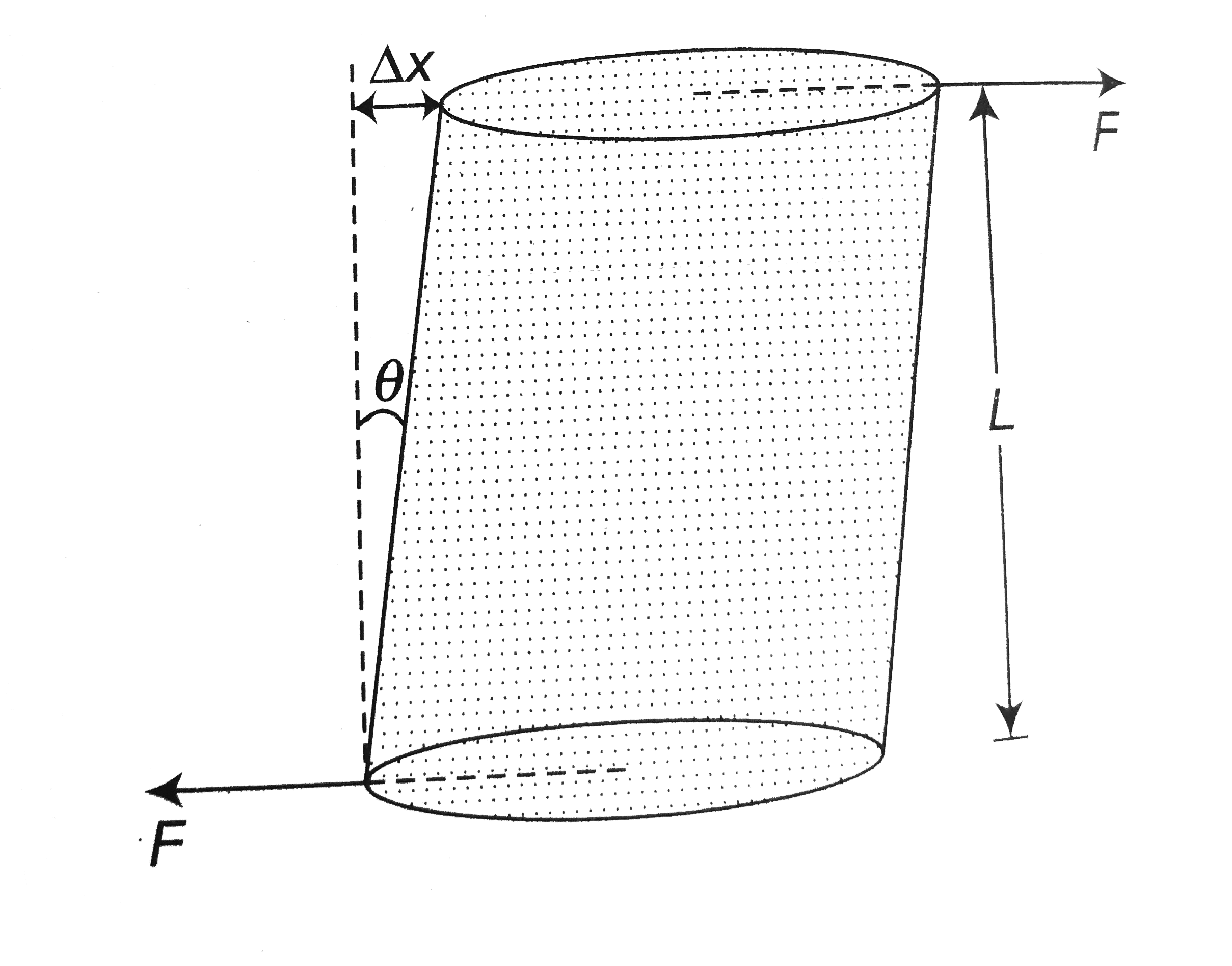
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROPERTIES OF MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Elasticity And Work Done In Stretching A Wire|25 VideosPROPERTIES OF MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Surface Tension And Surface Energy|29 VideosPROPERTIES OF MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|29 VideosOSCILLATION AND SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|29 VideosROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|29 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Bulk Modulus And Shear Modulus
- If two equal and opposite defirming forces are applied parallel to the...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cube is subjected to volume compression. If each side is dec...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure applied from all direction on a cube is P. How much its t...
Text Solution
|
- Mark the wrong statement
Text Solution
|
- What increase in pressure is required to decrease the volume of 200 li...
Text Solution
|
- Forces of 100 N each are applied in opposite direction on the upper an...
Text Solution
|
- Rigidity modulus of steel is eta and its Young's modulus is Y. A piece...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of a liquid has an initial volume of 1.5 L The volume is redu...
Text Solution
|
- When temperature of a gas is 20^@C and pressure is changed from p1=1.0...
Text Solution
|
- The compressibility of water is 4xx10^-5 per unit atmospheric pressure...
Text Solution
|
- A ball falling in a lake of depth 200 m shows a decrease of 0.1% in i...
Text Solution
|
- The compressibility of a material is
Text Solution
|
- When a pressure of 100 atmosphere is applied on a spherical ball, then...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cube is subjected to volume compression. If each side is dec...
Text Solution
|
- A ball falling in a lake of depth 200 m shows a decrease of 0.1% in i...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure applied from all direction on a cube is P. How much its t...
Text Solution
|
- When temperature of a gas is 20^@C and pressure is changed from p1=1.0...
Text Solution
|
- For a constant hydraulic stress on an object, the fractional change in...
Text Solution
|
- A cube of aluminium of sides 0.1 m is subjected to a shearing force of...
Text Solution
|
- The lower surface of a cube is fixed. On its upper surface, force is a...
Text Solution
|