Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct|130 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|10 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3.2|8 VideosNUCLEAR PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise ddp.5.5|14 VideosRAY OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 1.6|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT-Subjective
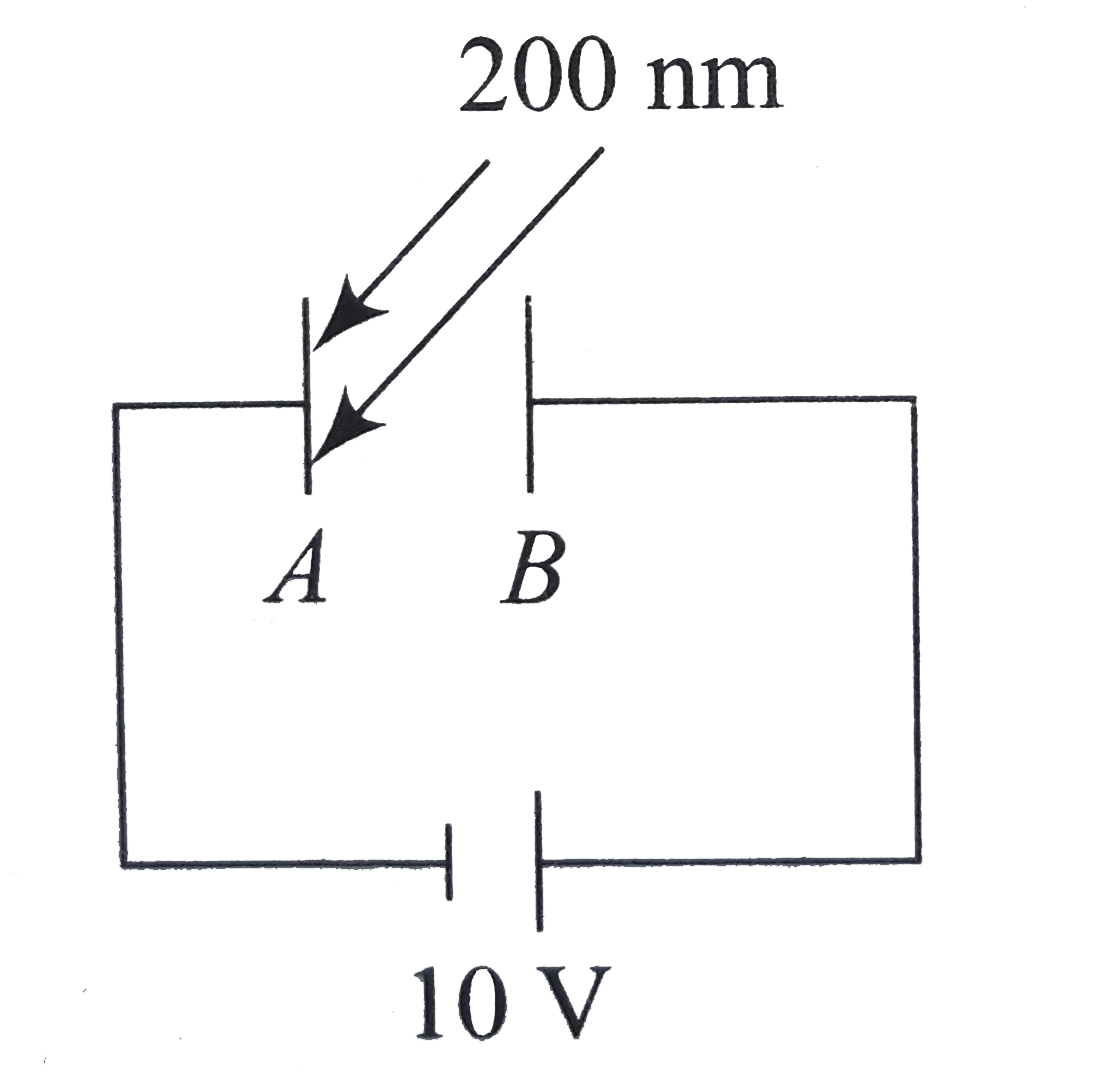
- In Fig. electromagnetic radiations of wavelength 200nm are incident on...
Text Solution
|
- The path of photoelectrons emitted due to electromagnetic radiation in...
Text Solution
|
- Photons of energy 5eV are incident on the cathode. Electrons reaching ...
Text Solution
|
- A plane light wave of intenstiy I=0.20 cm^(-2) falls on a plane mirror...
Text Solution
|
- Light of wavelength 180 nm ejects photoelectrons from a plate of met...
Text Solution
|
- When a surface is irradiated with light of wavelength 4950A, a photocu...
Text Solution
|
- The stopping potential for the photoelectrons emitted from a metal sur...
Text Solution
|
- A vacuum photocell consists of a central cathode and an anode. The int...
Text Solution
|
- The rediation emitted when an electron jumps from n = 3 to n = 2 orbi...
Text Solution
|
- A parellel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is incide...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 365xx10^-9m and in...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate de Broglie wavelength for an average helium atom in a furnac...
Text Solution
|
- What amount of energy sould be added to an electron to reduce its de B...
Text Solution
|
- What amount of energy should be added to an electron to reduce its de ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical rod of some laser material 5xx10^-2m long and 10^-2m in ...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 W sodium lamp is radiating light of wavelength 5890A, uniformly ...
Text Solution
|