Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|60 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|5 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 7.1|22 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Question Bank|39 VideosINDUCTANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Concept Based|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT-Subjective
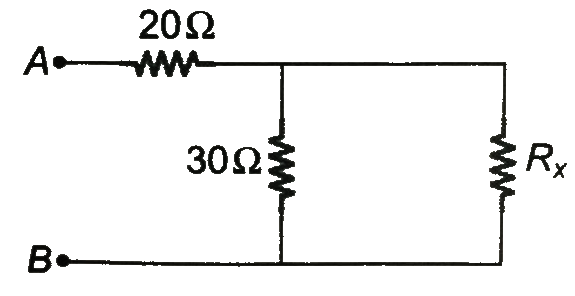
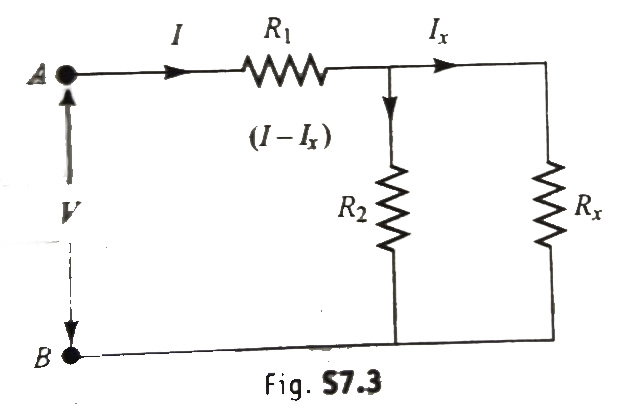
- A circuit shown in the figure has resistances 20 Omega and 30 Omega. A...
Text Solution
|
- A 1 k W heater is meant to operate at 200 V. (a) What is the resist...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor R(1) consumes electrical power P(1) when connected to an e...
Text Solution
|
- In a experiment , N identical electrical bulbs, each having resistance...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. 7.24 , all the resistors are rated at a m...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in Fig 7.25, (a) what must the emf epsilon of t...
Text Solution
|
- If two bulbs of 25 W and 100 W rated at 220 V are connected in series ...
Text Solution
|
- Three 60 W , 120 V light bulbs are connected across a 120 V power line...
Text Solution
|