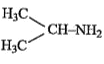
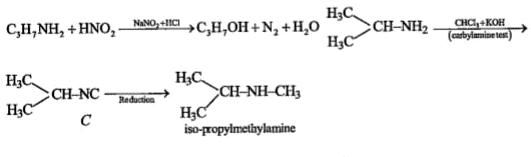
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NITROGEN COMPOUNDS
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-III (Multiple Choice Answer Type)|12 VideosNITROGEN COMPOUNDS
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-III (Numerical Type)|5 VideosNITROGEN COMPOUNDS
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-II|48 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise Level-II|37 VideosNUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-III (Linked Comprehension Type) |11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION-NITROGEN COMPOUNDS-LEVEL-III (Single Correct Answer Type)
- An organic compound (C3 H9 N) (A), when treated with nitrous acid, gav...
Text Solution
|
- CH3 NH2 reacts with alpha-beta-unsaturated ketone as shown Sele...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction shown below, the major product(s) formed is/are
Text Solution
|
- What is the product of the following reaction?
Text Solution
|
- In the following reactions, the product S is,
Text Solution
|
- Treatment of cyclobutylmethylamine with nitrous acid does not give
Text Solution
|
- 4-Nitrotoluene is treated with bromine water to get compound 'P'. P is...
Text Solution
|