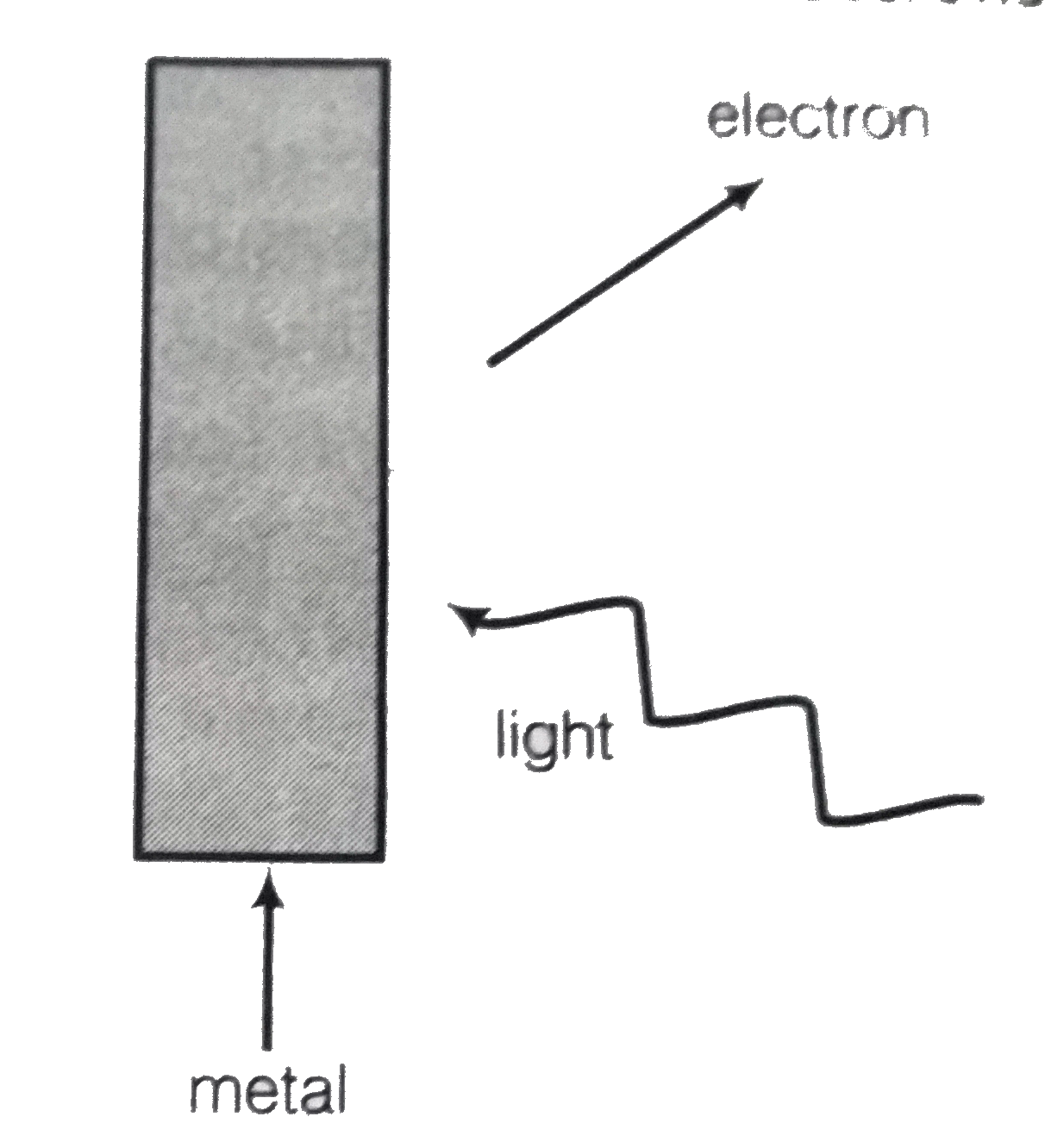
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Long answer|1 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Higher order thinking skills|1 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT Exerciese question|1 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
PRADEEP|Exercise Problems for Practice (B)|2 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATING CURRENT
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple Choice Questions|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems