Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise DPP 3.3|20 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise DPP 3.4|15 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise DPP 3.1|14 VideosELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise MCQ s|38 VideosELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise M.C.Q|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-ELECTRIC POTENTIAL-DPP 3.2
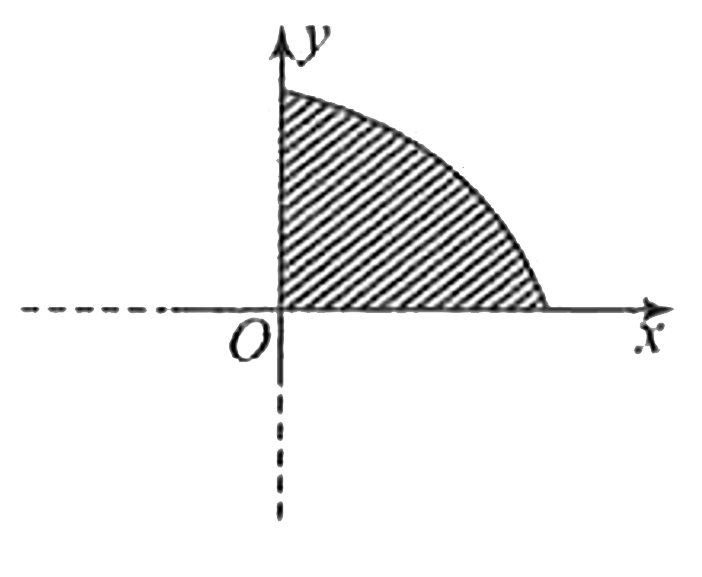
- A uniform surface charge of density sigma is given to a quarter of a d...
Text Solution
|
- The electric potential V at any point x,y,z (all in metre) in space is...
Text Solution
|
- Electric potential is given by V = 6x - 8xy^(2) - 8y + 6yz - 4z^(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two points 1 and 2 in a region outside a charged sphere. Two ...
Text Solution
|
- If V=-5x+3y+sqrt(15)z then find magnitude of electric field at point (...
Text Solution
|
- The figure gives the electric potential V as a function of distance th...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a charged conductor resting on an insulating stand. If at...
Text Solution
|
- The electrostatic potential on the surface of a charged concducting sp...
Text Solution
|
- If unifrom electric filed vecE = E(0)hati + 2E(0) hatj, where E(0) is ...
Text Solution
|
- There exists a uniform electric filed in the space as shown. Four poin...
Text Solution
|
- The potential field of an electric field vec(E)=(y hat(i)+x hat(j)) is
Text Solution
|
- A uniform electric field exists in x-y plane. The potential of points ...
Text Solution
|
- Four similar charges each of charge +q are placed at four corners of a...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinite parallel,non- conducting sheets carry equal positive char...
Text Solution
|
- About an electric field which of the following statements are not true...
Text Solution
|