Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Short answer questions|28 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Long answer questions|13 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Conceptual Problems|23 VideosGRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion-Reason Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY-Very short Answer questions
- For a given mass of a gas at a fixed temperature, what is the nature o...
Text Solution
|
- What does universal gas constant R signify?
Text Solution
|
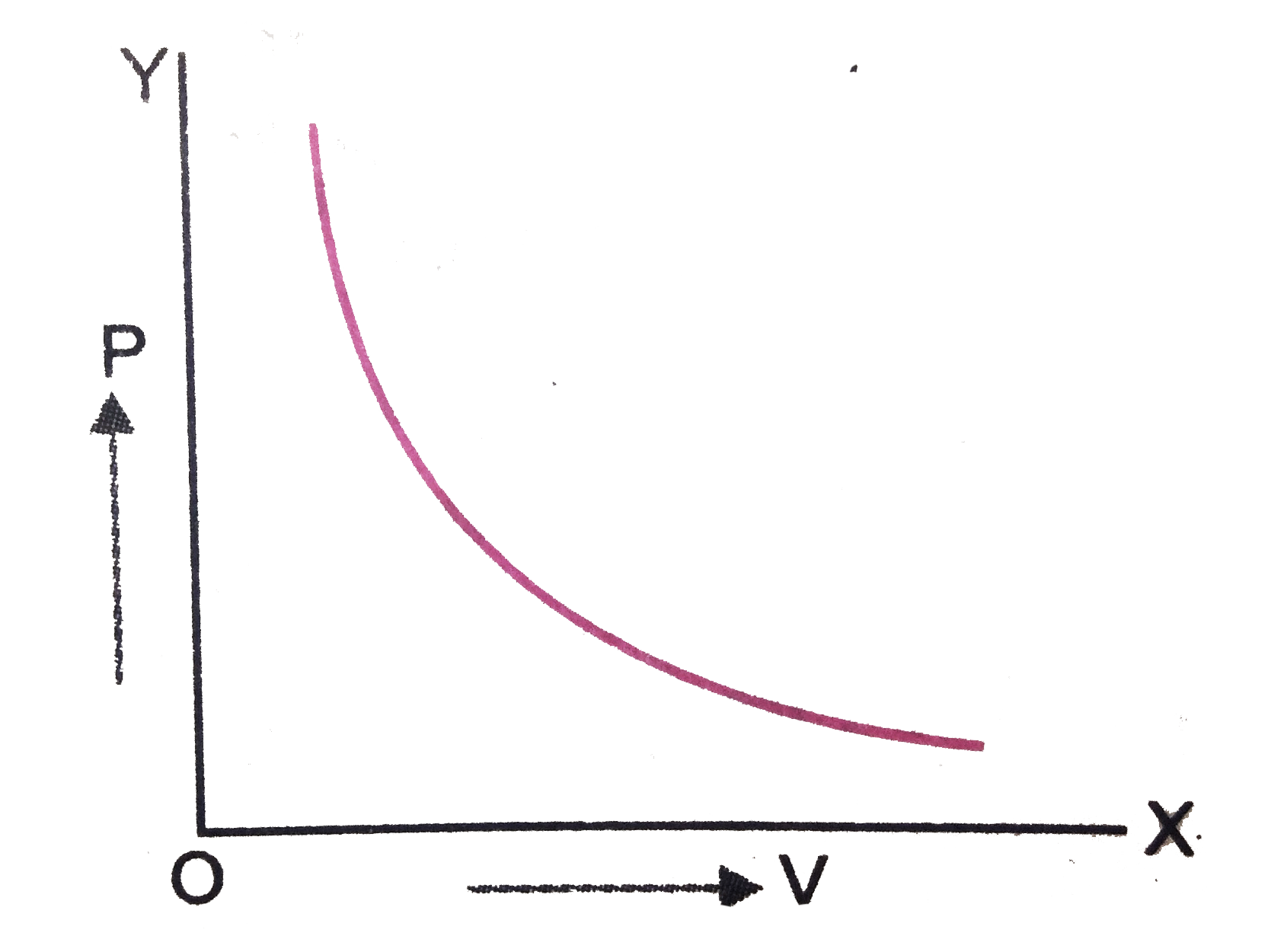
- What is the nature of graph of PV versus P for a given mass of a gas a...
Text Solution
|
- At a constant temperature, what is the relation between pressure P and...
Text Solution
|
- A gas enclosed in a vessel has pressure P, volume V and absolute tempe...
Text Solution
|
- What is the value of gas constant in cgs system for 1 gram or helium ?
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the dimensional formula for R used in the ideal gas equation, P...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by Boltzmann constant Calculate its value in SI units.
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of a gas at -173^(@) C is 1 atmosphere. Keeping the volum...
Text Solution
|
- Given samples of 1 c.c. of hydrogen and 1 c.c. of oxygen, both at N.T....
Text Solution
|
- What is the correct value of 0^(@) C on the Kelvin scale?
Text Solution
|
- Can the temperature of a gas increased keeping its pressure and volume...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical cylinders at same temp. Contains hydrogen at 2.5 atm. An...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of rms velocities of two gases at the same temperature is 1:...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel is filled with a mixture of two different gases. State with r...
Text Solution
|
- The velocities of three molecules are 3v, 4v and 5v. Calculate their r...
Text Solution
|
- Helium gas is filled in a closed vessel whose coefficient of thermal e...
Text Solution
|
- Oxygen and hydrogen are at the same temperature T. What is the ratio o...
Text Solution
|
- The absolute temperature of the gas is increased 3 times. What will be...
Text Solution
|
- If the forces of attraction between the molecules of a gas suddently d...
Text Solution
|