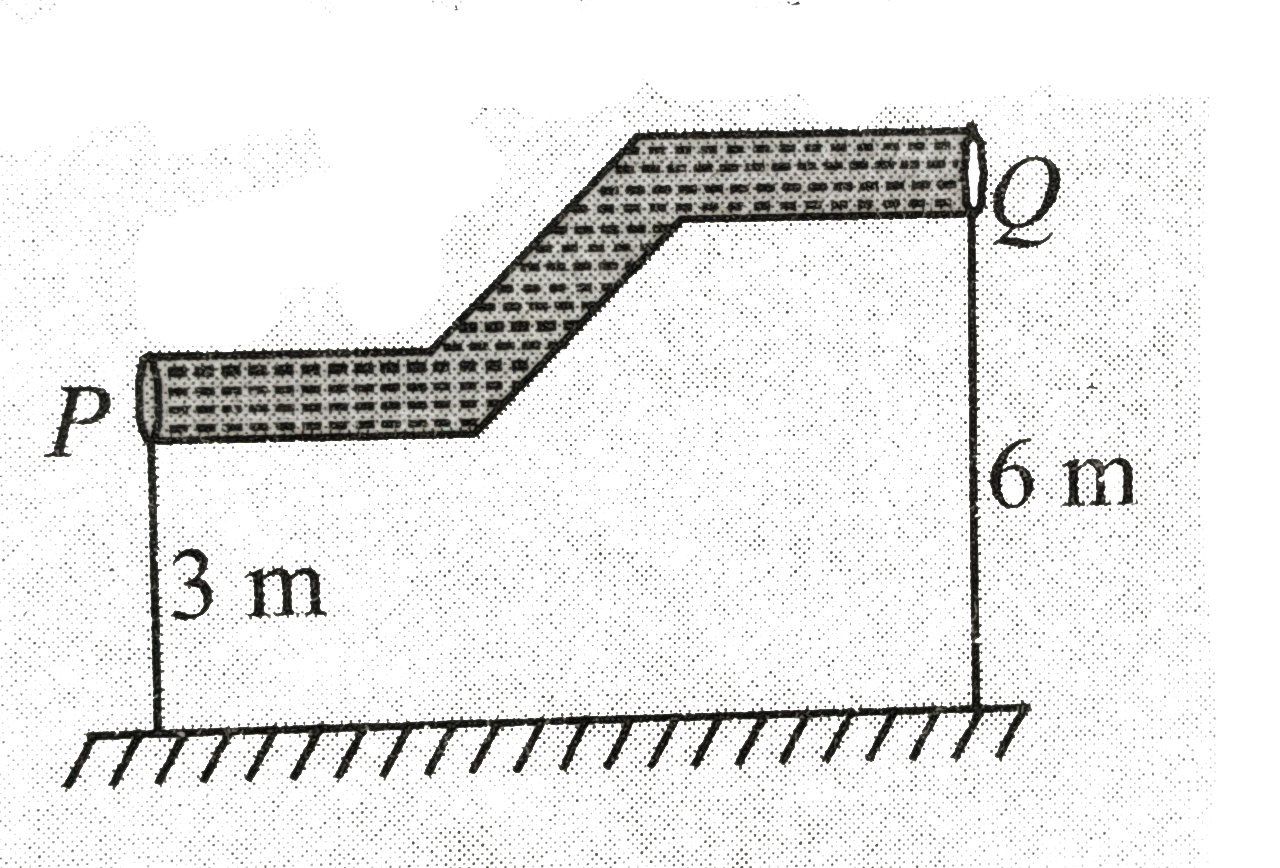
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
FLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|25 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|95 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 4.3|10 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|2 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-FLUID MECHANICS-Exercise 4.4
- A non-viscous liquid of constant density 500 kg//m^(3) flows in a vari...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal pipe of varying cross-sectional area carries water flowin...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of flow past the lower surface of a wing of an aeroplane is ...
Text Solution
|
- A gardener holds a pipe of inside cross-sectional area 3.60 cm^(2) at ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a stream of fluid emerging from a tube in the base of an ...
Text Solution
|
- It water flows horizontally through a pipe of varying cross section an...
Text Solution
|
- A pipe is running full of water. At a certain point A it tapers from 6...
Text Solution
|
- A pitot tube is fixed in a water pipe of diameter 14 cm and difference...
Text Solution
|
- Water is used as the manometric liquid in a pitot tube mounted in an a...
Text Solution
|
- Water flows out of a big tank along a tube bent at right angles, the i...
Text Solution
|