A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES ANDRADIATION
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise Exercise 2|50 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES ANDRADIATION
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET Corner|40 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES ANDRADIATION
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET Corner|40 VideosINTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION OF LIGHT
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET Corner|24 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET CORNER|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES ANDRADIATION-Exercise 1
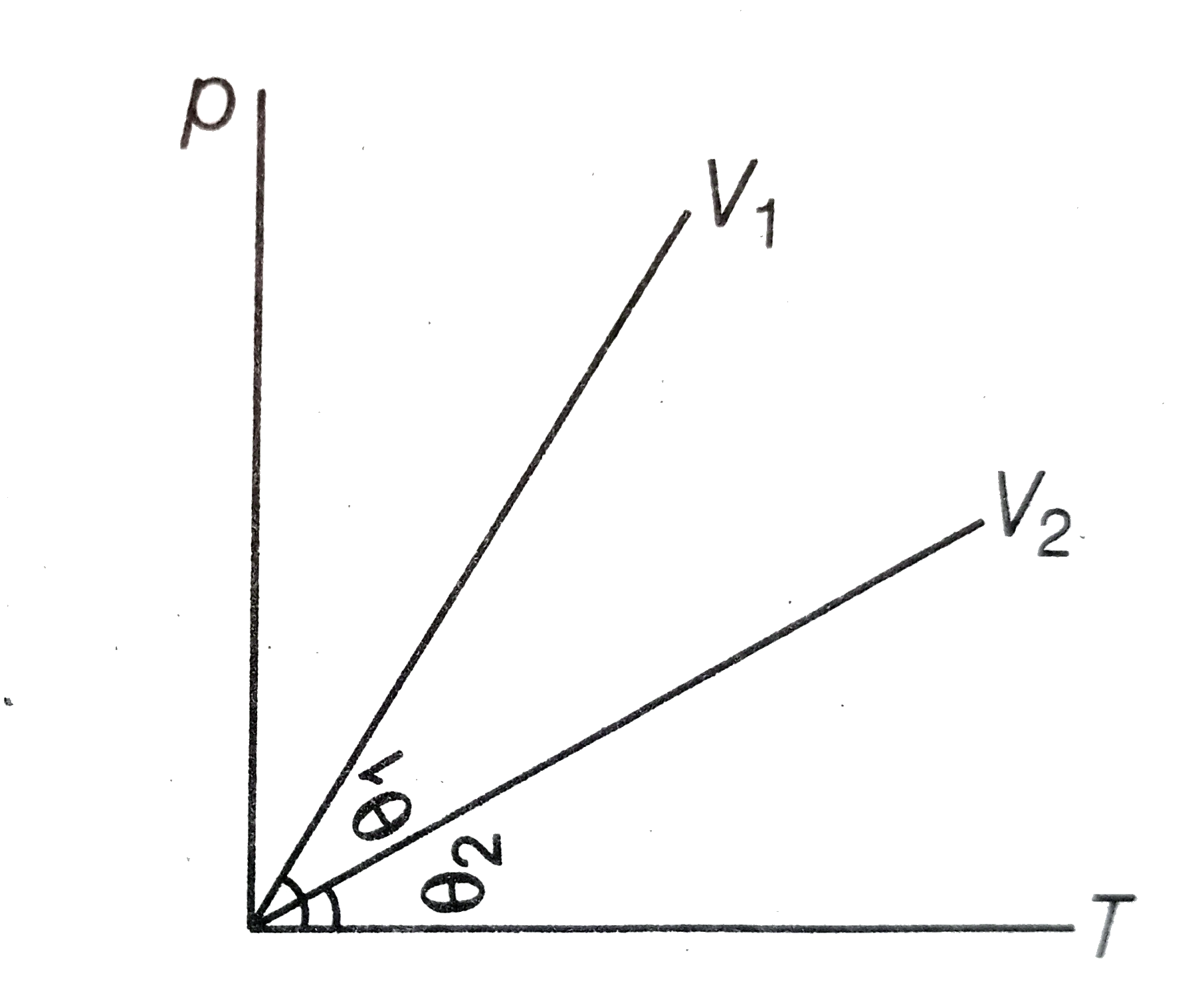
- The pressure p for a gas is plotted against its absolute temperature T...
Text Solution
|
- Air is pumped into an automobile tube upto a pressure of 200 kPa in th...
Text Solution
|
- Simple behaviour under all conditions of real gas is governed by the e...
Text Solution
|
- When a van der waals ' gas undergoes free expansion , then its tempera...
Text Solution
|
- At 10^(@)C, the value of the density of a fixed mass of an ideal gas d...
Text Solution
|
- One litre of an ideal gas st 27^(@)C is heated at a constant pressure ...
Text Solution
|
- Two ballons are filled, one with pure He gas and other by air, repecti...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal gas is contained in a cylinder fitted with a fri...
Text Solution
|
- During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law ...
Text Solution
|
- The gas in a vessel is subjected to a pressure of 20 atmosphere at a t...
Text Solution
|
- A real gas behaves like an ideal gas if its
Text Solution
|
- How much heat energy in joules must be supplied to 14gms of nitrogen a...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon contains 500m^(3) of He at 27^(@)C and 1 atm pressure. Then ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below shows the plot of (PV)/(nT) versus P for oxygen gas a...
Text Solution
|
- Temperature remaining constant, the pressure of gas is decreased by 20...
Text Solution
|
- A closed container of volume 0.02m^(3) contains a mixture of neon and ...
Text Solution
|
- The mean free path of collision of gas melecules varies with its diame...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperature will be the oxygen molecules have the same root me...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 120 K to 480 K. If a...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature at which the mean KE of the molecules of gas is one - ...
Text Solution
|