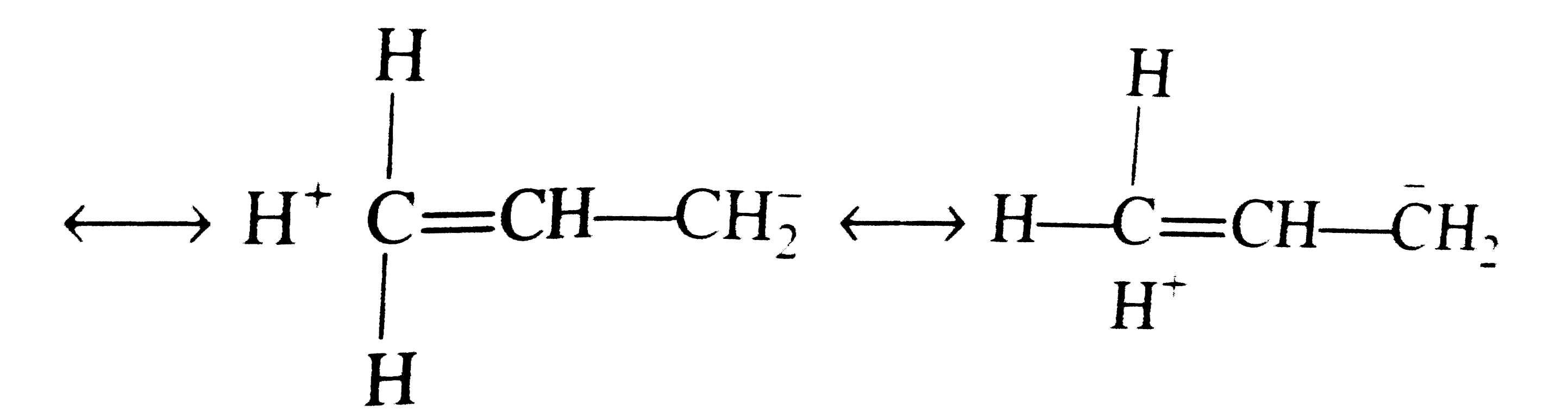A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)
OP TANDON|Exercise PASSAGE-IV|3 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)
OP TANDON|Exercise PASSAGE-V|5 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)
OP TANDON|Exercise PASSAGE-II|5 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES
OP TANDON|Exercise SECTION V INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTION|3 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
OP TANDON|Exercise Integer|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OP TANDON-BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)-PASSAGE-III
- Hyperconjugation describes the orbital interactions between the pi-sys...
Text Solution
|
- Hyperconjugation describes the orbital interactions between the pi-sys...
Text Solution
|
- Hyperconjugation describes the orbital interactions between the pi-sys...
Text Solution
|
- Hyperconjugation describes the orbital interactions between the pi-sys...
Text Solution
|
- Hyperconjugation describes the orbital interactions between the pi-sys...
Text Solution
|