Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-SAMPLE PAPER-1 (SOLVED)-Questions
- Calculate the magnetic field inside a solenoid when the number of turn...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells each of 5V are connected in series across a 8 Omega resisto...
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on transformer.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the alpha decay process with example.
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for the energy stored in a parallel plate capaci...
Text Solution
|
- Explain any three recent advancements in medical technology.
Text Solution
|
- Two light sources with amplitudes 5 units and 3 units respectively int...
Text Solution
|
- An electron moves in a circular orbit with a uniform speed v. It produ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the construction and working of photo emissive cell.
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure, the input voltage Vi = +5 V, V(BE)...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for electric field due to an uniformly charge sp...
Text Solution
|
- Write any five properties of electromagnetic waves.
Text Solution
|
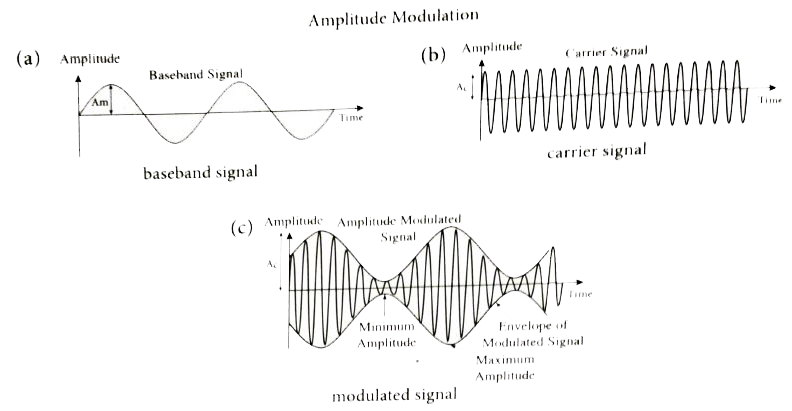
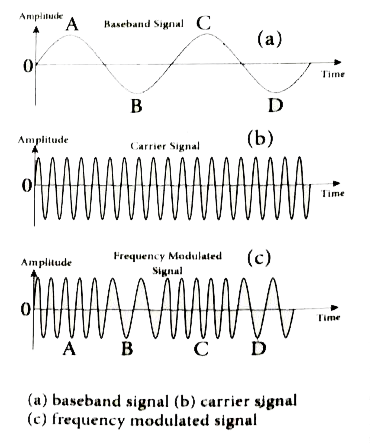
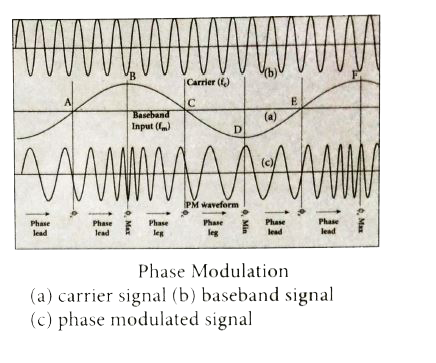
- What is modulation? Explain the types of modulation with necessary dia...
Text Solution
|
- Find the expression for the mutual inductance between a pair of coils ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for the radius of the orbit of the electron and ...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the working of cyclotron in detail.
Text Solution
|
- Obtain lens maker's formula and medium its signification. Lens maker'...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the construction and working of a full wave rectifier.
Text Solution
|
- An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 81V. What...
Text Solution
|
- A cell supplies a current of 0.9 A through a 1 Omega resistor and a cu...
Text Solution
|