Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
QUESTIONS BASED ON DIAGRAMS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Lenses|7 VideosQUESTIONS BASED ON DIAGRAMS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Metallurgy|4 VideosQUESTIONS BASED ON DIAGRAMS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Heat|1 VideosPROPERTIES/CHARACTERISTICS/USES,ETC.
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise CARBON COMPOUNDS|4 VideosQUESTIONS BASED ON EXAMPLES
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise CARBON COMPOUNDS|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD-QUESTIONS BASED ON DIAGRAMS -Refraction of Light
- With a neat labeeled diagram, prove that if the angle of incidence and...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following ray diagram to show refraction of light through...
Text Solution
|
- With a neat labelled diagram, explain the terms total internal reflect...
Text Solution
|
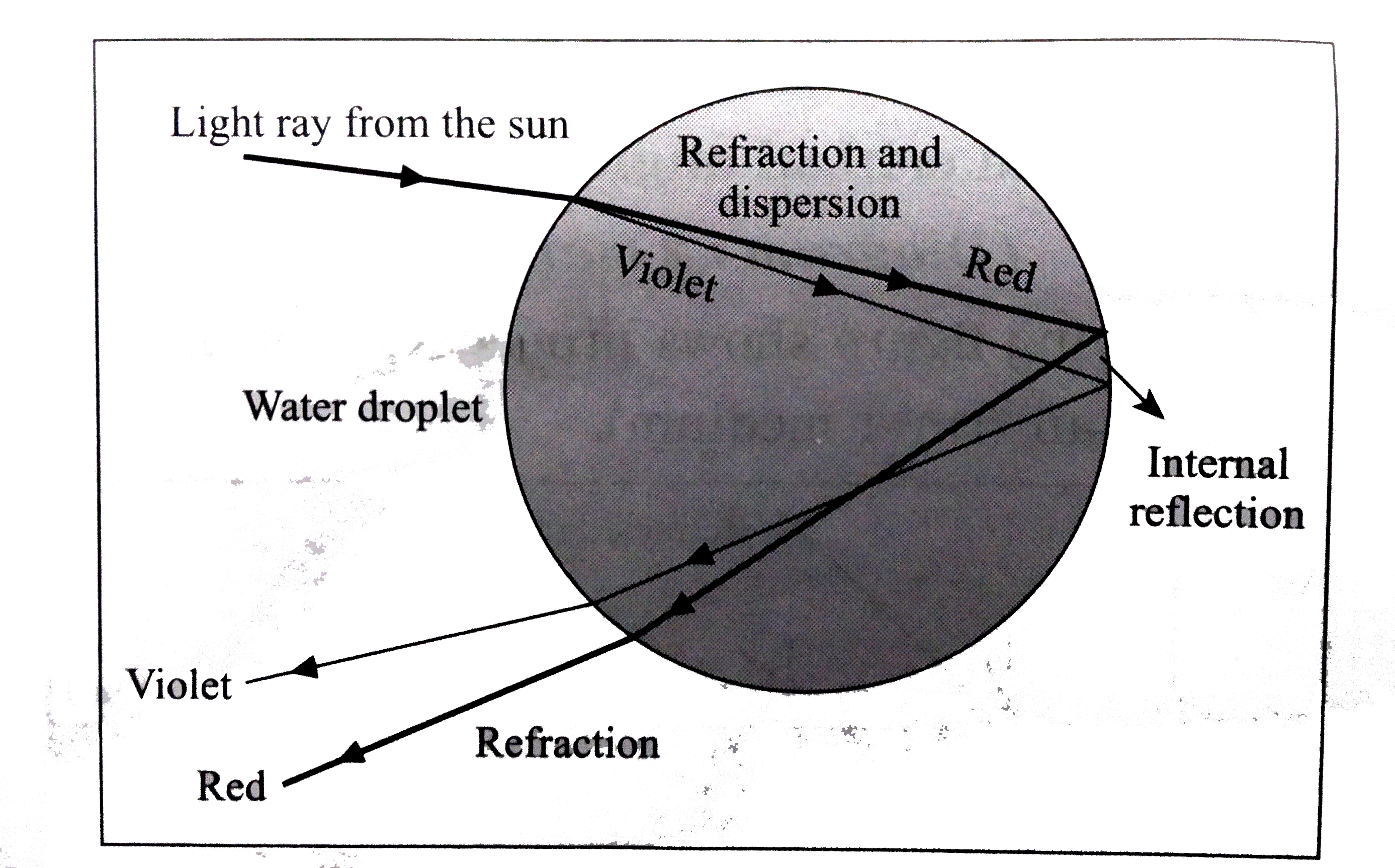
- With a neat labelled diagram, explain how a rainbow is formed.
Text Solution
|
- Prove the following statement : A rainbow is the combined effect (an e...
Text Solution
|