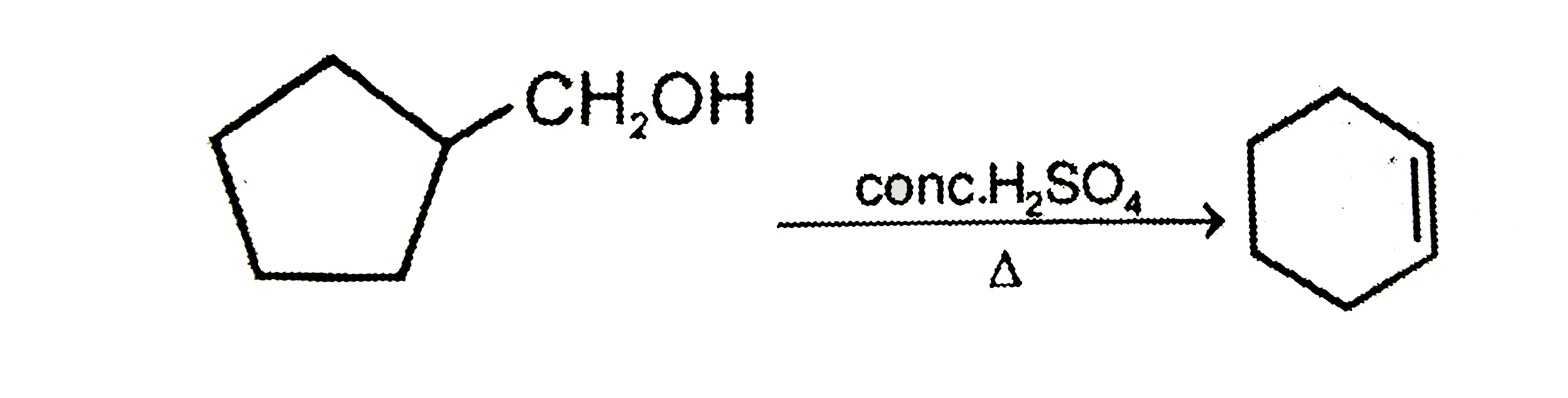A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IV
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-3 Part-1|18 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IV
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-3 Part-2 JEE (MAIN ) OFFLINE PROBLEMS|10 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IV
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 Part-3|10 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise APSP Part - 3|22 VideosPERIODIC TABLE & PERIODICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IV-Exercise-2 Part-4
- Alcohols undergo acid catalysed elimination reactions to produce alken...
Text Solution
|
- Alcohols undergo acid catalysed elimination reactions to produce alken...
Text Solution
|
- The incorrect statement about step-1 is :
Text Solution
|
- The product 'E' is :
Text Solution
|
- The product 'F' is :
Text Solution
|
- The bimolecular reaction is represented by :
Text Solution
|
- The dehydration reaction is represented by :
Text Solution
|
- The unimolecular nucleophilic substitution is represented by :
Text Solution
|