Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BIOMOLECULES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT (EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (With answers, Hints And Solution) (Multiple Choice Questions-I )|19 VideosBIOMOLECULES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT (EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (With answers, Hints And Solution) (Multiple Choice Questions-II )|9 VideosBIOMOLECULES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT (QUESTIONS AND EXERCISES) WITH ANSWERS (NCERT INTEXT UNSOLVED QUESTIONS)|8 VideosAPPENDIX
PRADEEP|Exercise MODEL TEST PAPER <br> (Section C )|15 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
PRADEEP|Exercise ADVANCED PROBLEMS FOR COMPETITIONS|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-BIOMOLECULES -NCERT (EXERCISES)
- What are monosaccharides?
Text Solution
|
- What are reducing sugars ?
Text Solution
|
- Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Text Solution
|
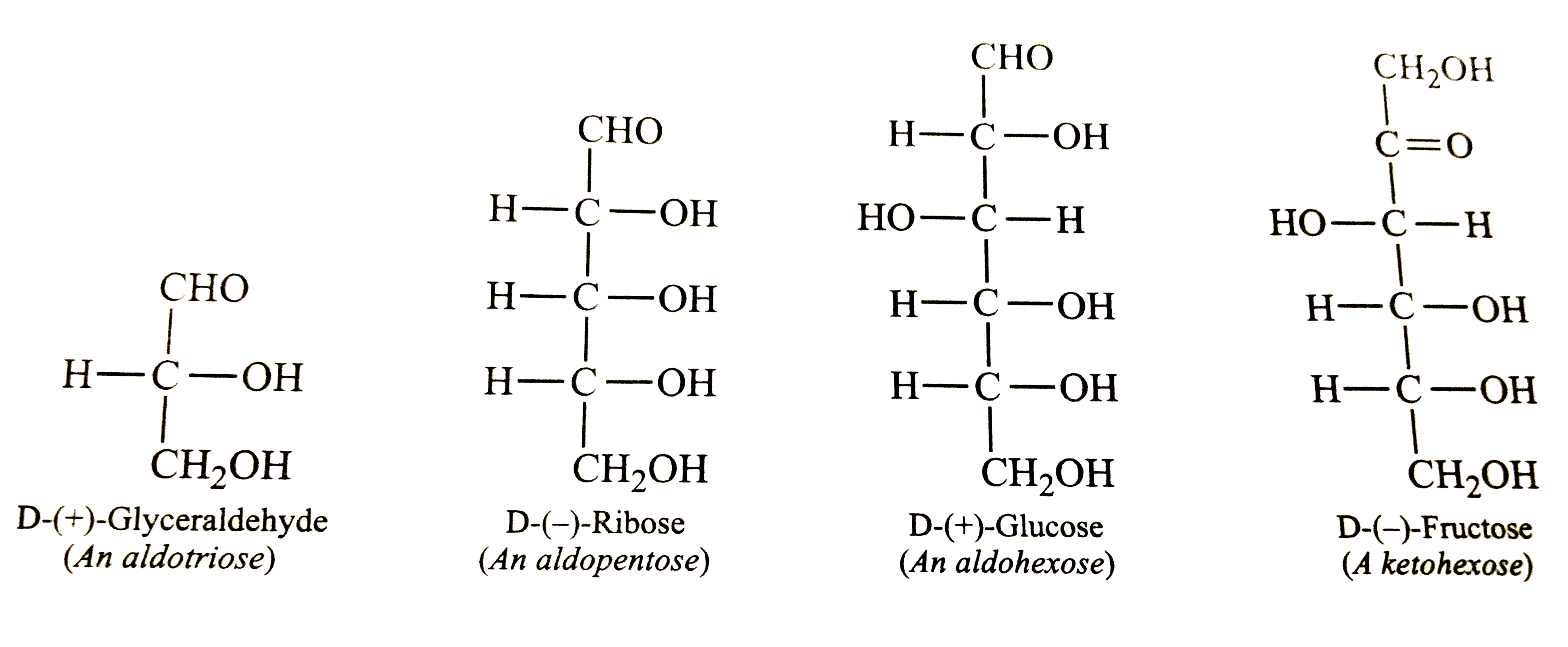
- Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides: Ribose,...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Text Solution
|
- What is glycogen? How is it different from starch?
Text Solution
|
- What are the hydrolysis products of (i) sucrose and (ii) lactose?
Text Solution
|
- What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Text Solution
|
- What happenes when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents? ...
Text Solution
|
- Enumerate the reactions of D-Glucose which cannot be explained by its ...
Text Solution
|
- What are essential and non-essential amino acids ? Give two examples o...
Text Solution
|
- Define the following as related to proteins : (i) Peptide linkage ...
Text Solution
|
- What are the common types of secondary structures fo proteins?
Text Solution
|
- What type of bonding helps in stabilising the alpha-helix structure of...
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins.
Text Solution
|
- How do you explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids ?
Text Solution
|
- What are enzymes ?
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Text Solution
|
- How are vitamins classified? Name the vitamin responsible for the coag...
Text Solution
|
- Why are vitamin A and vitamin C essential for us? Give their important...
Text Solution
|
 .
.