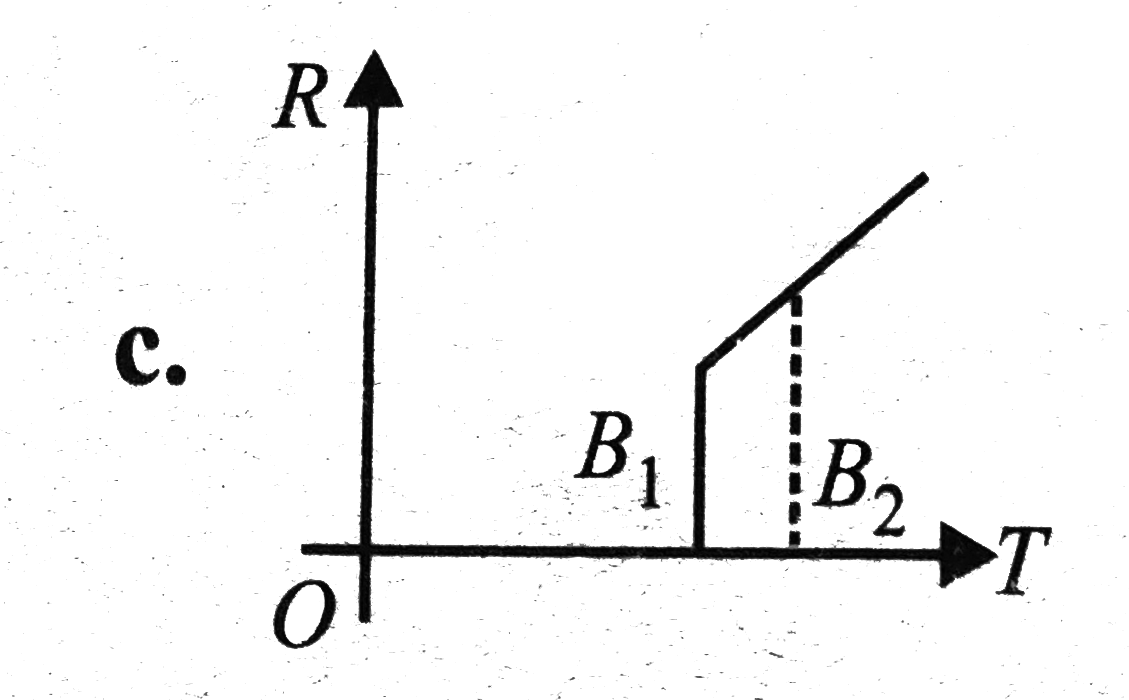
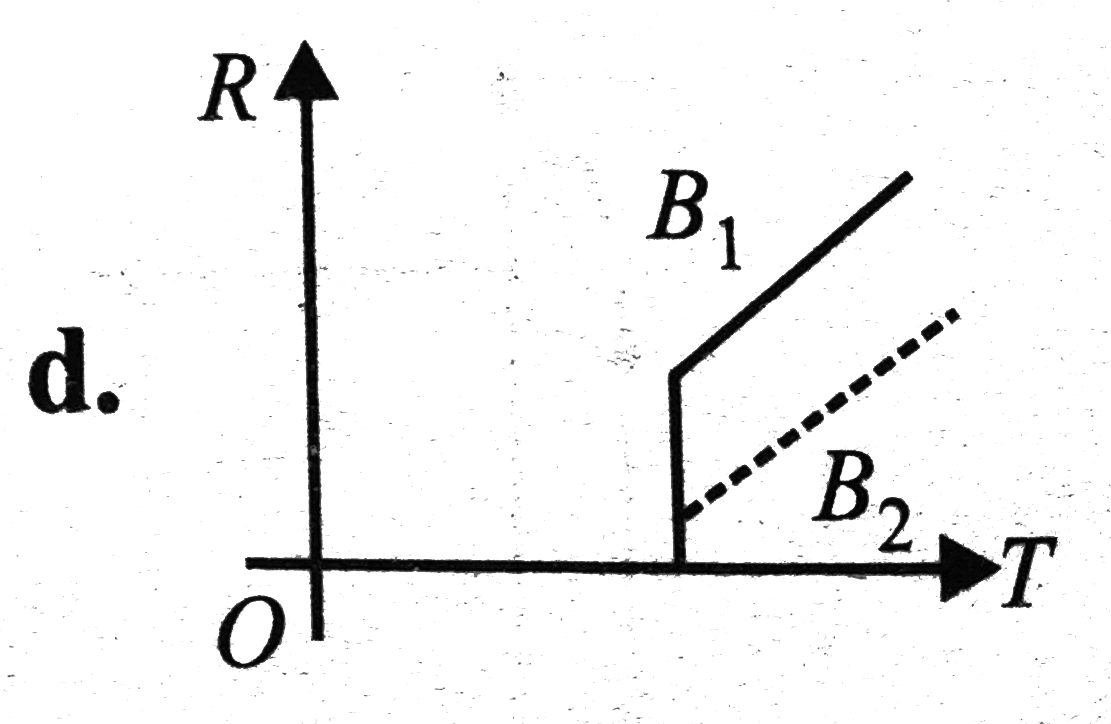
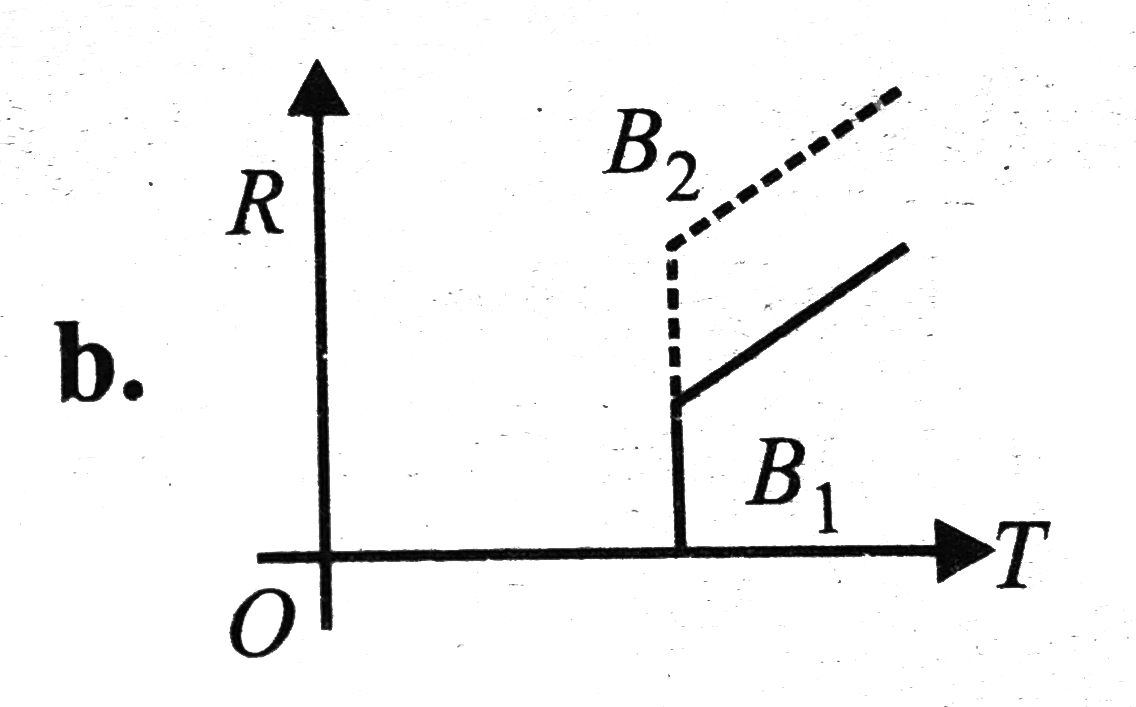
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Integer|1 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Assertion-reasion|1 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Multiple Correct|9 VideosINDUCTANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Concept Based|8 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise True and False|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
 .
.