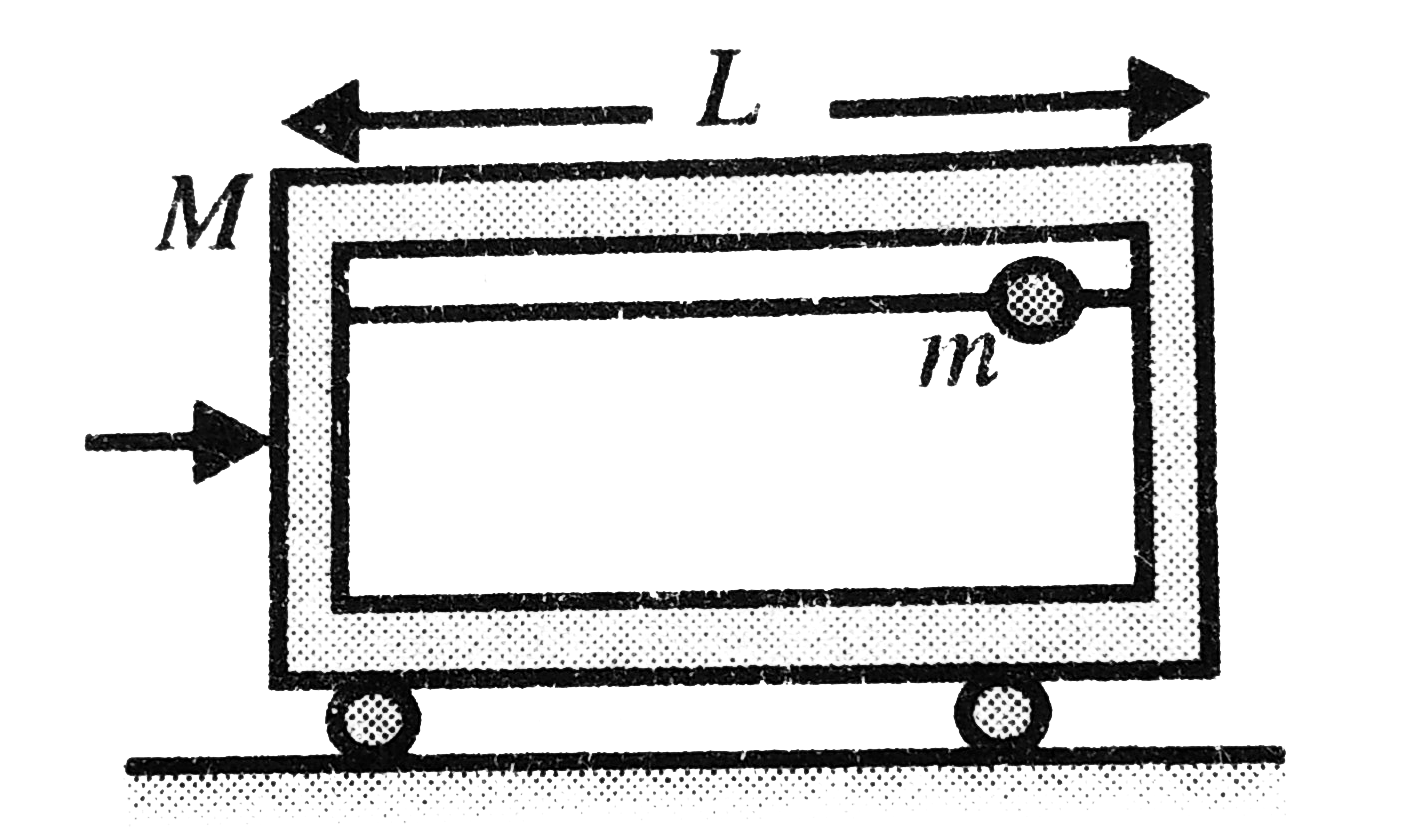
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|16 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Fill In The Blanks|2 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion - Reasoning|2 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-CENTRE OF MASS-Linked Comprehension
- A pan of mass m = 1.5 kg and a block of mass M = 3 kg are connected to...
Text Solution
|
- A pan of mass m = 1.5 kg and a block of mass M = 3 kg are connected to...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal frictionless rod is threaded through a bead of mass m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal frictionless rod is threaded through a bead of mass m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal frictionless rod is threaded through a bead of mass m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- An initially stationary box on a frictionless floor explodes into two ...
Text Solution
|
- An initially stationary box on a frictionless floor explodes into two ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of mass '2m' and radius '3r' is resting on a flat fric...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of mass '2m' and radius '3r' is resting on a flat fric...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of mass '2m' and radius '3r' is resting on a flat fric...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected by an ideal sprit, of...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected by an ideal sprit, of...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected by an ideal sprit, of...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball B of mass m is suspended with light inelastic string of l...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball B of mass m is suspended with light inelastic string of l...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball B of mass m is suspended with light inelastic string of l...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball B of mass m is suspended with light inelastic string of l...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball of mass 1 kg is kept in circular path of radius 1 m Insid...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball of mass 1 kg is kept in circular path of radius 1 m Insid...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball of mass 1 kg is kept in circular path of radius 1 m Insid...
Text Solution
|