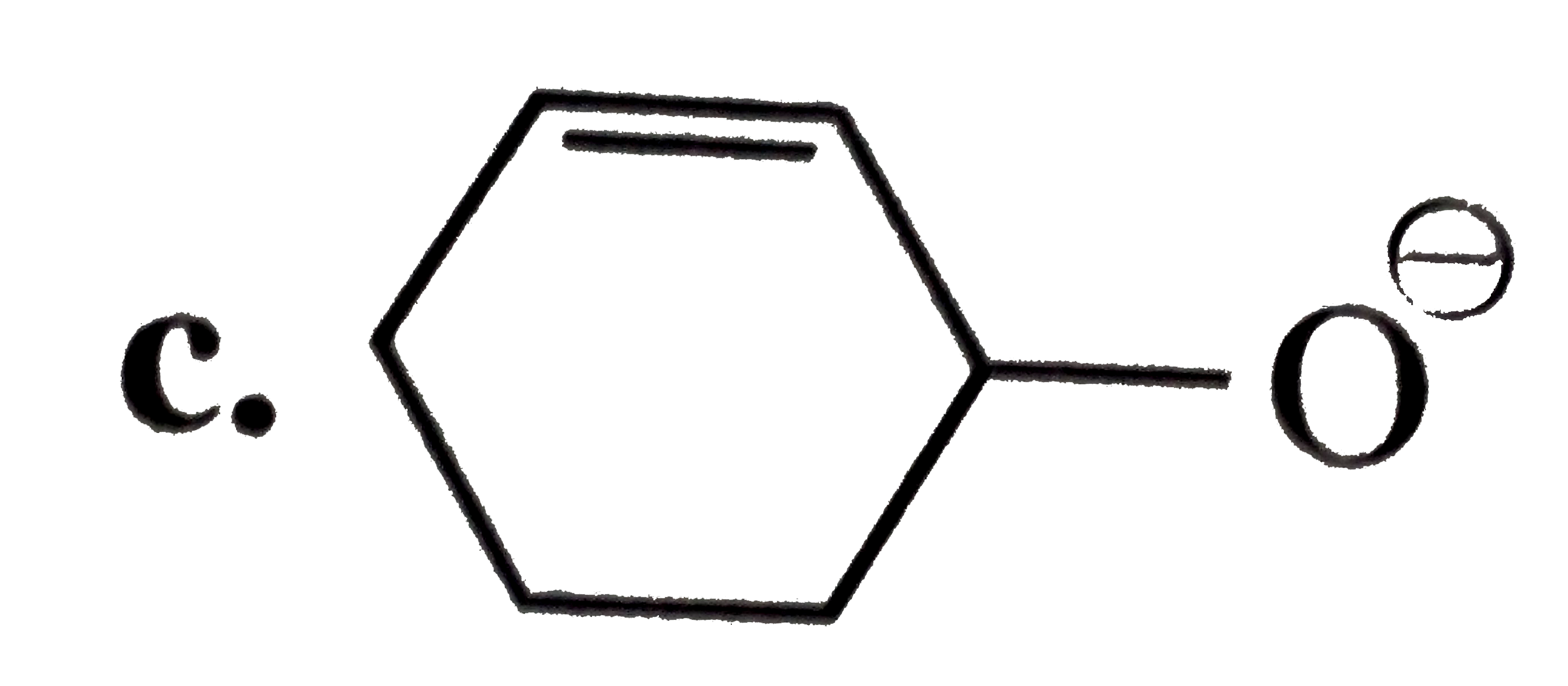
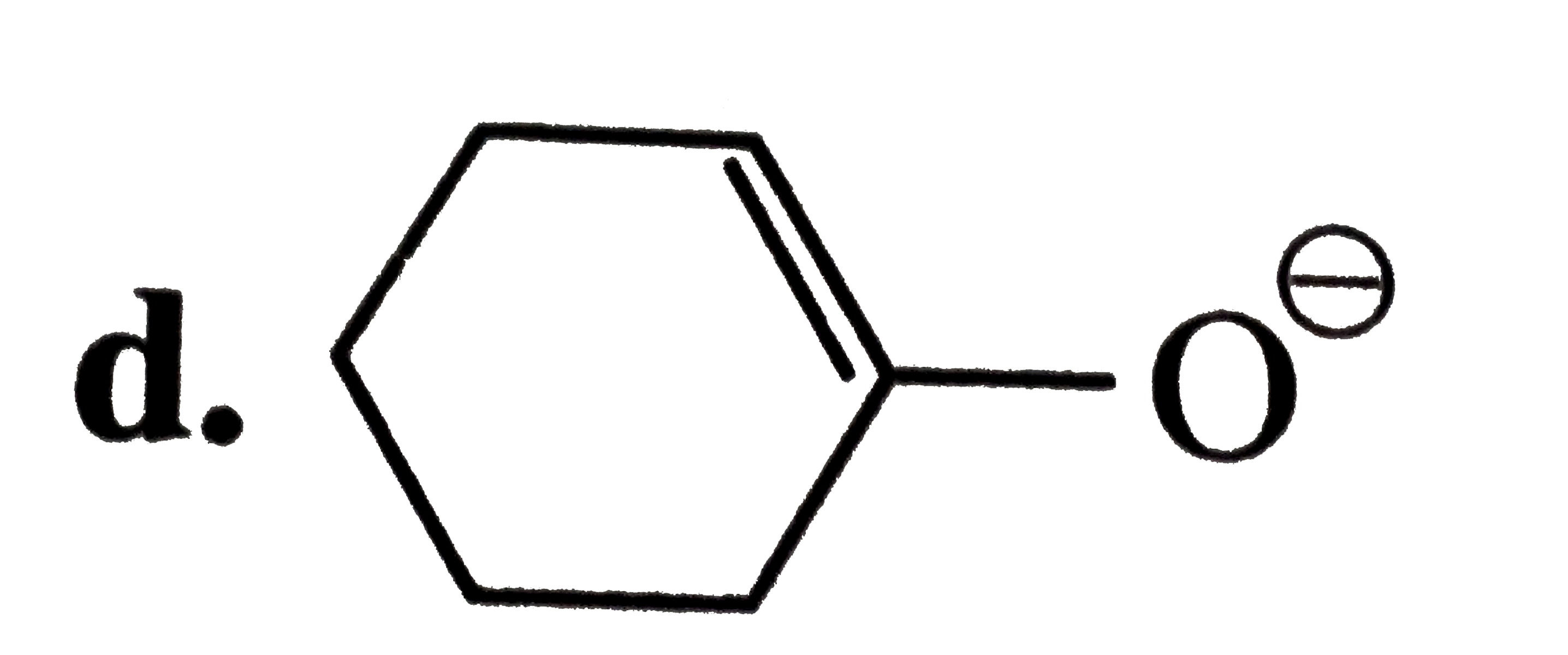
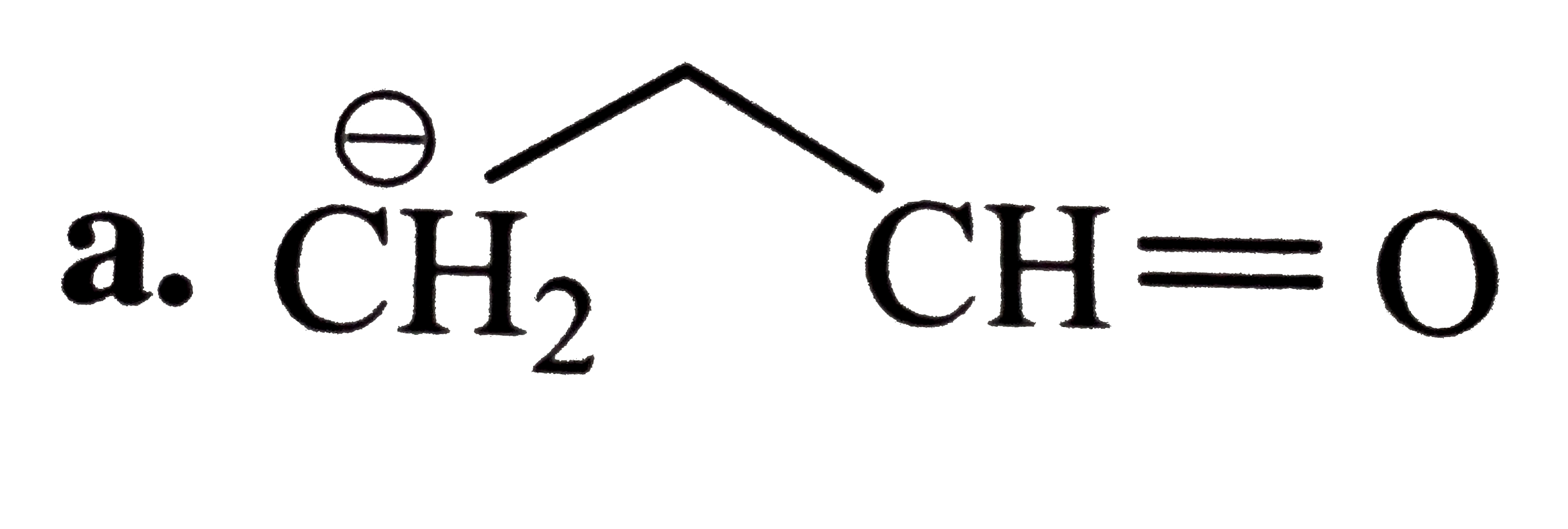A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Single Correct|71 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Assertion-Reasoning|6 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Linked Comprehension|59 VideosALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Analytical And Descriptive|15 VideosAPPENDIX INORGANIC VOLUME 2
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer Type|179 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES-Exercises Multiple Correct
- Which of the following statements are correct about the reaction given...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are correct reactions ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are correct about the bisulphite add...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the statements are correct about the following reactions ? ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are Perkin reactions ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are correct reactions ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are true about the benzoin reaction ...
Text Solution
|
- Give a reaction where Lead iodide is formed as one of the product.
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the least and the best H^(Θ) ion donor, respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the best and the least H^(Θ) ion donor, respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the least and the best H^(Θ) ion donor, respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the best and the least H^(Θ) ion donor, respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction using isotopically labelled Cl^(35), C...
Text Solution
|
- Select the compounds undergoing inter- or intra-molecular Cannizzaro r...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are correct about the following reac...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are wrong about the given reaction ?
Text Solution
|
- How is pH scale related to concentration of Hydronium ions?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are correct about the above reaction...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are not ambident carbanions ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are correct (B) and (C ) products, respectively...
Text Solution
|