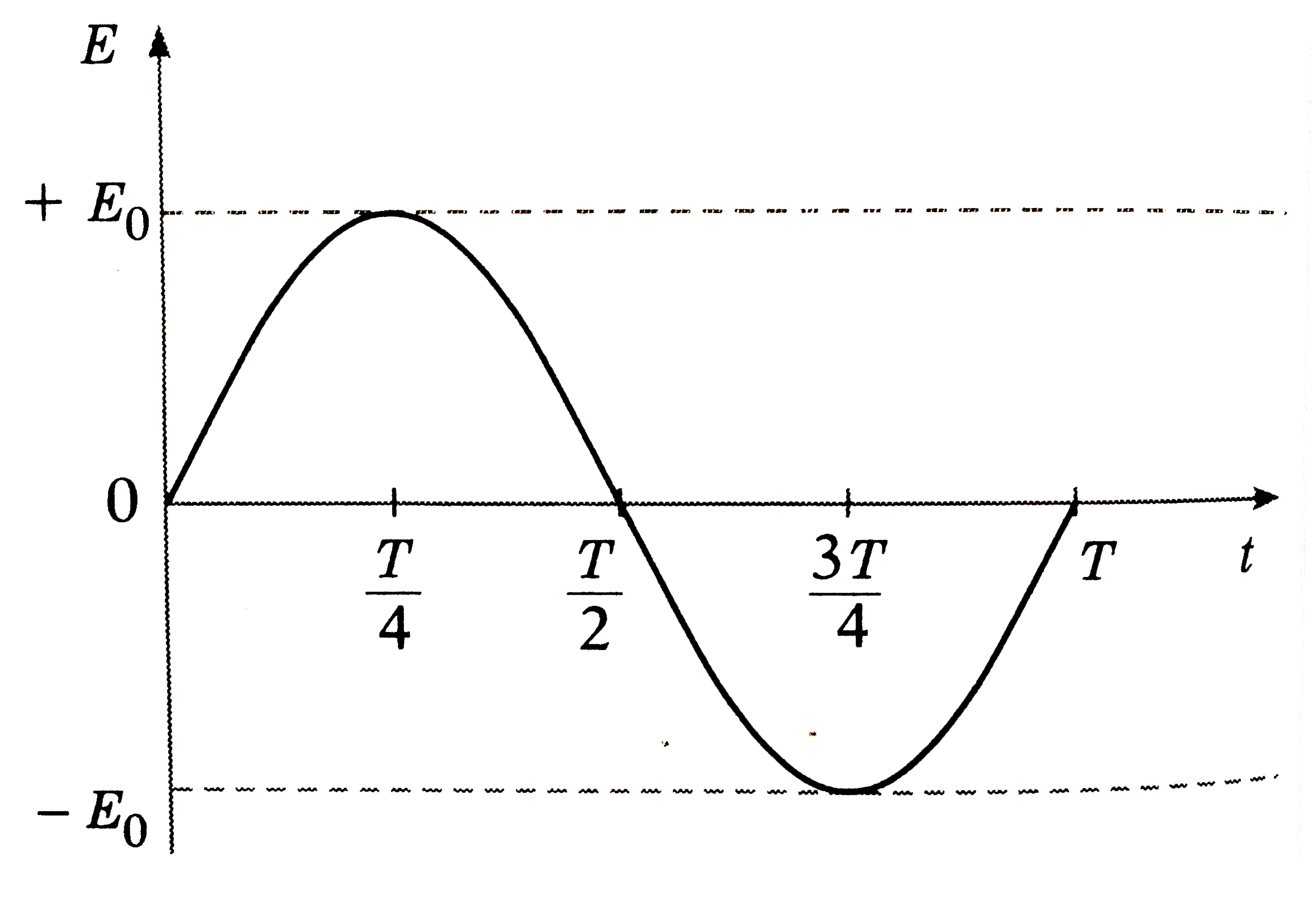
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
DERIVATIONS-II
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Atoms, Molecules and Nuclei|7 VideosDERIVATIONS-II
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Semiconductors|1 VideosDERIVATIONS-II
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Magnetism|1 VideosDERIVATIONS-I
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Assignments|9 VideosDISTINGUISH BETWEEN
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Assingment|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD-DERIVATIONS-II-Electromagnetic Induction
- prove that the charge induced does not depend on the rate of change of...
Text Solution
|
- Prove theoretically E=-(d Phi)/(dt).
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for motional emf induced in a conductor moving i...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by self-inductance of a coil? Obtain an expression for t...
Text Solution
|
- What is a capacitor ? Define its capacitance. Explain the units of ca...
Text Solution
|
- The average power in LCR series circuit is
Text Solution
|