Topper's Solved these Questions
TRIANGLES
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN|Exercise Exercise 7b|15 VideosTRIANGLES
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN|Exercise Revision Exercise (very Short Answer Questions)|10 VideosTRIANGLES
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN|Exercise Problems From NCERT/exemplar|5 VideosSURFACE AREA AND VOLUME
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN|Exercise Revision Exercise (long Answer Questions)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN-TRIANGLES-Exercise 7a
- Find the value of x and y in each of the following figures containing ...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, angleBAC=angleBDC and angleABC=angleBCD. Prov...
Text Solution
|
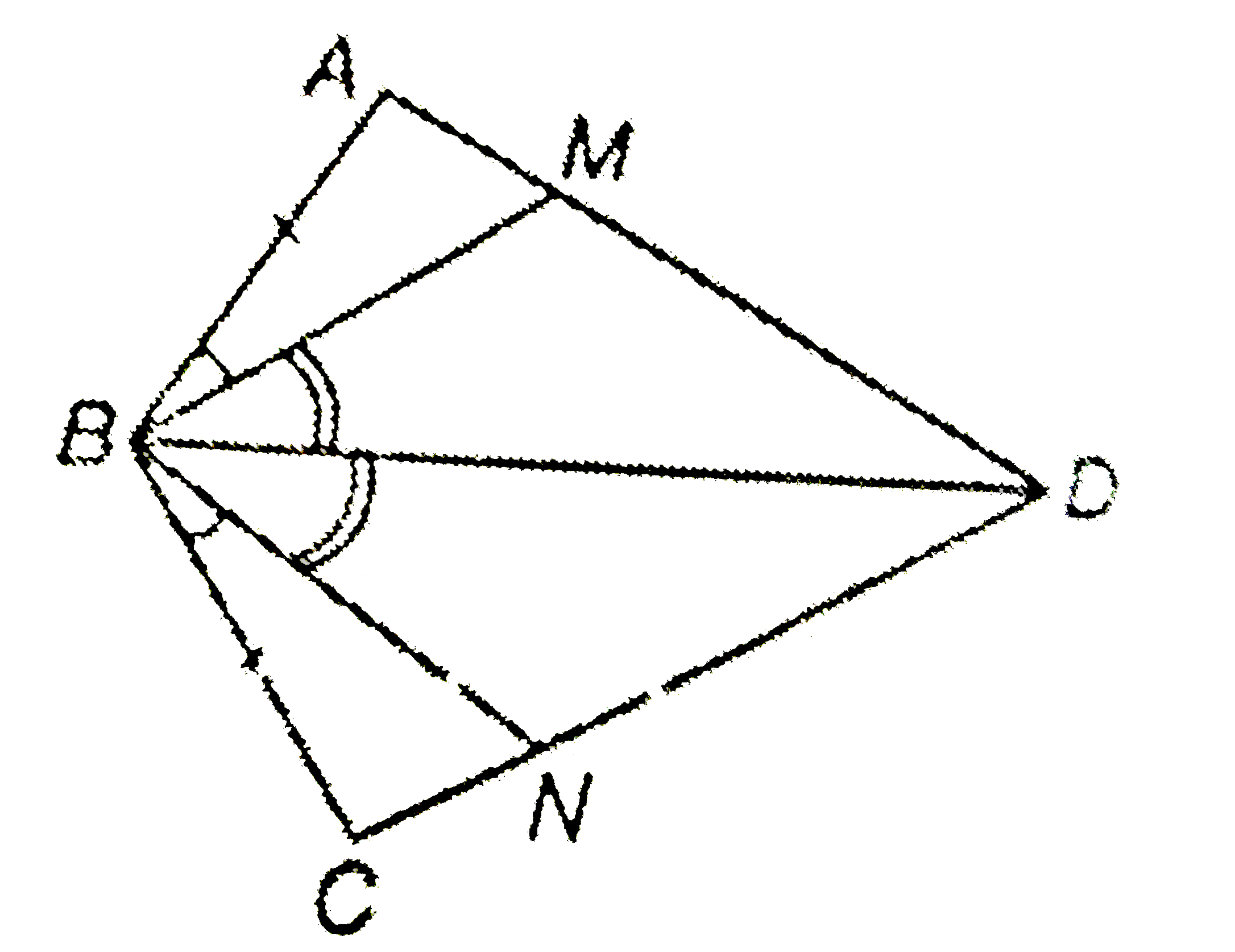
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral. M and N are the poin...
Text Solution
|
- Given AD=DC and DB biscets angleADC. (i) Prove that, DeltaADB cong D...
Text Solution
|
- The adjoining figure shows a square ABCD and an equilateral triangle D...
Text Solution
|
- Equilateral triangles ABD and ACE are drawn on sides AB and AC respect...
Text Solution
|
- The following figure shows a square ABCD and an equilateral triangle D...
Text Solution
|
- The given figure showns a parallelogram ABCD. Squares ABPQ and ADRS ar...
Text Solution
|
- In a DeltaABC, BD is the median to the side Ac, BD is produced to E su...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, angleBDC=angleBEA and AB = BC. Show that AE=CD.
Text Solution
|
- If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angle, ...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, BM and DN are the perpendiculars from B and D...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, AB=EF, BC=DE, angleABC=angleFED=90^(@), prove...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. If angleMBC = angleN...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, QX and RX are the bisectors of the angles Q a...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure, OA = OC and AB = BC. Prove that : (i) angle...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a paralogram. The side AB is produced...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figures, AB=PQ, AC=PR and AM=PN. Prove that DeltaABC ...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that the medians of an equilateral triangle are equal.
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a square EF is parallel to BD. R is the mid-point of EF. Prove...
Text Solution
|