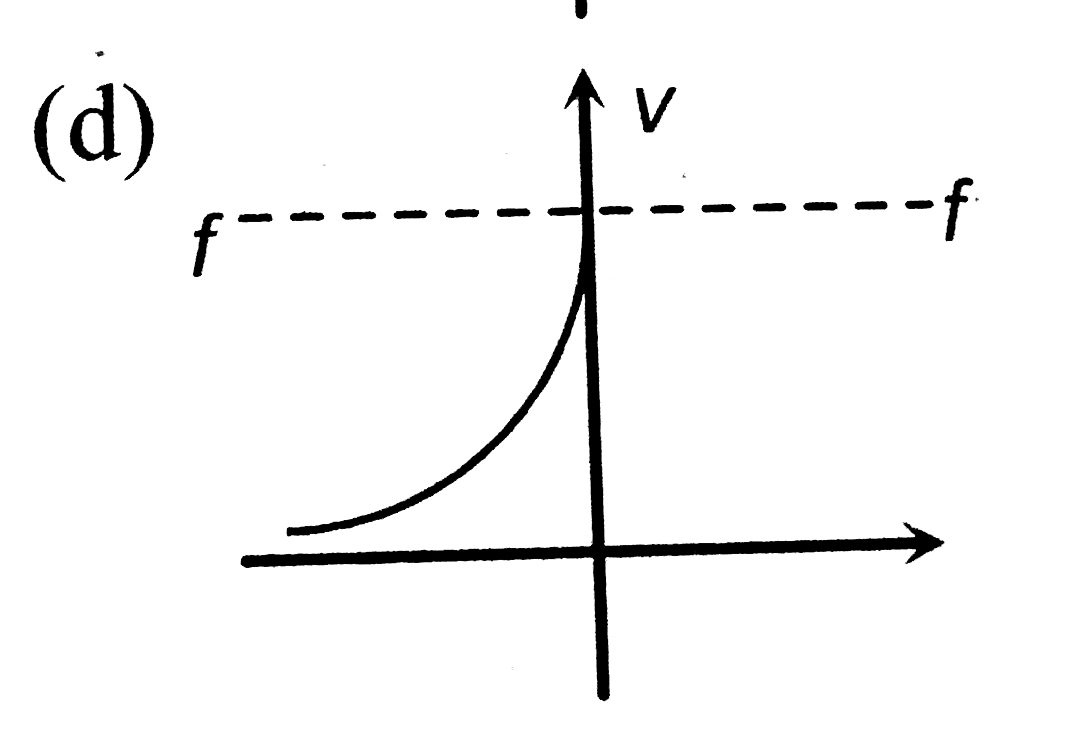A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
A2Z|Exercise Refraction At Curved Surface|64 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
A2Z|Exercise Prism Theory And Dispersion Of Light|45 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 VideosMAGNETISM AND MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Section D - Chapter End Test
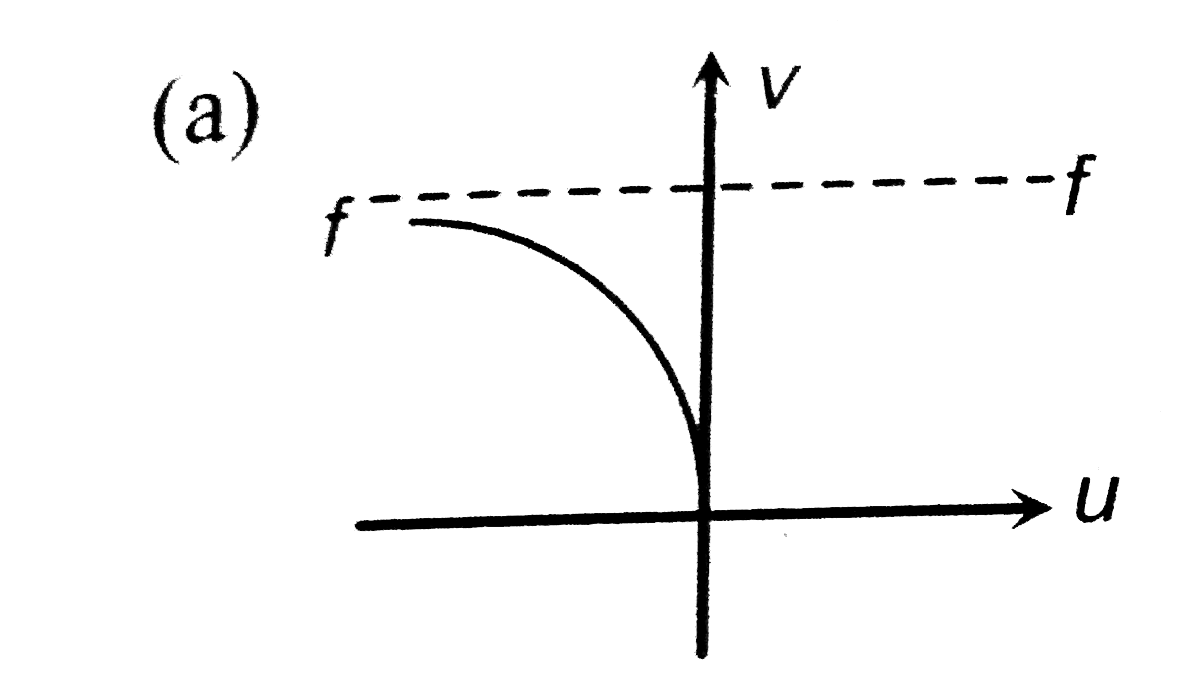
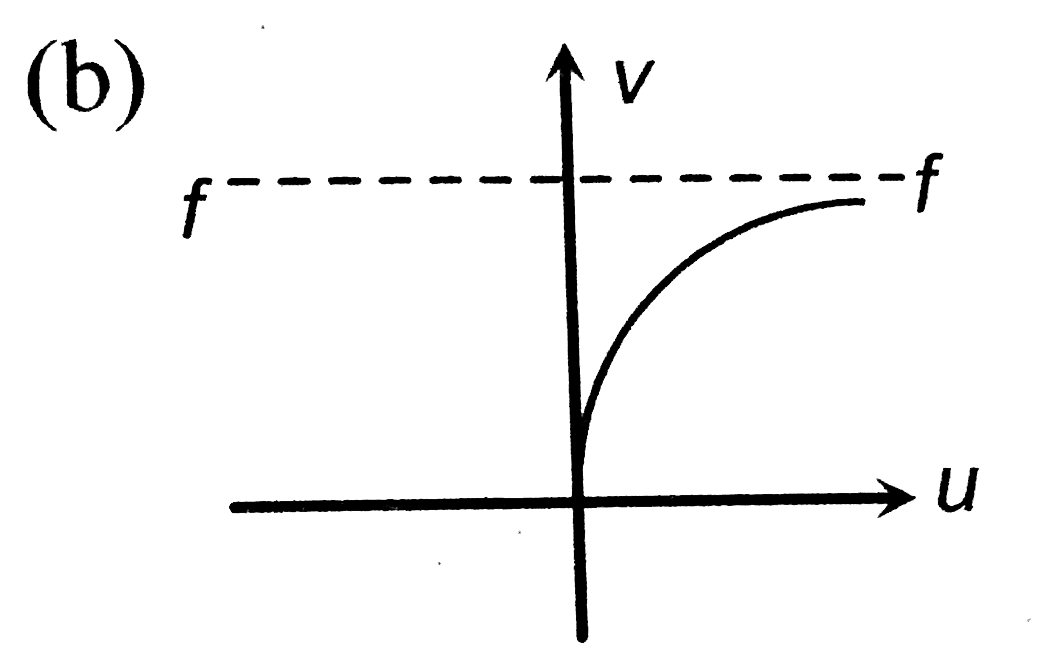
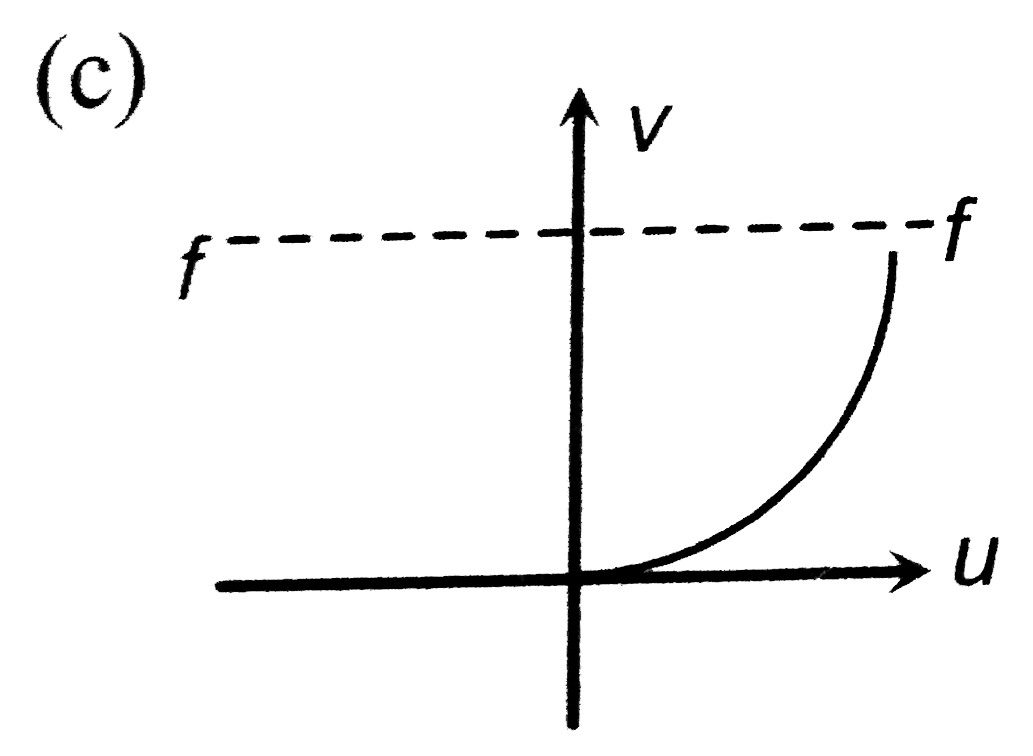
- The graph between u and v for a convex mirrorr is
Text Solution
|
- Wavelength of light used in an optical instrument are lambda(1)=400 Å ...
Text Solution
|
- A plano convex lens of refractive index 1.5 and radius of curvature 30...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident perpendicularly to one face of a 90^circ prism...
Text Solution
|
- A thin glass (refractive index 1.5) lens has optical power of -5D in a...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following graphs is the magnification of a real image aga...
Text Solution
|
- A thin prism P(1) with angle 4degree and made from glass of refractive...
Text Solution
|
- A converging lens is used to form an image on a screen. When the upper...
Text Solution
|
- A diminished image of an object is to be obtained on a screen 1.0 m fr...
Text Solution
|
- An object 15cm high is placed 10cm from the optical center of a thin l...
Text Solution
|
- A lens forms a virtual, diminished image of an object placed at 2 m fr...
Text Solution
|
- When the distance between the object and the screen is more than 4 f....
Text Solution
|
- a convex lens of power +6 diopter is placed in contact with a concave ...
Text Solution
|
- A concave lens of focal length 20 cm product an image half in size of ...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 1.0m and a concave lens of focal length ...
Text Solution
|
- If in a planoconvex lens, the radius of curvature of the convex surfac...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens A of focal length 20cm and a concave lens G of focal le...
Text Solution
|
- The radii of curvature of the two surfaces of a lens are 20cm and 30 c...
Text Solution
|
- A lens forms a virtual image 4 cm away from it when an object is place...
Text Solution
|
- A concave lens of focal length (1)/(3)m forms a real, inverted image t...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed at a distance of f//2 from a convex lens. The imag...
Text Solution
|