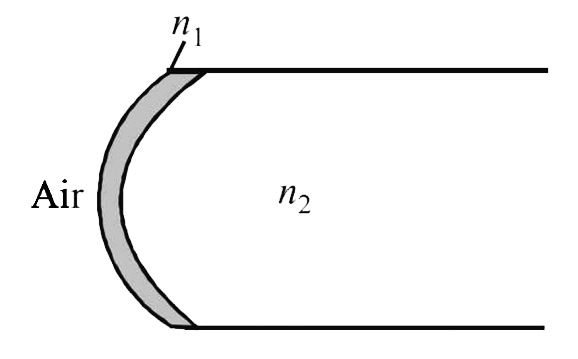
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.15|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.16|9 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.13|20 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise High Level Problems (HIP)|21 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise 3|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM-DPP No.14
- A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index n(1)...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two cars moving perpendicular to each other as shown. Initia...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation in Fig. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting p...
Text Solution
|
- Two rays are incident on a spherical mirror of radius R = 5 cm paralle...
Text Solution
|
- Airplanes A and B are flying with constant velocity in the same vertic...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars A and B are racing along straight line. Car A is leading, suc...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is projected from level ground with speed u and ann at angle t...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is projected from level ground with speed u and ann at angle t...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is projected from level ground with speed u and ann at angle t...
Text Solution
|