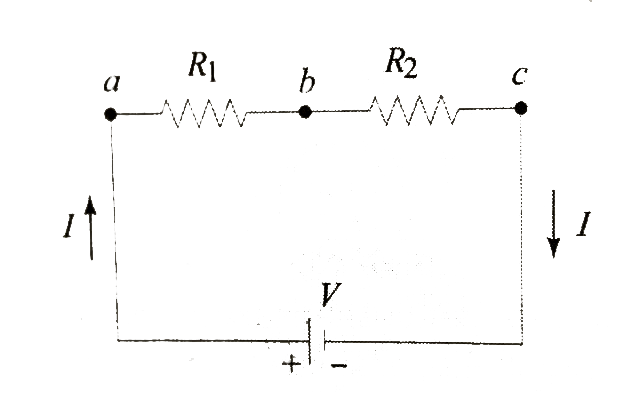
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|8 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|60 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Examples|13 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|39 VideosINDUCTANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Concept Based|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT-Exercise 7.1
- (a) what is the rate at which energy being delivered to a light bulb ...
Text Solution
|
- A heater joined in series with a 50 W bulb is connected to the mains ...
Text Solution
|
- Each of three resistors in fig. 7.12 has a resistance of 2 Omega and c...
Text Solution
|
- An electric bulb rated 220 V and 60 W is connected in series with anot...
Text Solution
|
- We have a 30 W, 6 V bulb , which we want to glow by a supply of 120 V ...
Text Solution
|
- Two heater coils made of the same material are connected in parallel a...
Text Solution
|
- A series circuit consists of three identical lamps connected to a batt...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of the same material and having the same uniform area of cro...
Text Solution
|
- Water boils in an electric kettle in 15 min after being switched on . ...
Text Solution
|
- An electric motor operating on a 50 V dc supply draws a current of 12...
Text Solution
|
- A fuse with a circular cross - sectional radius of 0.15 mm blows at 1...
Text Solution
|
- A motor operating on 120 V draws a current of 2 A . If the heat is dev...
Text Solution
|
- The walls of a closed cubical box of edge 40 cm are made of a material...
Text Solution
|
- Two tungsten lamps with resistances R(1) and R(2), respectively , are ...
Text Solution
|
- n identical bulbs are connected in series and illuminated by a power s...
Text Solution
|
- An electric motor is designed to work at 100 Vand draws a current of ...
Text Solution
|
- A house is fitted with certain numbers of 100 W, 230 V incandescent la...
Text Solution
|
- A house is fitted with seven tubelights of rating 220 V, 40 W each , t...
Text Solution
|
- Two bulbs are marked 200 V, 300 W and 200 V, 600 W, respectively. The ...
Text Solution
|
- A servo voltage stabiliser restricts the voltage output to 220 V +- 1%...
Text Solution
|