Collision cross-section is an area of an imaginary sphere of radius `sigma` around the molecule within which the centre of another molecule cannot penetrate.
The volume swept by a single molecule in unit time is
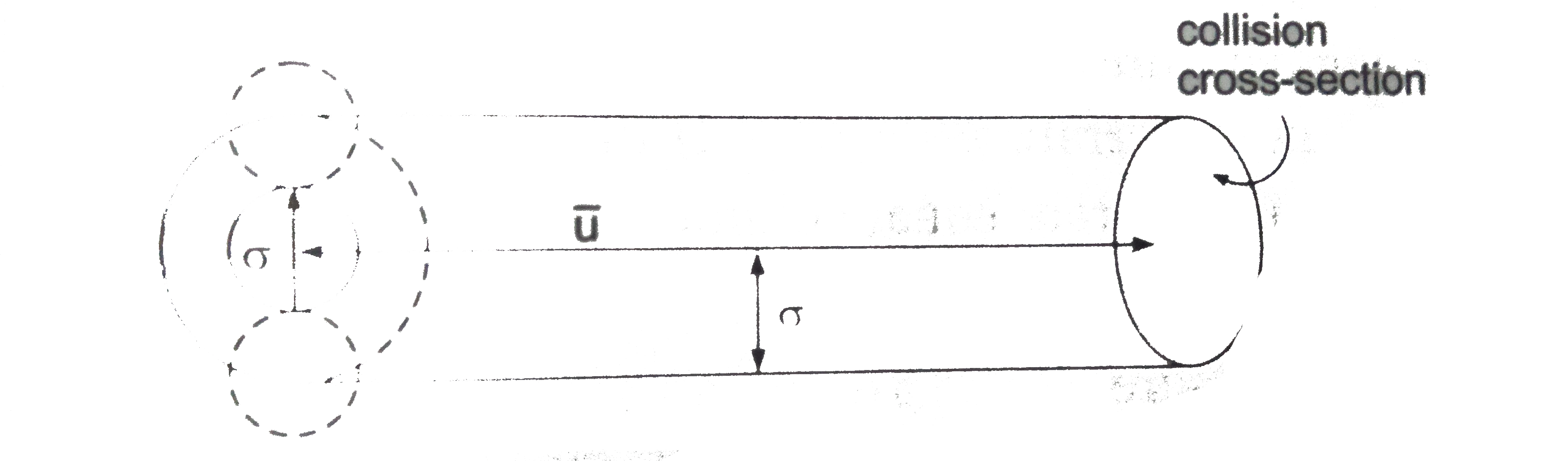
`V=(pisigma^(2))overline(u)` where `overline(u)` is the average speed
If `N^(**)` is the number of molecules per unit volume, then the number of molecules within the volume V is
`N=VN^(**)=(pisigma^(2)overline(u))N^(**)`
Hence, the number of collision made by a single molecule in unit time will be
`Z=N=(pi sigma^(2)overline(u))N^(**)`
In order to account for the movements of all molecules, we must consider the average velocity along the line of centres of two coliding molecules instead of the average velocity of a single molecule . If it is assumed that, on an average, molecules collide while approaching each other perpendicularly, then the average velocity along their centres is `sqrt(2)overline(u)` as shown below.
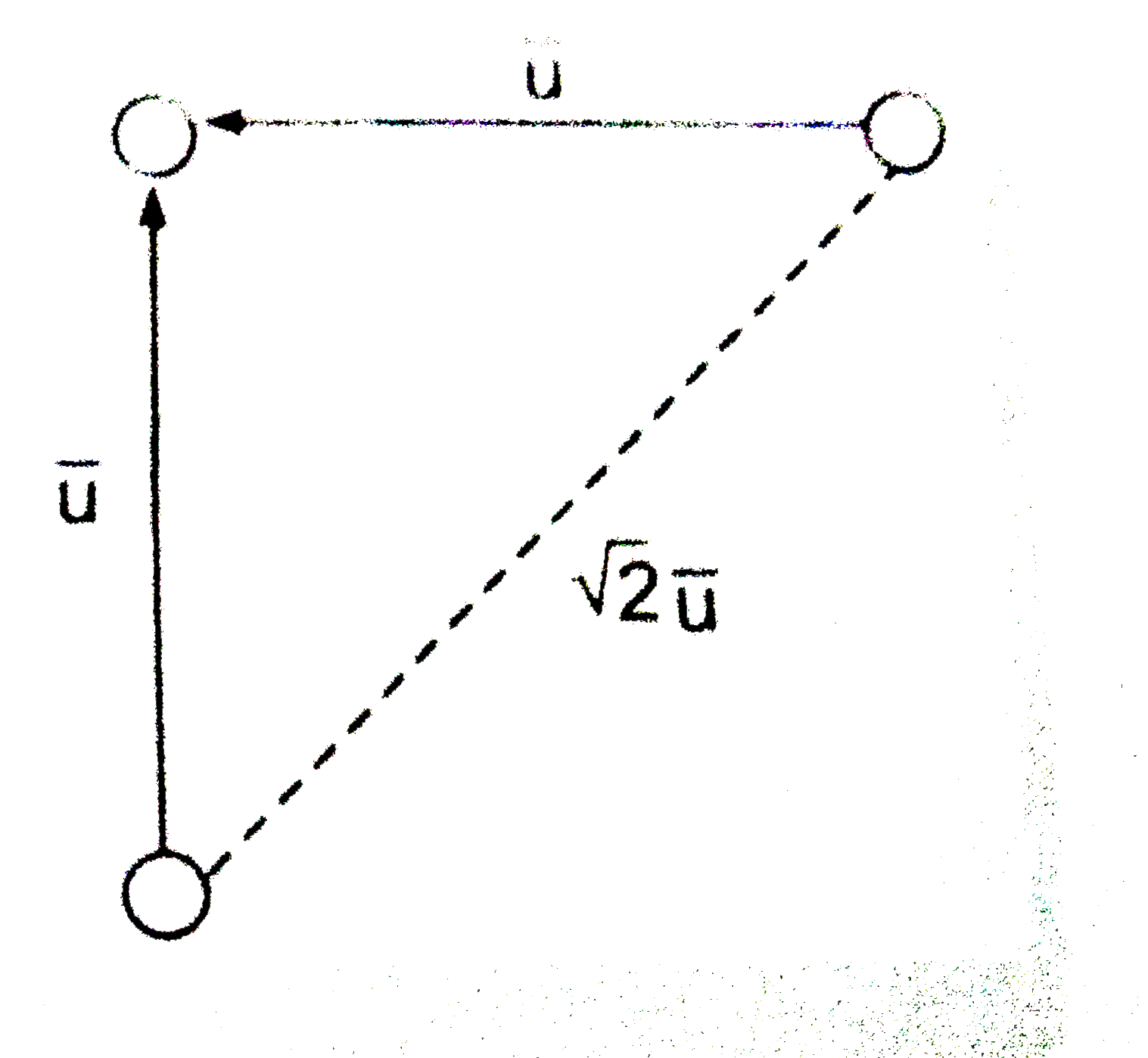
Number of collision made by a single molecule with other molecule per unit time is given by
`Z_(1)=pisigma^(2)(overline(u)_("rel"))N^(**)=sqrt(2) pisigma^(2)overline(u)N^(**)`
The total number of bimolecular collisions `Z_(11)` per unit volume per unit time is given by
`Z_(11)=(1)/(2)(Z_(1)N^(**))"or" Z_(11)=(1)/(2)(sqrt(2)pisigma^(2)overline(u)N^(**))N^(**)=(1)/(sqrt(2))pisigma^(2)overline(u)N^(**2)`
If the collsion involve two unlike molecules then the number of collisions `Z_(12)` per unit volume per unit time is given as
`Z_(12)= pisigma _(12)^(2)(sqrt((8kT)/(pimu)))N_(1)N_(2)`
where `N_(1)` and `N_(2)` are the number of molecules per unit volume of the two types of molecules, `sigma_(12)` is the average diameter of the two molecules and `mu` is the reduced mass. The mean free path is the average distance travelled by a molecule between two successive collisions. We can express it as follows :
`lambda=("Average distance travelled per unit time")/("NO. of collisions made by a single molecule per unit time")=(overline(u))/(Z_(1))`
`"or "lambda=(overline(u))/(sqrt(2)pisigma^(2)overline(u)N^(**))implies(1)/(sqrt(2)pisigma^(2)overline(u)N^(**))`
For a given gas the mean free path at a particular pressure is :