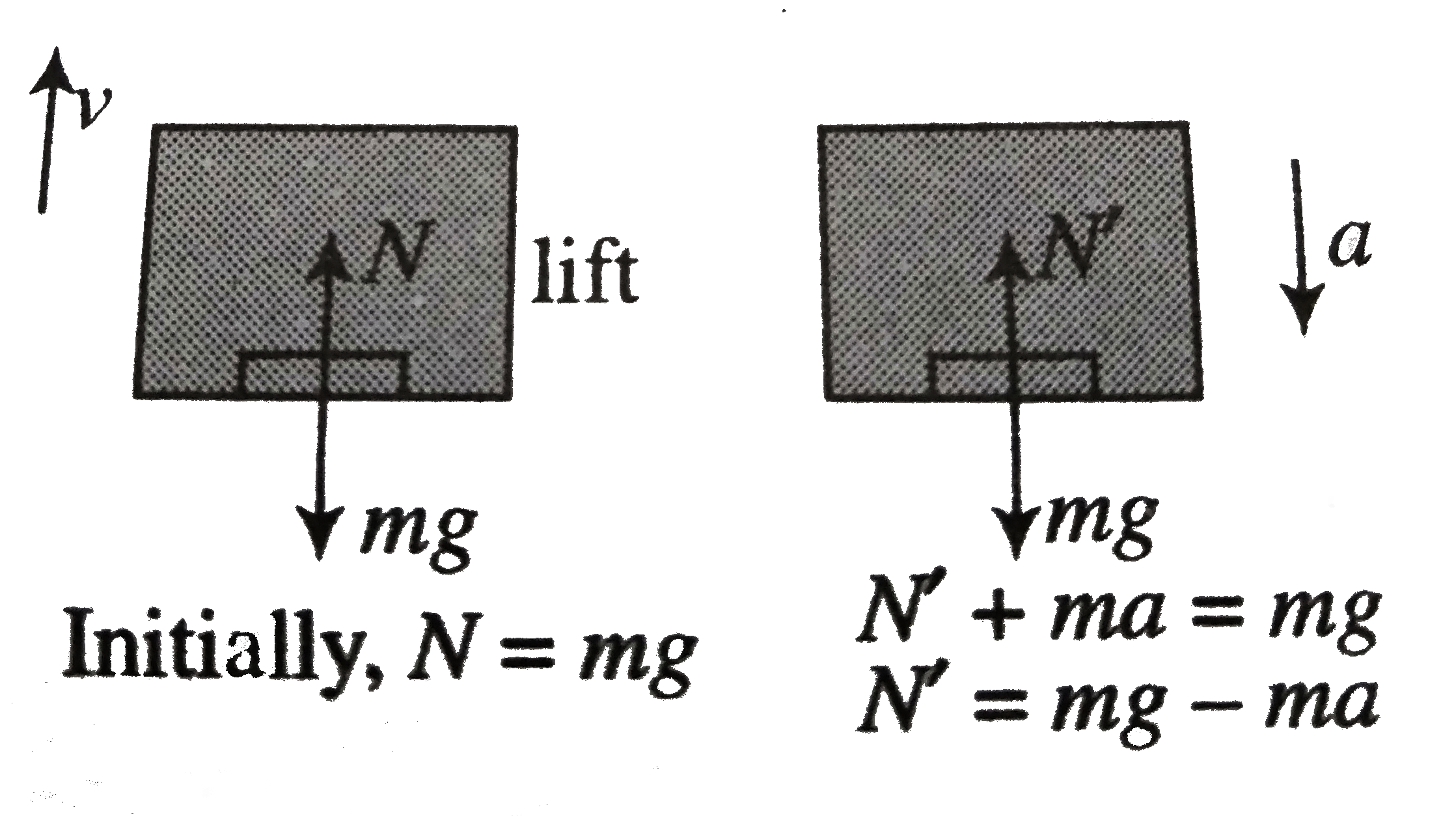
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|11 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-reasoning|15 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|15 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1-Single Correct
- A painter of mass M stands on a platform of mass m and pulls himself u...
Text Solution
|
- A block is lying on the horizontal frictionless surface. One end of a ...
Text Solution
|
- A 60kg man stands on a spring scales in a lift. At some instant. He fi...
Text Solution
|
- Figure, represents a light inextensible string ABCDE in which AB=BC=CD...
Text Solution
|
- If block A is moving with an acceleration of 5ms^(-2), the acceleratio...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B each of mass m are kept stationary by applying a...
Text Solution
|
- A block of metal weighing 2kg is resting on a frictionless plane. It i...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal liquid of density rho is pushed with velocity v through the c...
Text Solution
|
- Two uniform solid cylinders A and B each of mass 1 kg are connected by...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of point A on the rod is 2ms^(-1) (leftwards) at the inst...
Text Solution
|
- Two small rings O and O' are put on two vertical stationary rods AB an...
Text Solution
|
- A U-shaped smooth wire has a semi-circular bending between A and B as ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identicle particles A and B, each of mass m, are interconnected by...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown in fig is in equilibrium . Masses m(1) and m(2) are 2...
Text Solution
|
- In fig. the block of mass M is at rest on the floor . At what accelera...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m(1) lies on the top of fixed wedge as shown in fig. a...
Text Solution
|
- In the situation shown in fig., all the strings are light and inextens...
Text Solution
|
- In fig., a person wants to rise a block lying on the ground to a heigh...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden box is placed on a table. The normal force on the box from th...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in fig., if the acceleration of B is vec(a). ...
Text Solution
|