Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-Exercise
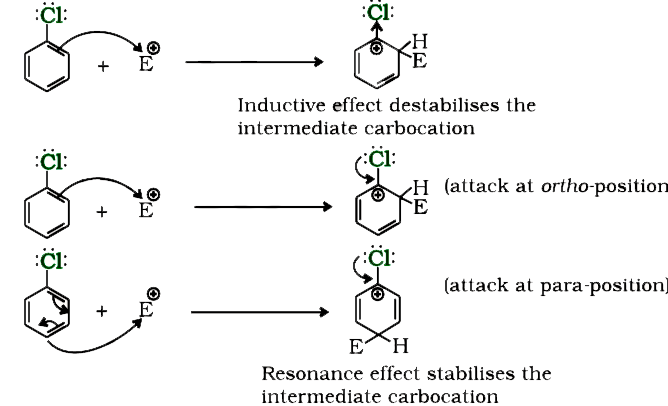
- Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet it is ortho-, ...
Text Solution
|
- Write structures of the following compounds: (i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpe...
Text Solution
|
- Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI...
Text Solution
|
- Write structures of different dihalogen derivatives of propane.
Text Solution
|
- Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C(5)H(12), identify th...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the followin...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points. ...
Text Solution
|
- Which alkyl halide from the following pairs would you expect to react ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify A, B, C, D, E, R and R^(1) in the following:
Text Solution
|
- Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them...
Text Solution
|
- Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds: (i) CH(3)CH(Cl)CH(B...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds. (i)...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following has the highest dipole moment? (i) CH(2)C...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrocarbon C(5)H(10) does not react with chlorine in dark but gives...
Text Solution
|
- Write the isomers of the compound having formula C(4)H(9)Br.
Text Solution
|
- Write the equations for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from (i) 1-b...
Text Solution
|
- What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
Text Solution
|
- Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in S(N...
Text Solution
|
- Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of...
Text Solution
|
- How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) Ethanol to ...
Text Solution
|