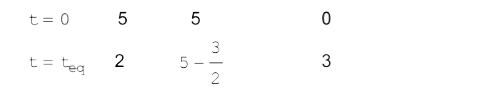A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Main (Archive)|24 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|28 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level 1|75 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING-I & II
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|98 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|52 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM-Level 2
- 5 moles of SO(2)and 5 moles of O(2) are allowed to react .At equilibr...
Text Solution
|
- At 600^(@)C,K(P) for the following reaction is 1 atm. X(g) rarr Y(g) ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reaction, NO(2) rarr 1/2N(2) + O(2),K(1) , N(2)O(4) rarr...
Text Solution
|
- Equilivalent amounts of H(2) and I(2) are heated in a closed vessel ti...
Text Solution
|
- 56 g of nitrogen and 8 g hydrogen gas are heated in a closed vessel. A...
Text Solution
|
- An amount of solid NH4 HS is placed in a flask already containing a...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction N(2(g)) + O(2(g))hArr2NO((g)), the value of K(c) at 8...
Text Solution
|
- A(g) + 3B(g) rarr 4C(g)Initially concentration of A is equal to that o...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of PCl(5) is heated in a closed vessel of 2 L capacity. When...
Text Solution
|
- At 550 K, the Kc for the following reaction is 10^(4) mol^(-1)L . X(g)...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction H(2)(g)+CO(2) (g)hArrCO(g)+H(2)O(g), if the initial ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the percent dissociation of H(2)S(g) if 0.1 mol of H(2)S is ...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction equilibrium, N2O4 (g) hArr 2NO2 (g) the concent...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant for the reaction N(2)(g)+O(2)(g) hArr 2NO(g...
Text Solution
|
- Which factor will shift the following equilibrium in forward direction...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, 2NO2 (g) hArr 2NO(g) +O2(g), (Kc= 1.8 xx 10...
Text Solution
|
- For the following homogeneous gas phase reaction 4NH(3)+5O(2)hArr 4NO+...
Text Solution
|
- What is the value of k(c) for the reaction at 1473 K I(2)(g) hArr 2I...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reaction :- 2CO(g)+2H(2)O((g))hArr2CO(2(g))+2H(2(g))eq....
Text Solution
|
- 0.1 mole of N(2)O(4)(g) was sealed in a tude under one atmospheric con...
Text Solution
|