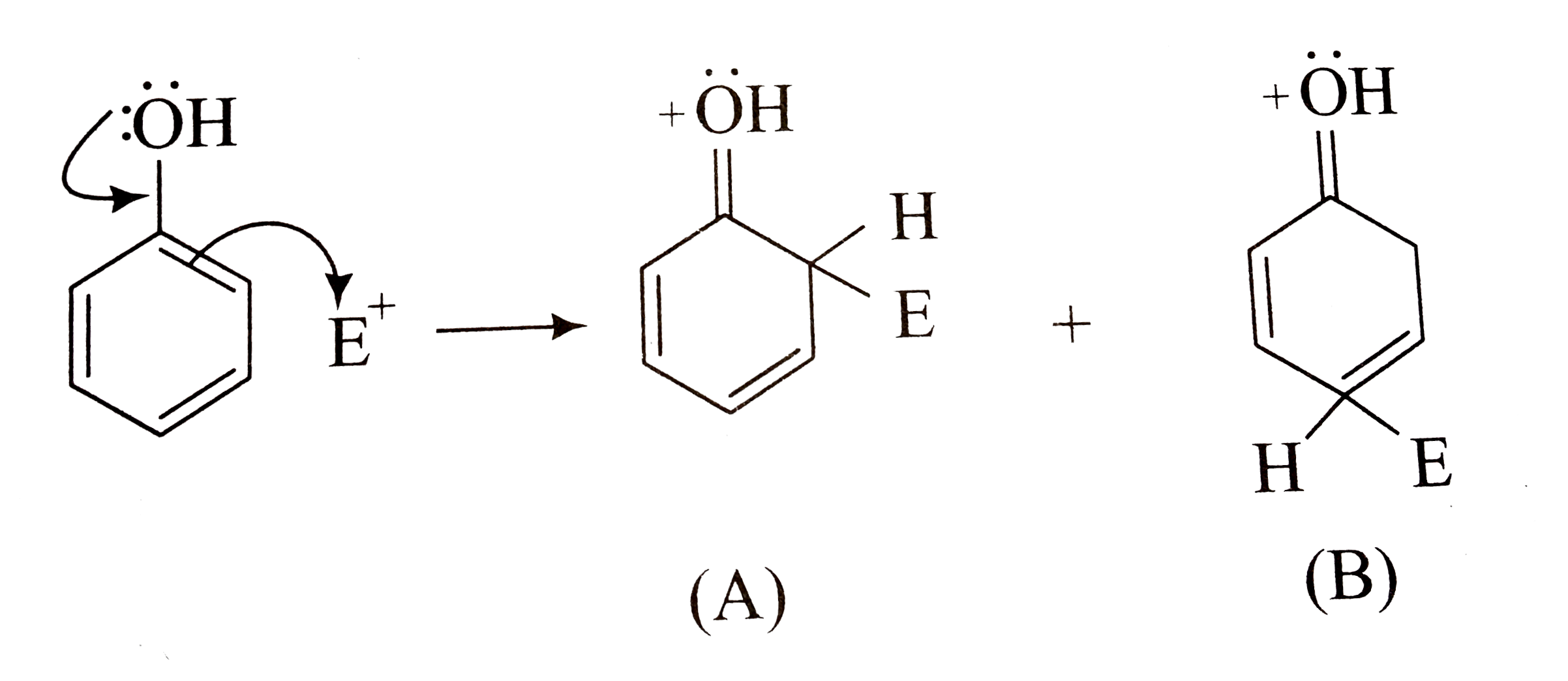
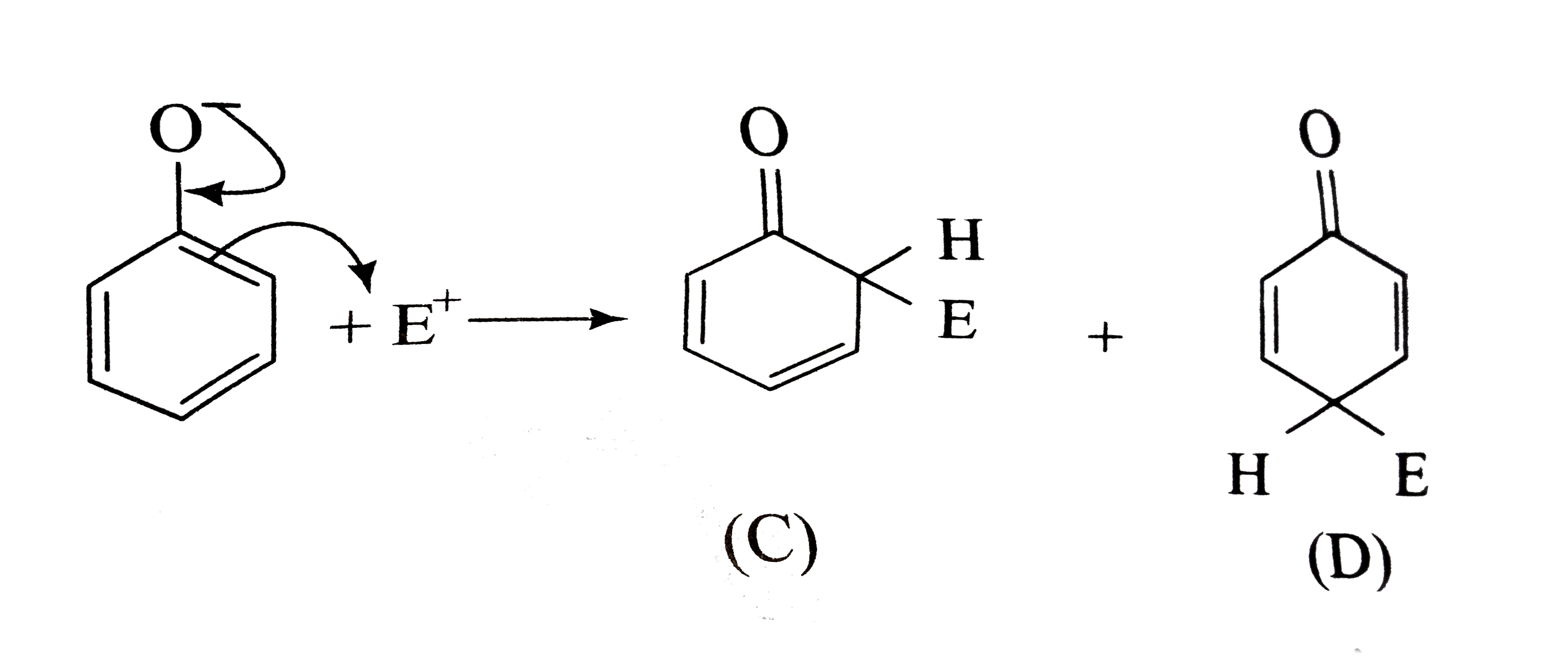
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
R SHARMA-ALCOHOL, PHENOL AND ETHERS-Follow -Up Test -11
- The OH group of phenol
Text Solution
|
- When phenol in treated with excess bromine water, it gives
Text Solution
|
- Phenol reacts with bromine in carbon disulphide at low temperature to ...
Text Solution
|
- The product of the reaction between phenyl benxoate and one mole of br...
Text Solution
|
- Phenol is converted by concentrated nitric acid into
Text Solution
|
- Treatment of phenol with cold dilute nitric acid gives
Text Solution
|
- Phenol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 110^(@)C. The maj...
Text Solution
|
- Phenol does not react with
Text Solution
|
- Phenol reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of dilute NaOH to ...
Text Solution
|
- The principle organic product of the reaction is
Text Solution
|
- Phenol couples in the p-position with diazonium salts in alkaline solu...
Text Solution
|
- When sodium or potassium phenoxide is heated with carbon dioxide, foll...
Text Solution
|
- Treatment of a phenol with -------and aqueous hydroxide introduces an ...
Text Solution
|
- Gattermann aldehyde synthesis is carried out by treating phenol with a...
Text Solution
|
- In the Lederer-Manasse reaction, phenol is treated at low temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reagents will reduce phenol to benzene?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following oxidizes phenol to p-benzoquinone?
Text Solution
|